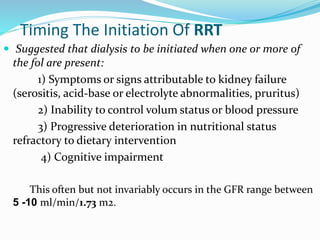
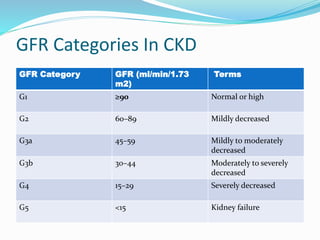
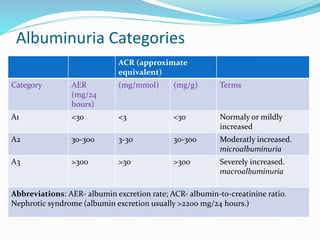
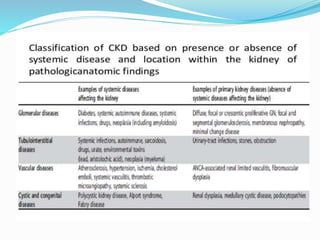
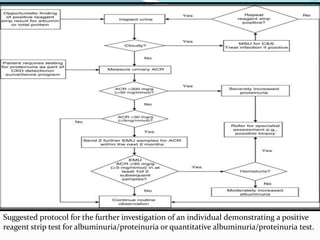
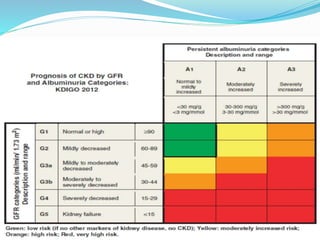
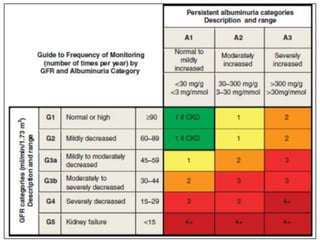
The document defines chronic kidney disease (CKD) and provides guidelines for evaluating and managing CKD according to the KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline. It defines CKD based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albuminuria categories. It recommends evaluating CKD severity annually and monitoring for progression. It provides guidance on managing complications of CKD like anemia, bone disease, and cardiovascular risk. It also addresses medication management, specialist referral indications, and timing the initiation of renal replacement therapy.




![Criteria For CKD (Either Of The Following
Present For >3 Months)
Markers of kidney damage (one or more)
- Albuminuria (AER <30 mg/24 hours; ACR <30 mg/g [<3
mg/mmol])
-Urine sediment abnormalities
-Electrolyte and other abnormalities due to tubular
disorders
-Abnormalities detected by histology
-Structural abnormalities detected by imaging
-History of kidney transplantation
Decreased GFR
GFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckddr-150821032151-lva1-app6892/85/Ckd-dr-shanjida-5-320.jpg)



















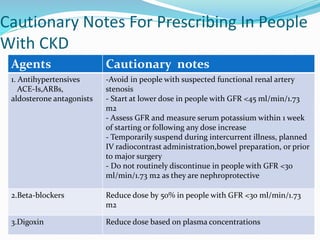
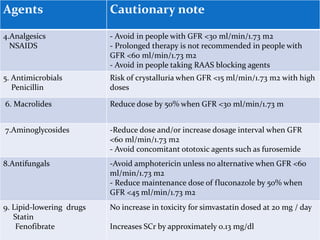
![Referral To Specialists
KDIGO recommendation is in the following circumstances
1) AKI or abrupt sustained fall in GFR;
2) GFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2 (GFR categories G4-G5)
3) consistent finding of significant albuminuria (ACR >300
mg/g [>30 mg/mmol]
4) progression of CKD
5)urinary red cell casts, RBC >20 per high power field
sustained and not readily explained
6) CKD and hypertension refractory to treatment with 4 or
more antihypertensive agents
7) persistent abnormalities of serum potassium;
8) recurrent or extensive nephrolithiasis.
9) hereditary kidney disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckddr-150821032151-lva1-app6892/85/Ckd-dr-shanjida-34-320.jpg)