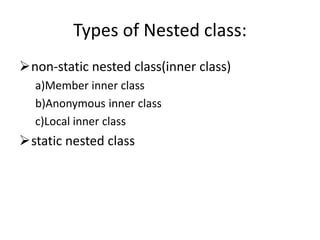
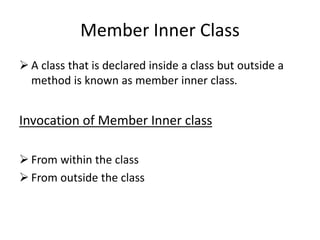
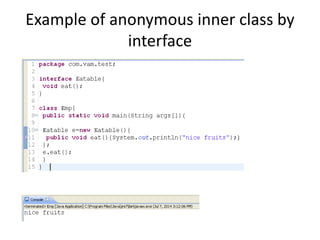
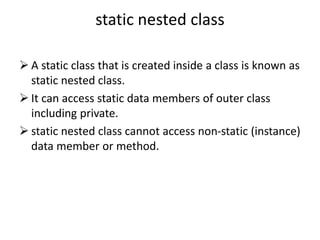
Nested classes allow one class to be defined within another, enabling inner classes to access members of the outer class. There are several types of nested classes: inner classes that can be member, anonymous, or local; and static nested classes. Member inner classes can access outer class members and be invoked from within or outside the outer class. Anonymous inner classes have no name and are created from an abstract class or interface. Local inner classes exist only within a method. Static nested classes can access static members of the outer class but not instance members.