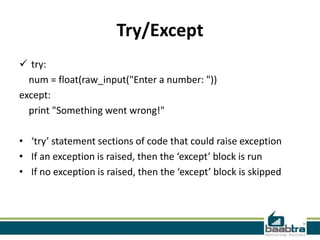
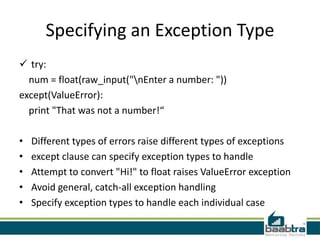
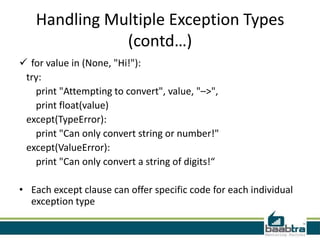
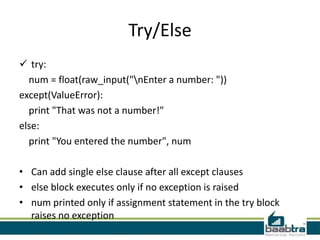
This document provides an overview of handling exceptions in Python. It discusses try/except blocks to catch exceptions, try/finally to ensure some code runs whether an exception occurs or not, specifying exception types in except clauses to handle specific errors, using try/else to execute code if no exception occurs, and handling multiple exception types in a single block. The document was created by trainees of Baabtra as part of a mentoring program and does not represent Baabtra's official documentation. It includes contact information for Reshmi R and links to learn more about Baabtra.