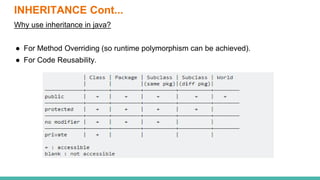
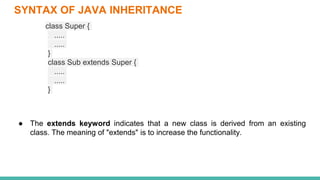
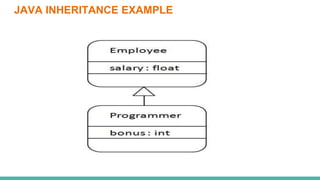
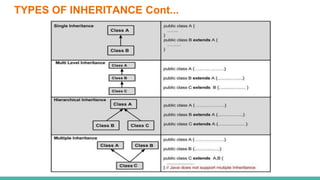
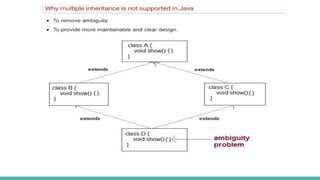
This document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as a parent-child relationship between classes that allows sharing of behavior through code reuse. The key points are: inheritance allows child classes to inherit and optionally override methods and fields from the parent class; the "extends" keyword is used to create a subclass that inherits from an existing superclass; and the "super" keyword differentiates members and calls parent constructors.