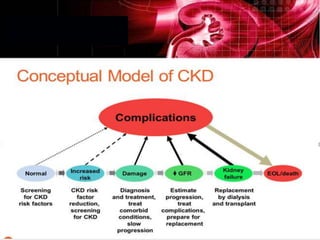
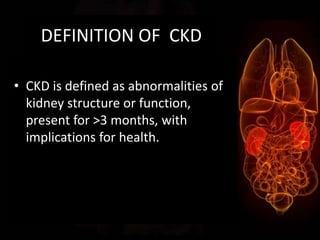
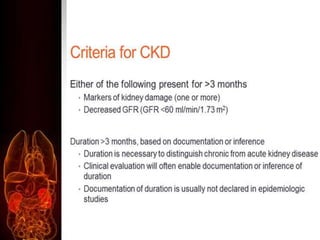
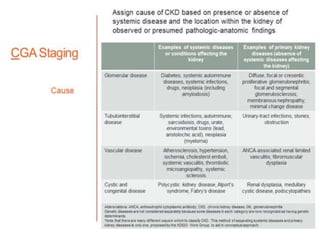
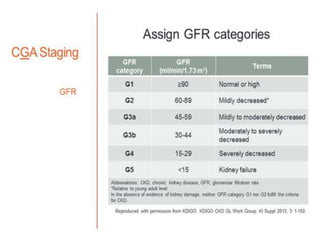
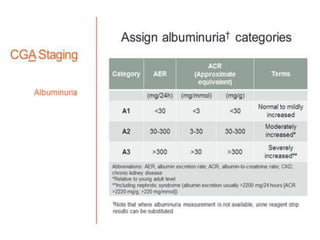
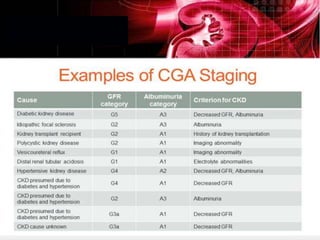
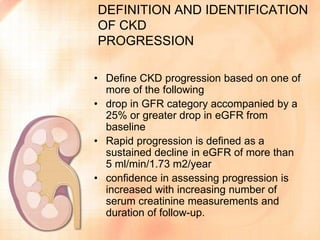
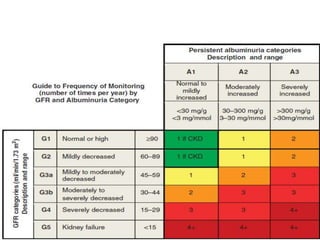
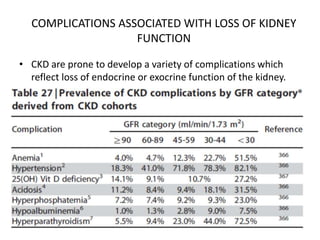
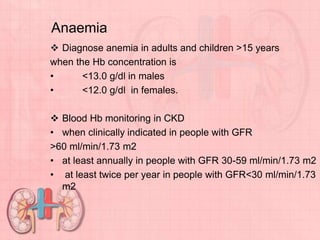
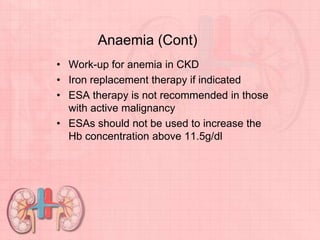
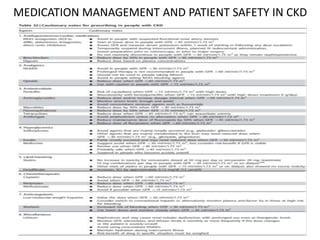
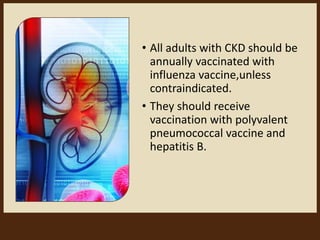
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function lasting over 3 months. CKD is evaluated based on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and markers of kidney damage. Progression is defined as a sustained decline in GFR or a 25% drop from baseline. Management focuses on preventing progression through blood pressure control, ACE inhibitors/ARBs, glycemic control, salt restriction, and lifestyle changes like exercise and smoking cessation. Complications include anemia, bone disease, vitamin D deficiency, acidosis, cardiovascular disease, and increased risk of infection. Dialysis is initiated when symptoms develop or control of volume, pressure, or nutrition cannot be maintained.