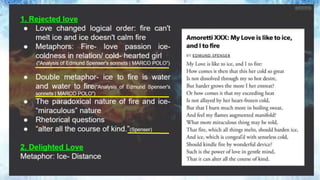
The document outlines the importance of citation in academic work, explaining how it gives credit to source authors and helps readers locate original materials. It details various citation styles (MLA, APA, Chicago, Turabian, CSE) relevant to different academic disciplines and emphasizes the proper format for in-text citations and reference lists. Additionally, it touches on updates and variations in citation practices, including the acceptance of online handles and the inclusion of URLs.