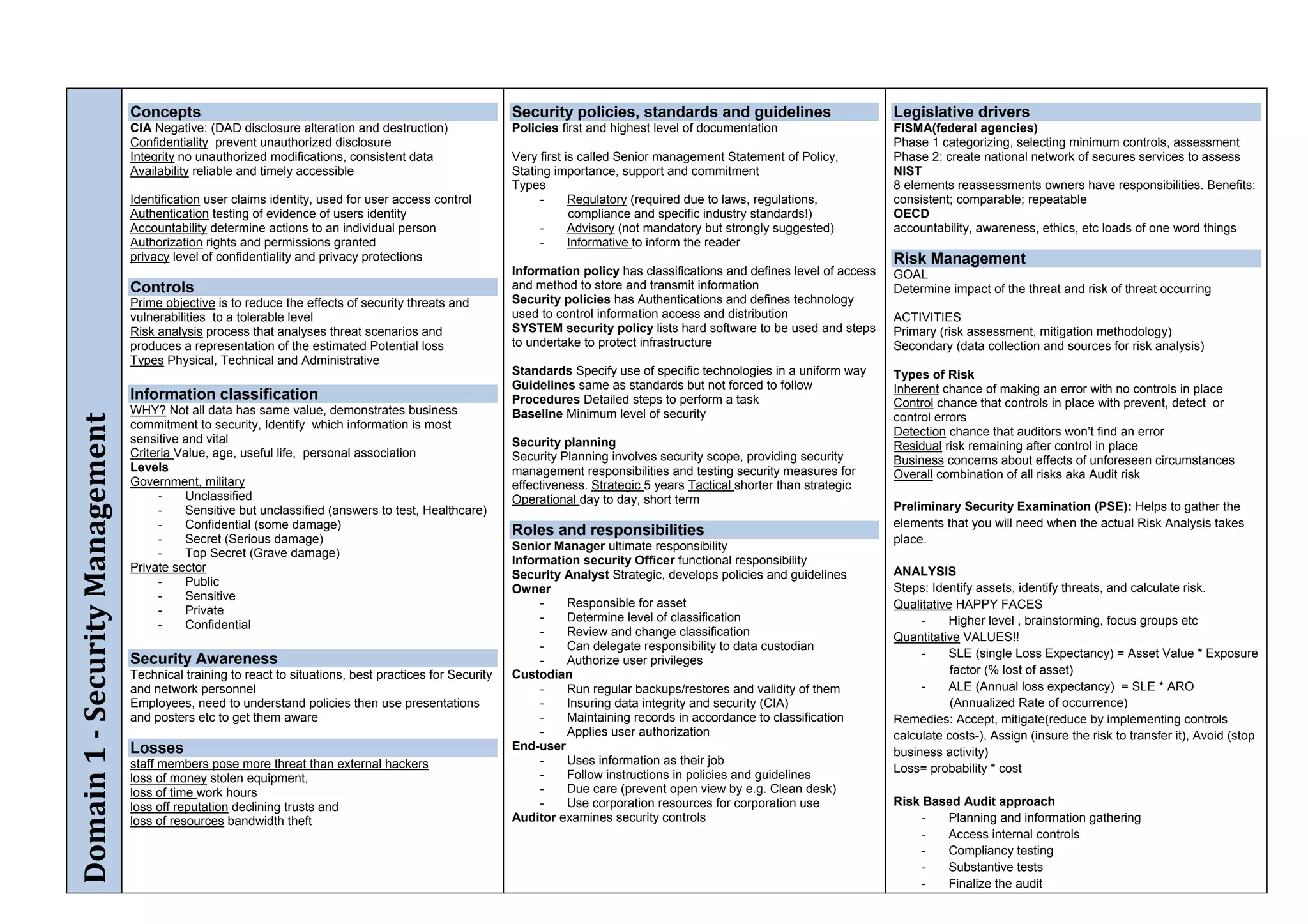
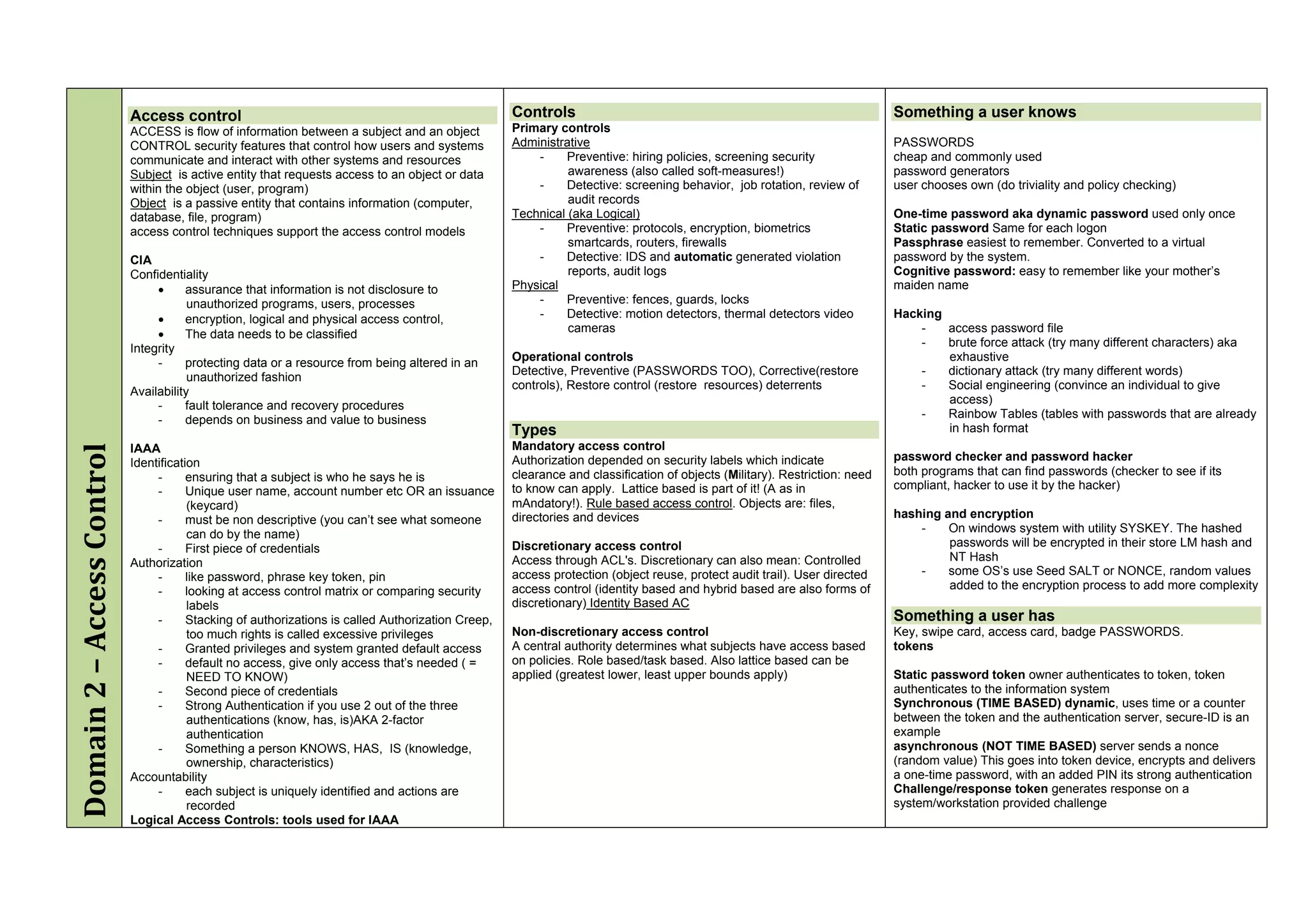
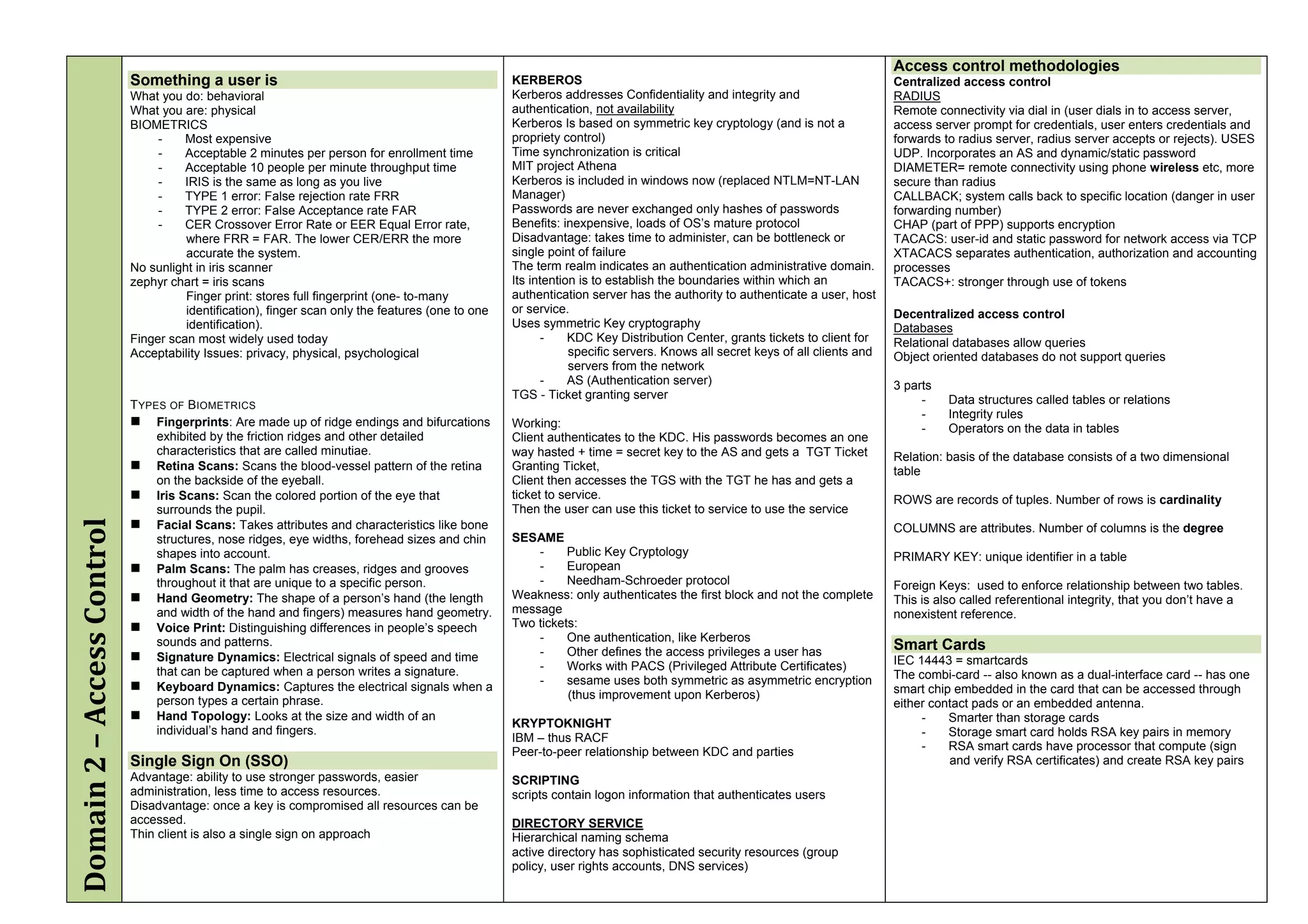
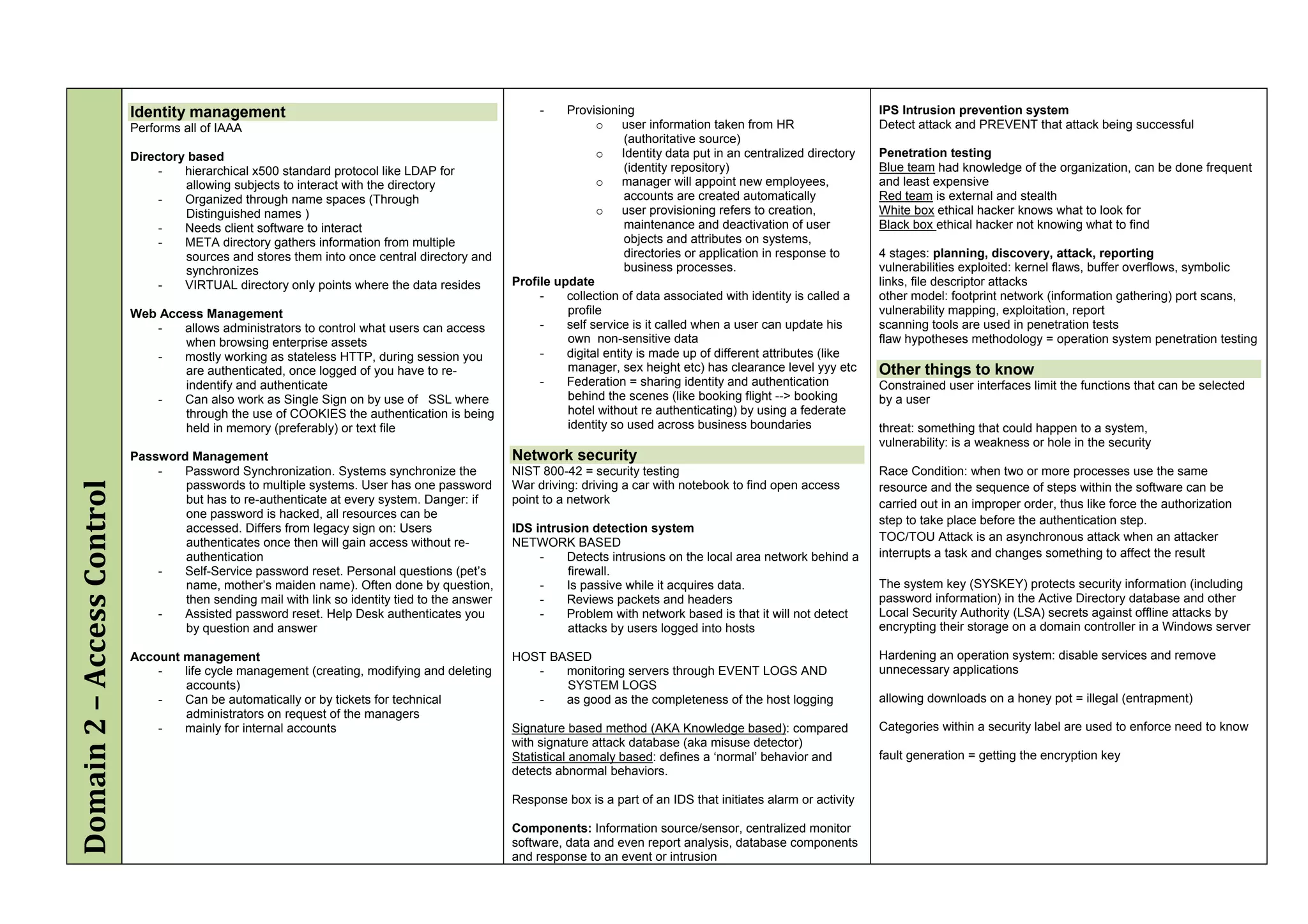
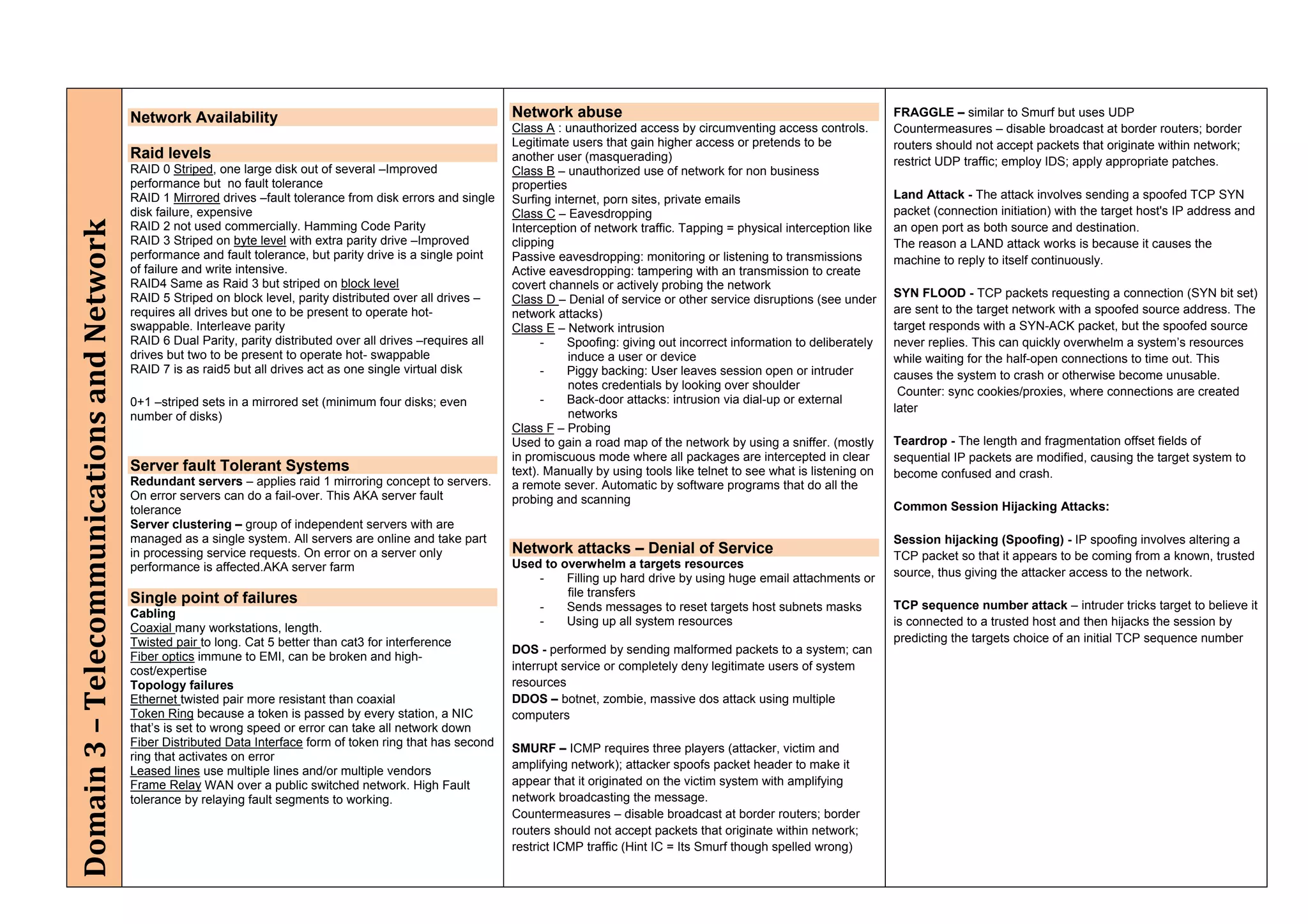
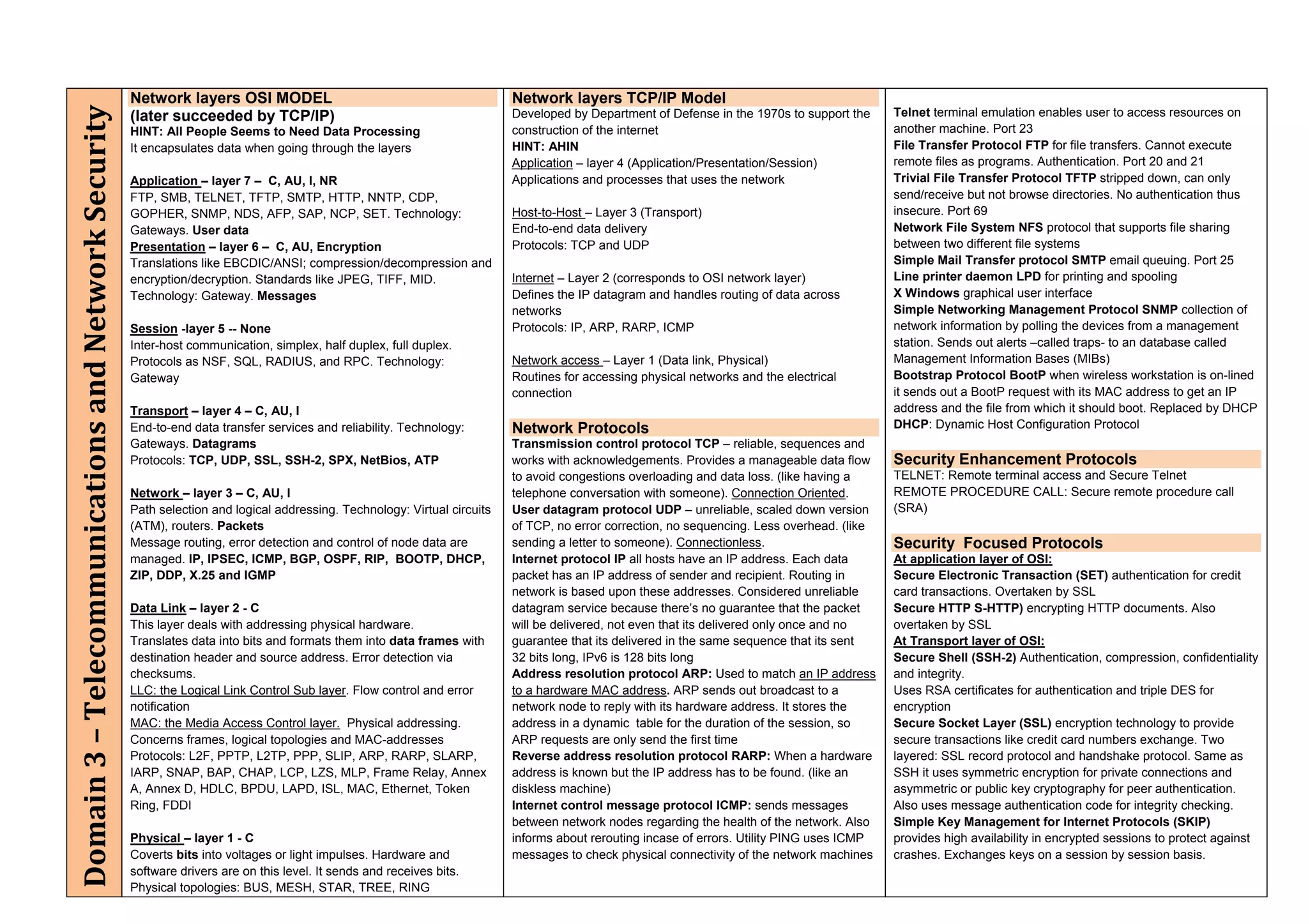
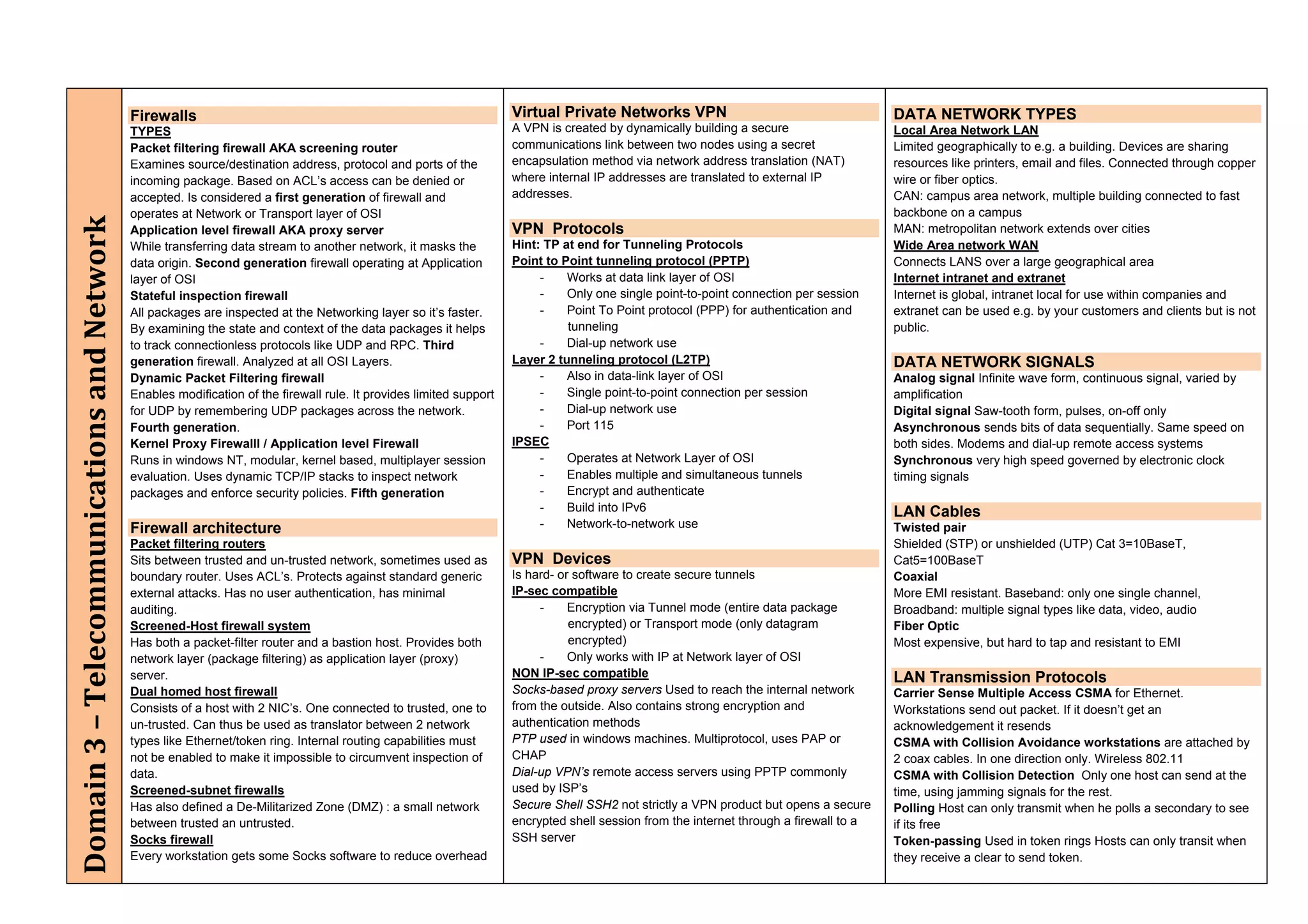
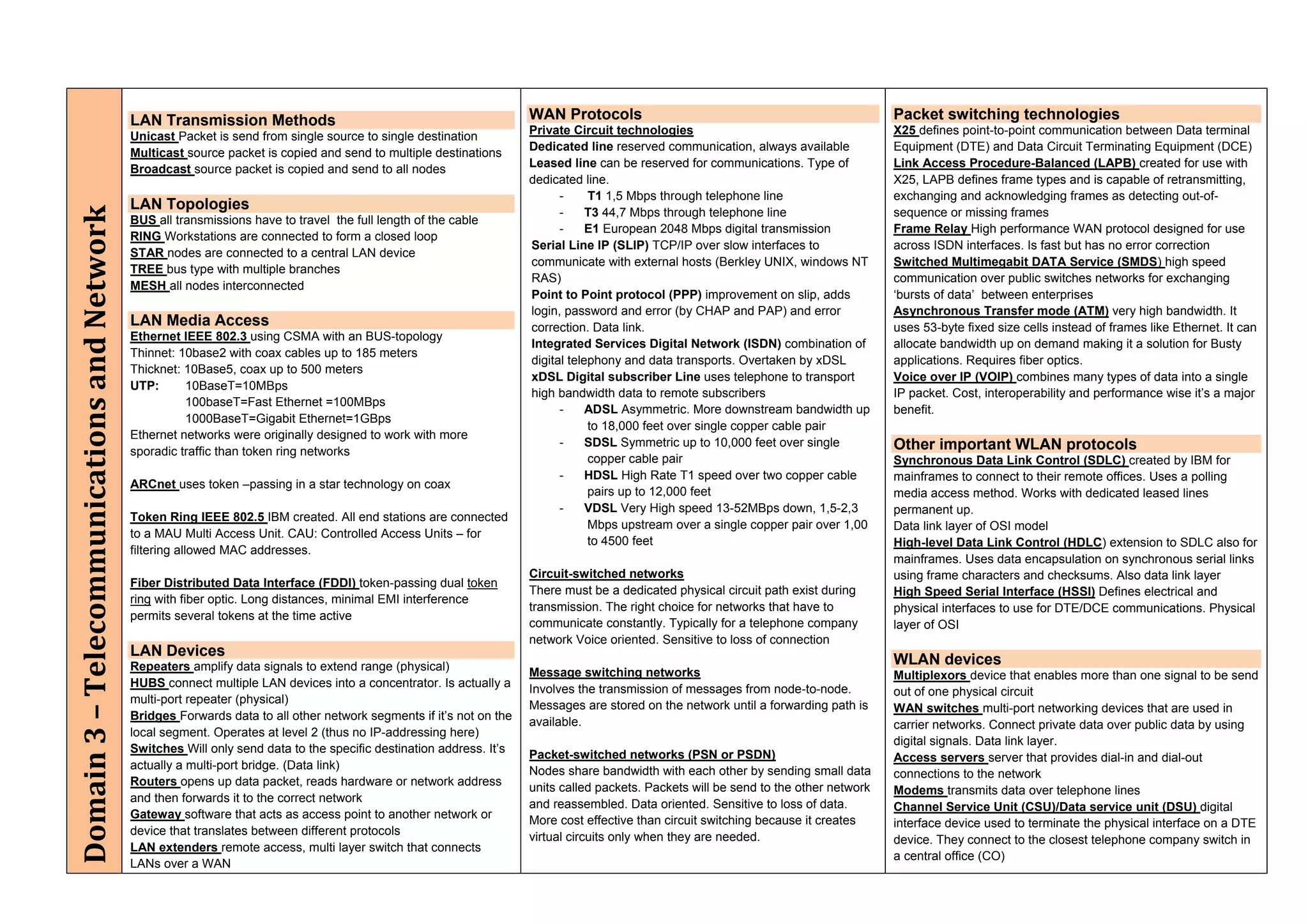
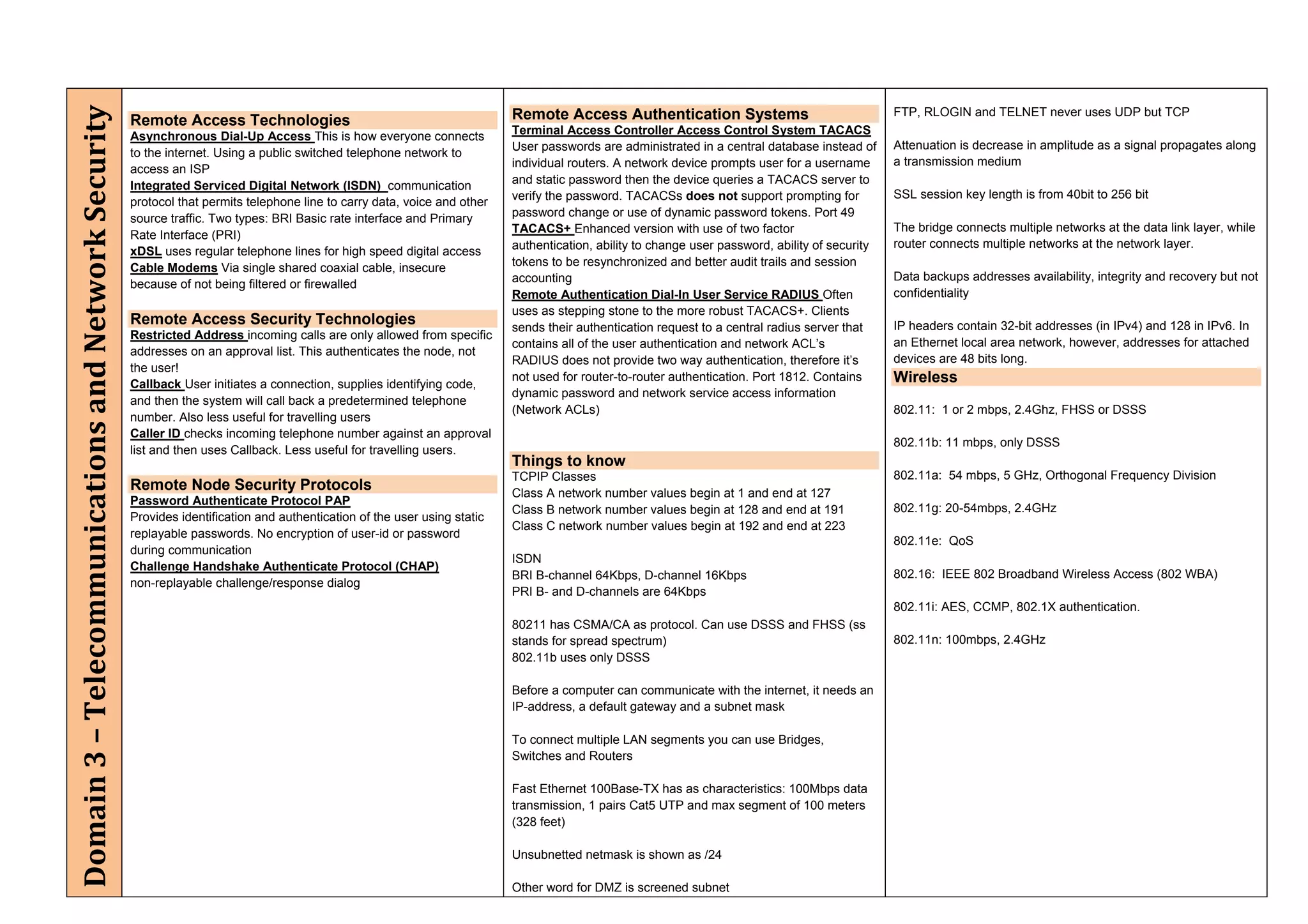
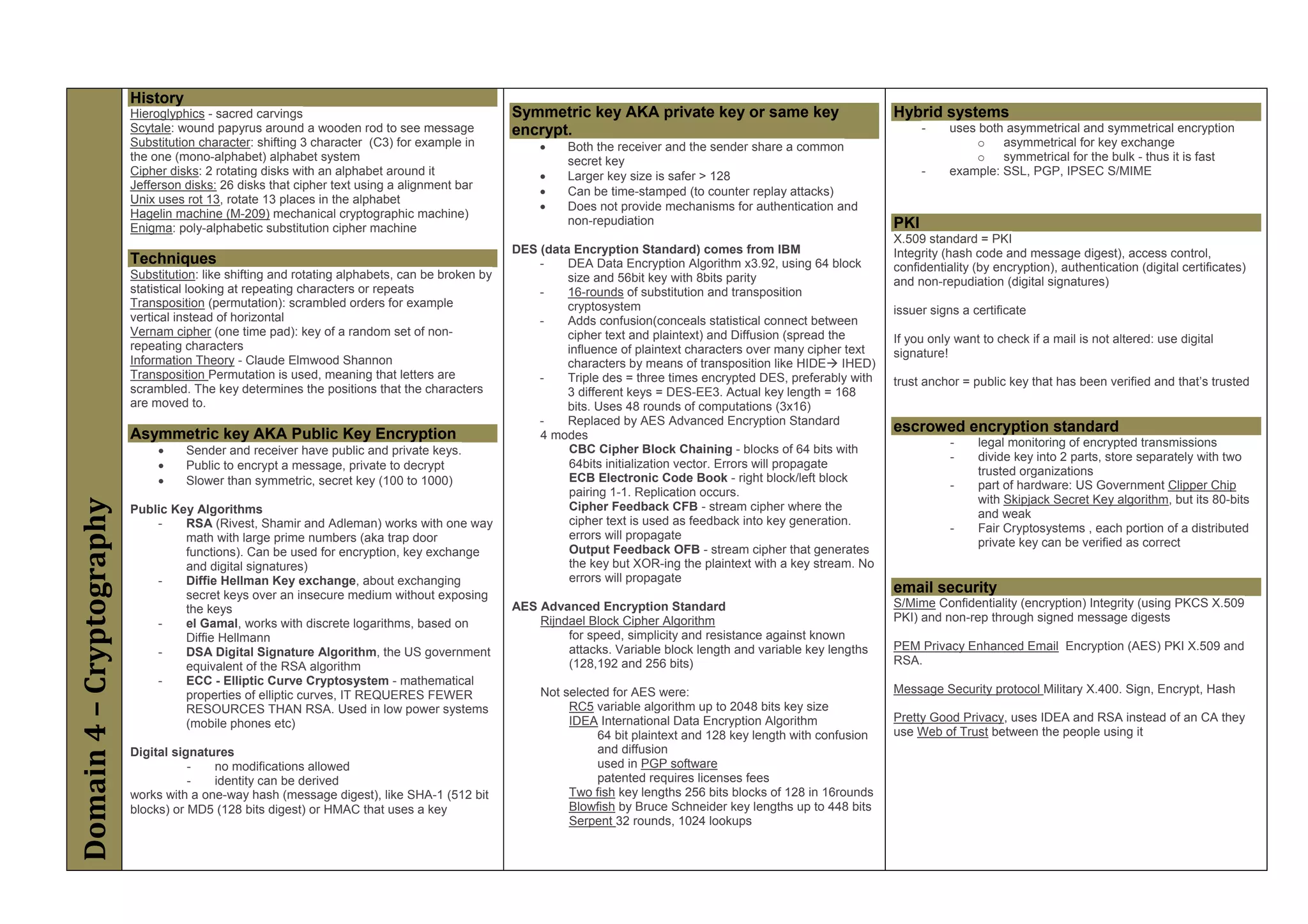
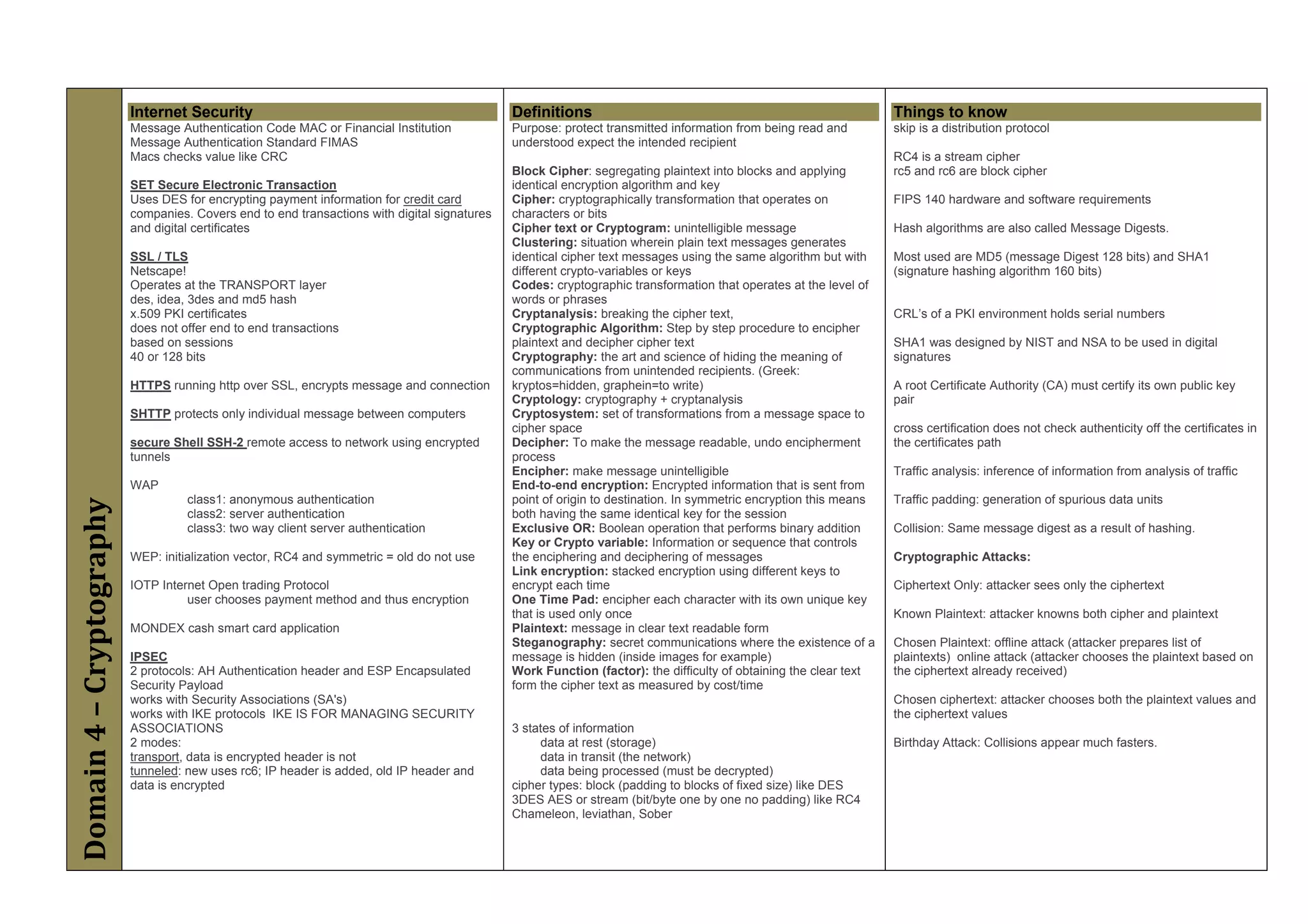
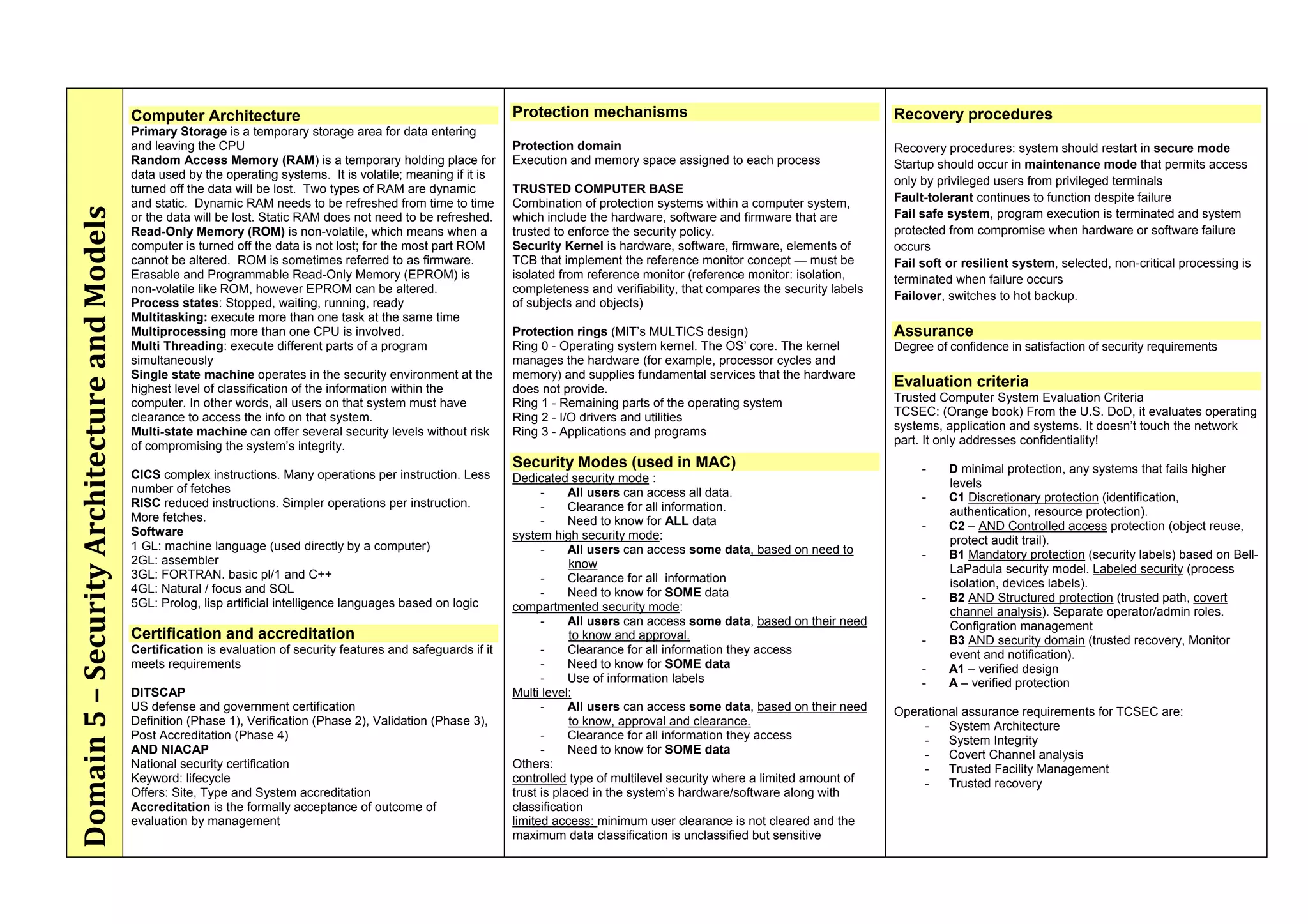
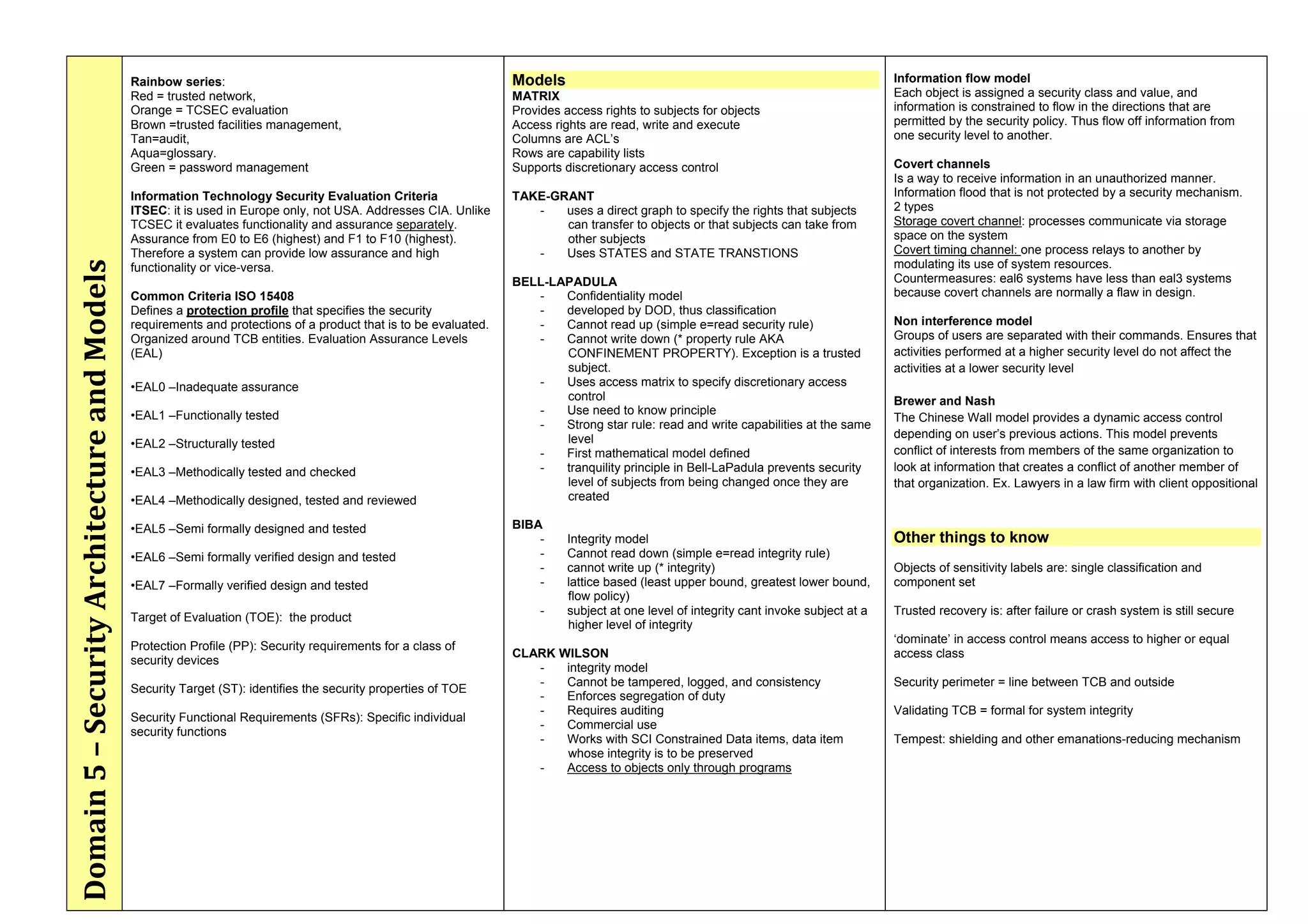
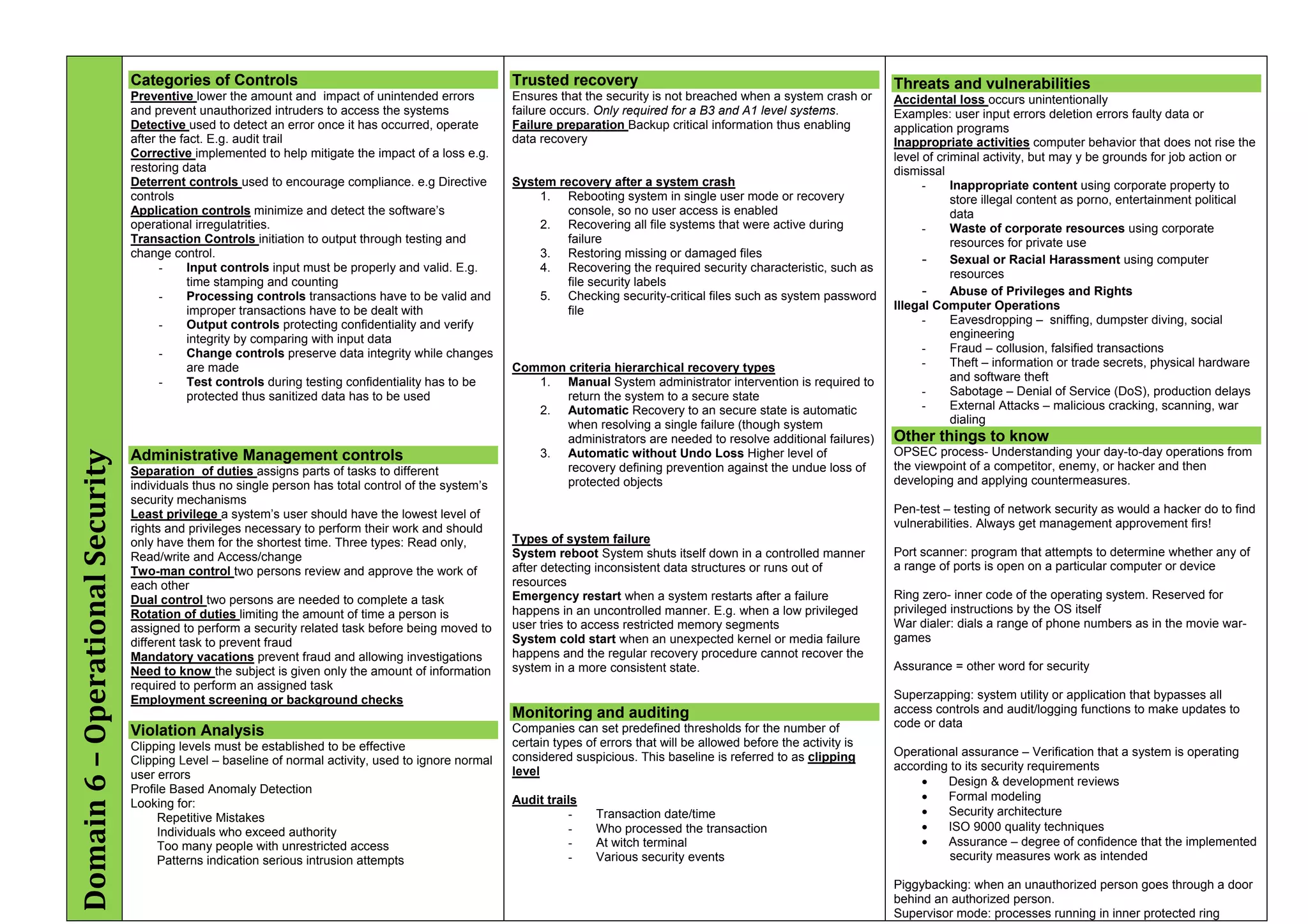
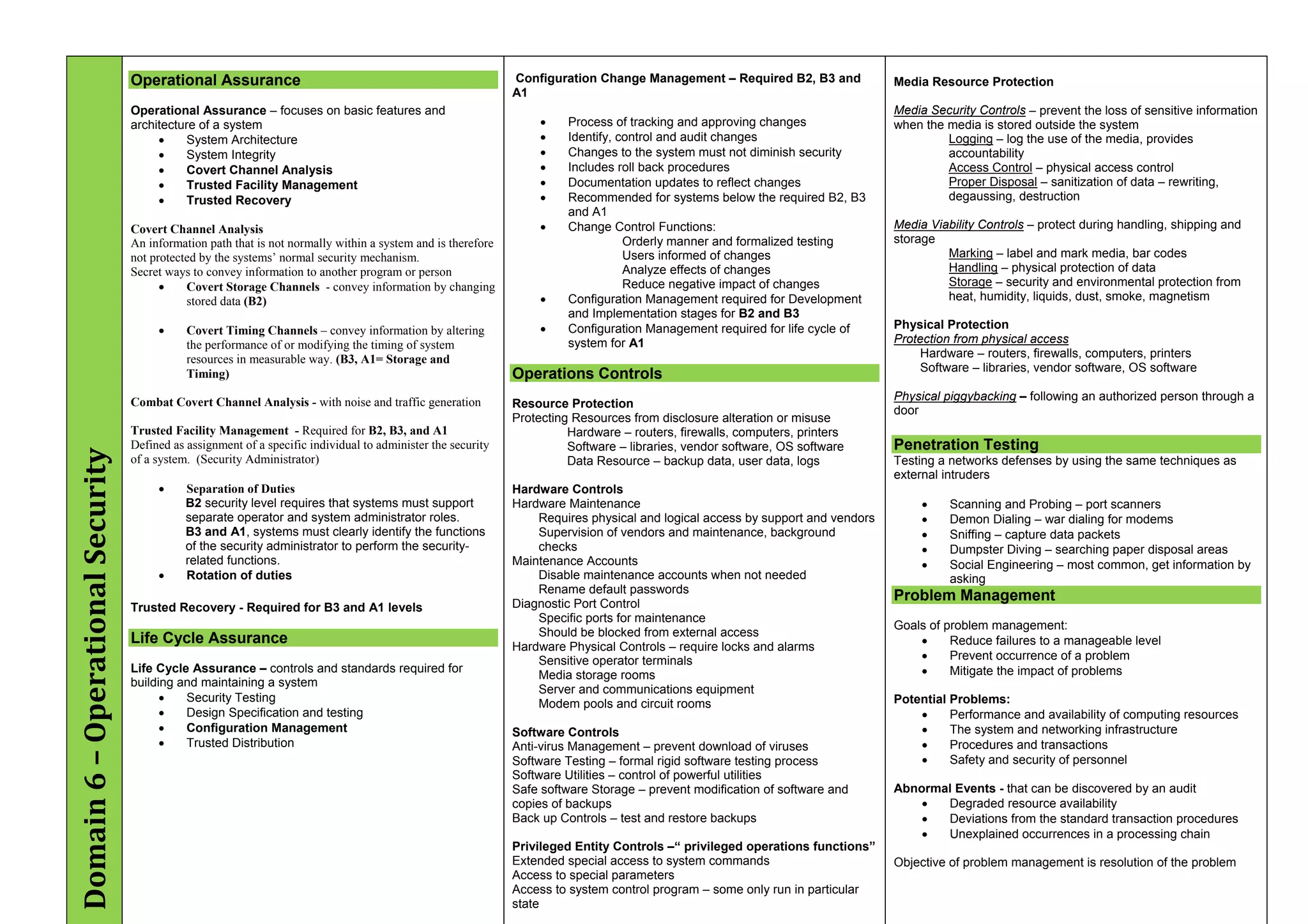
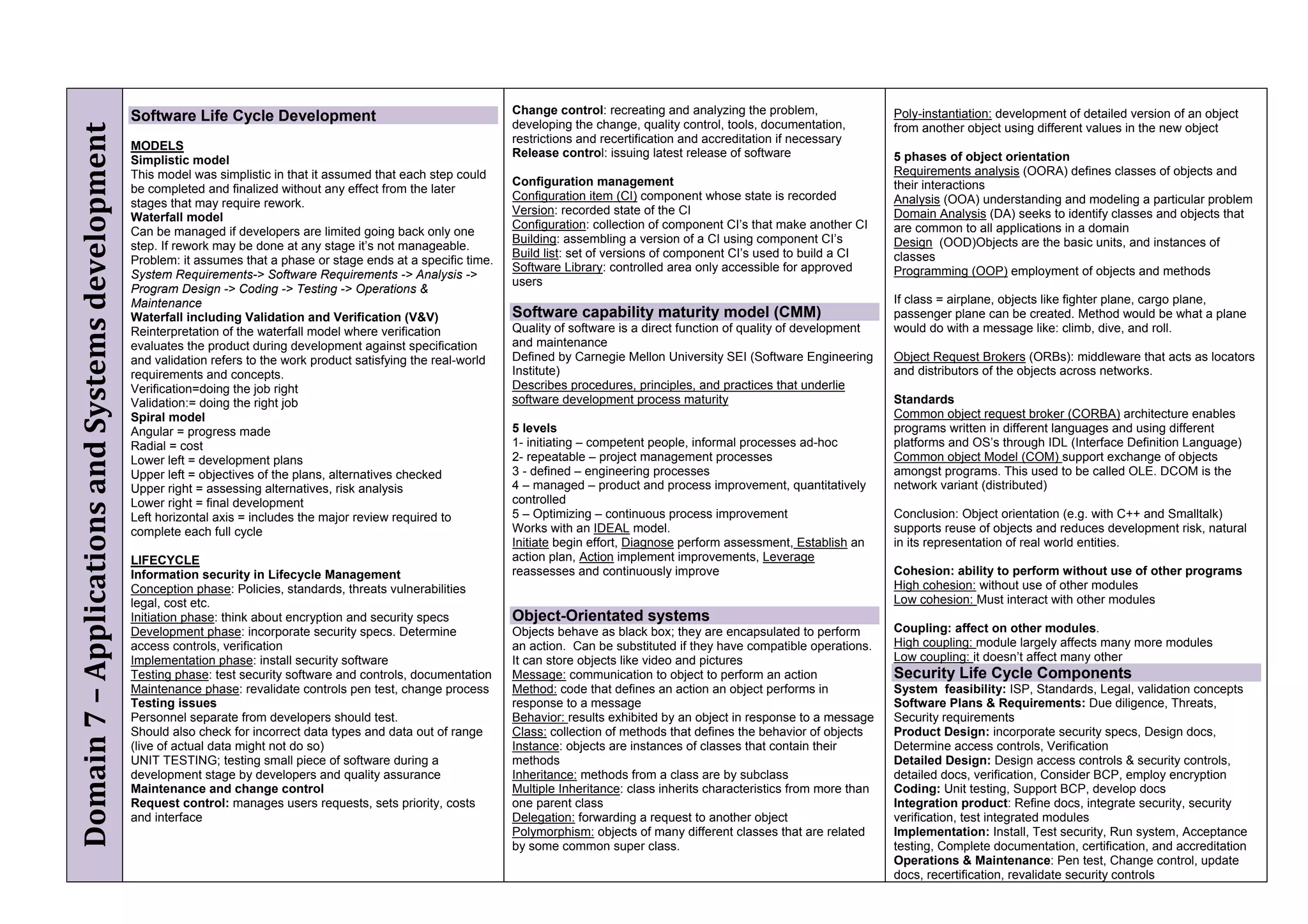
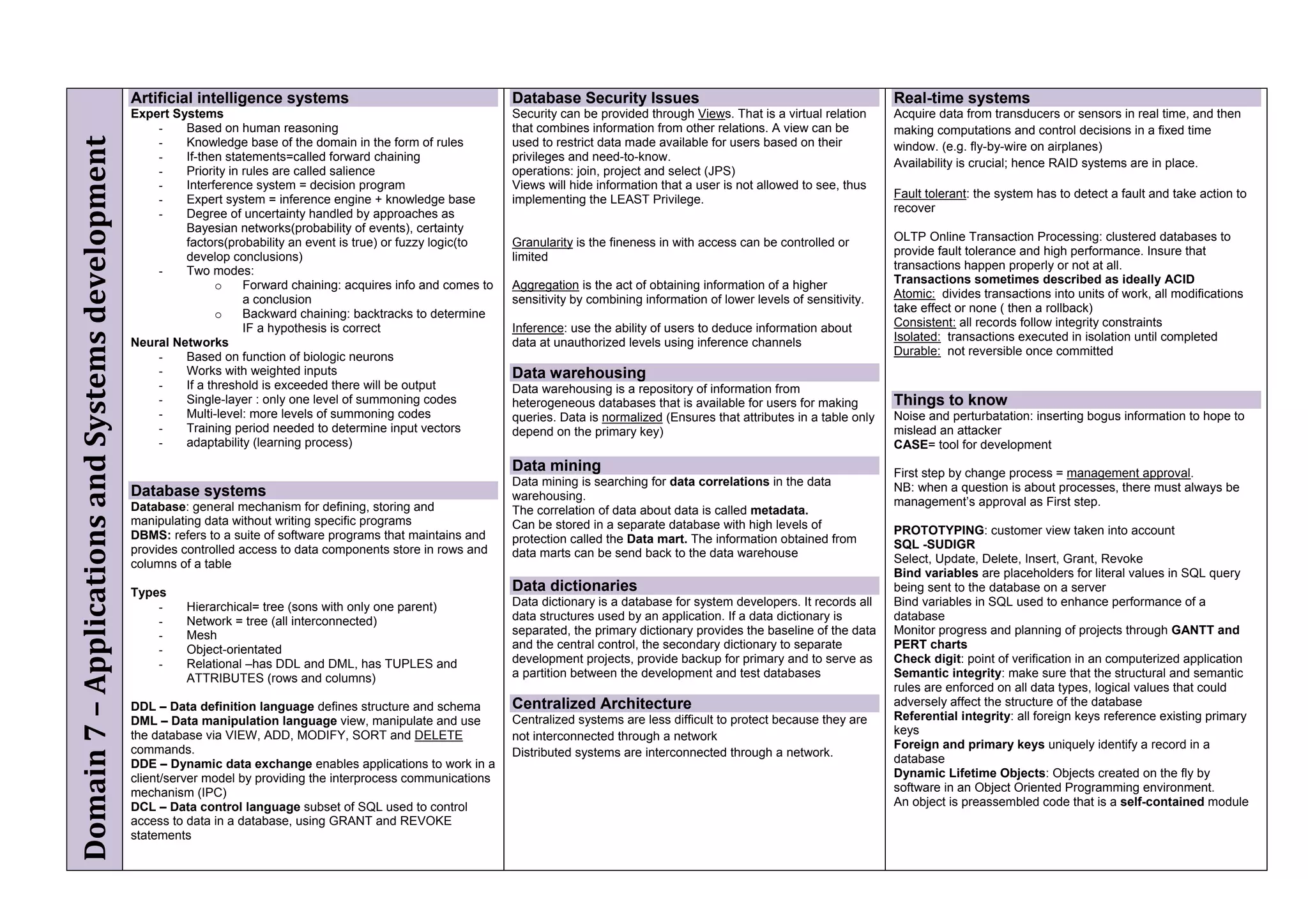
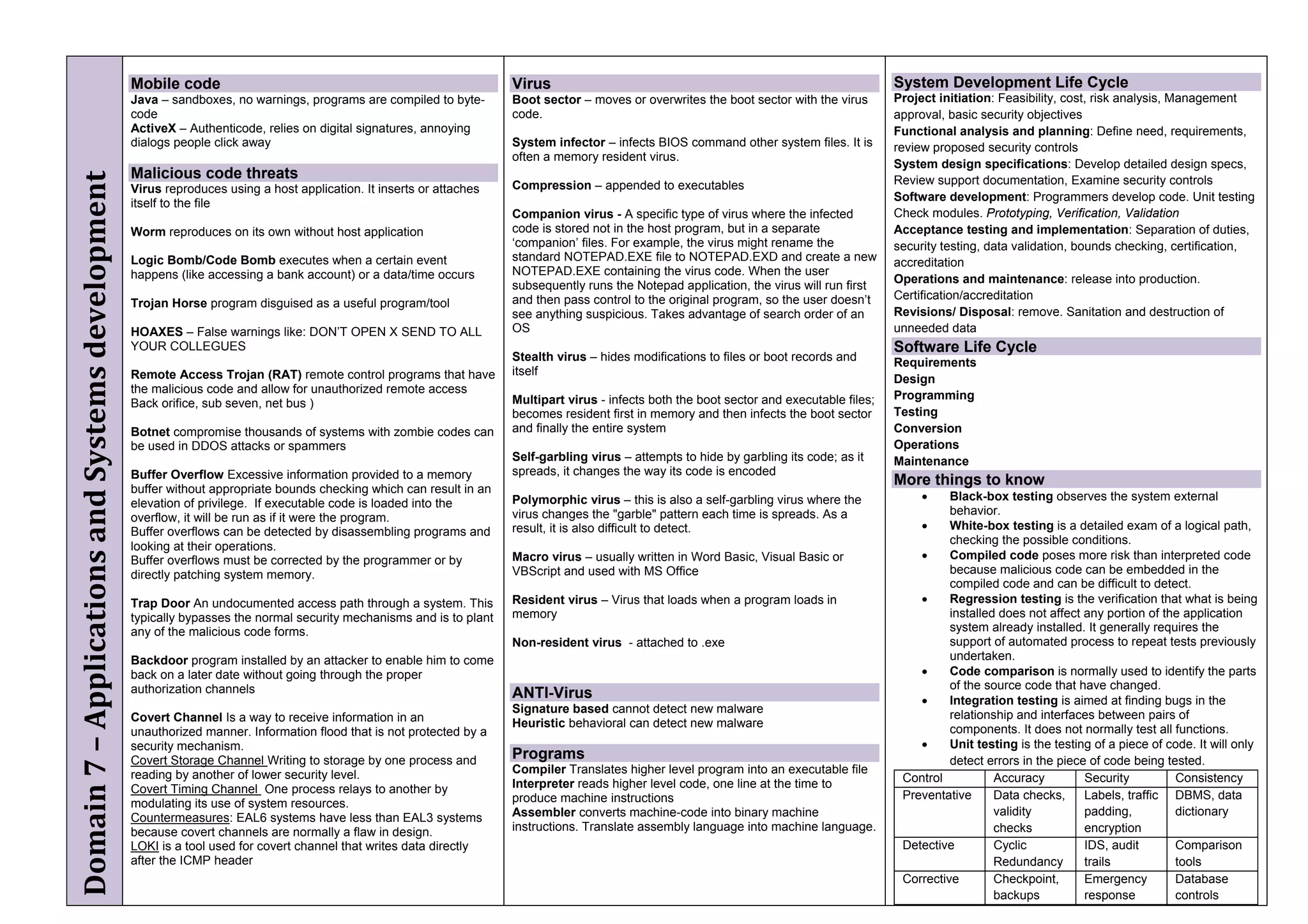
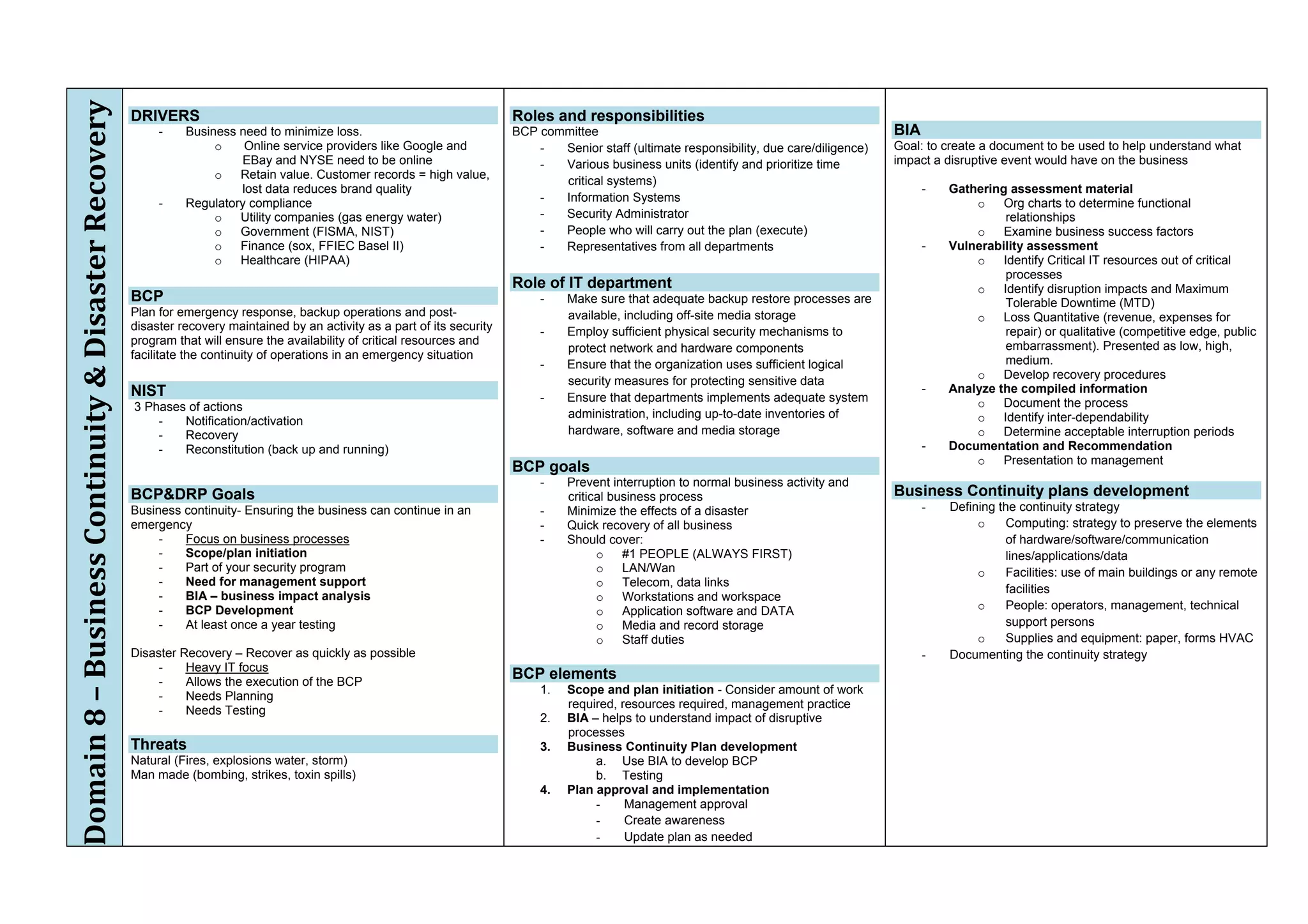
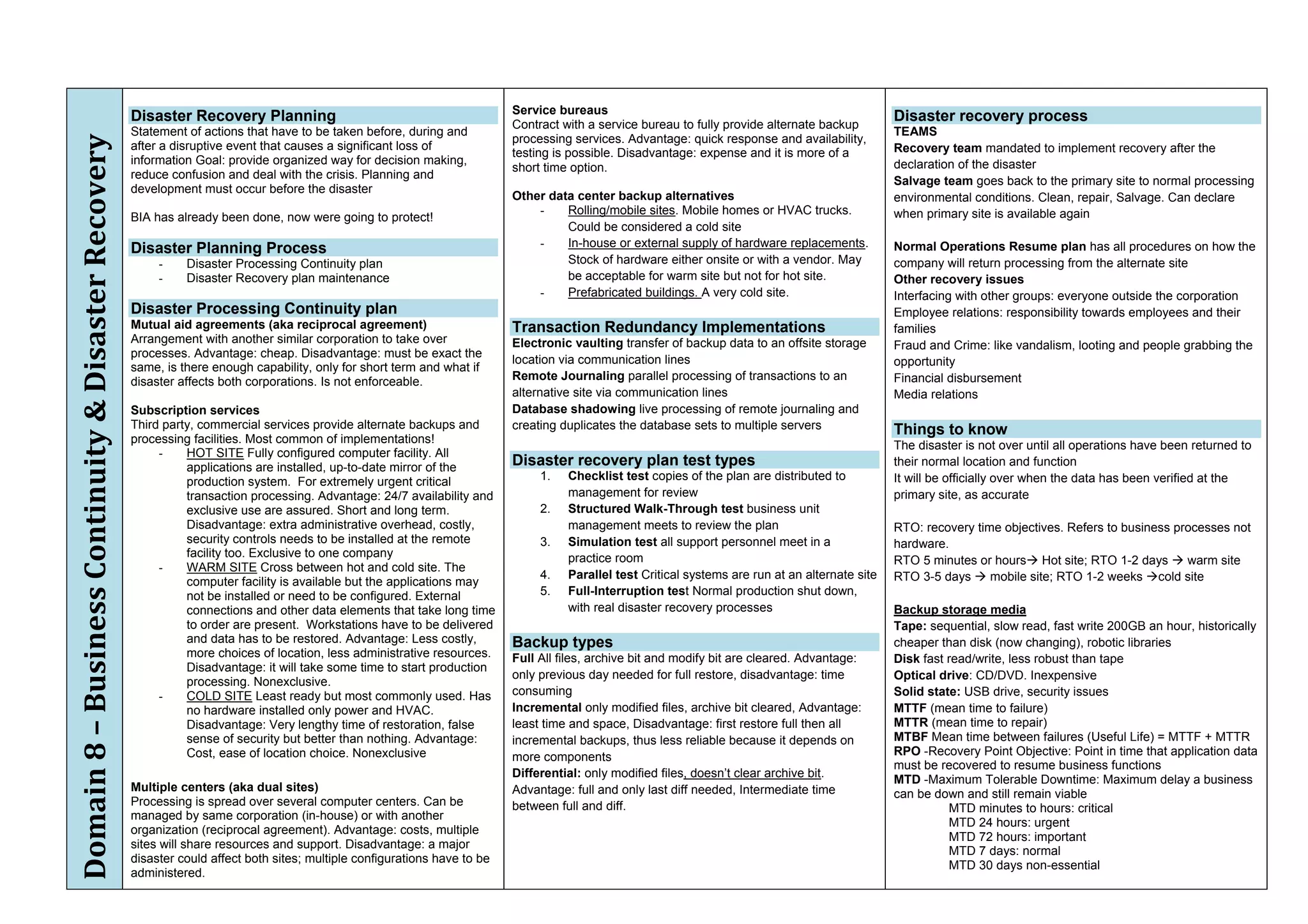
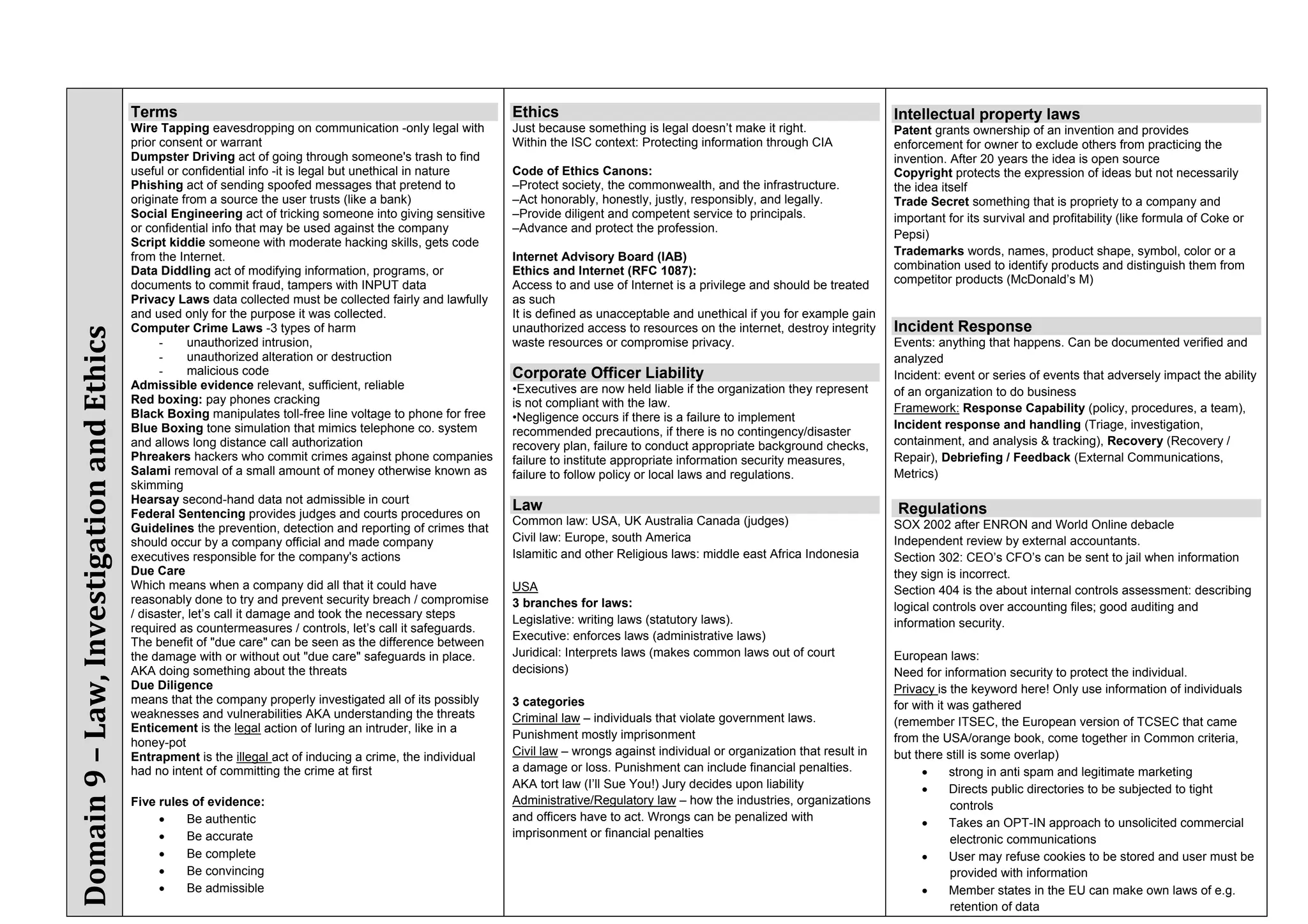
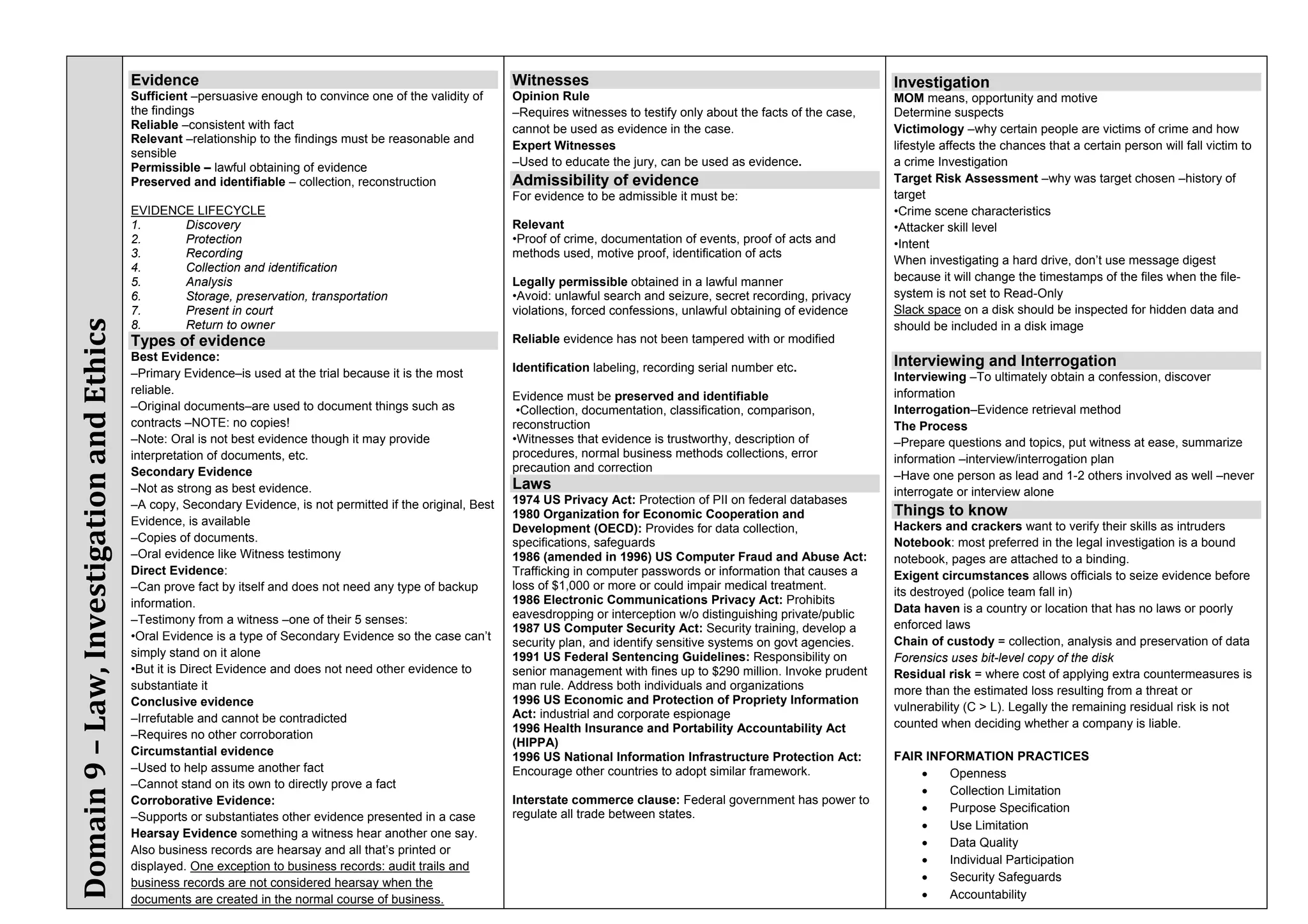
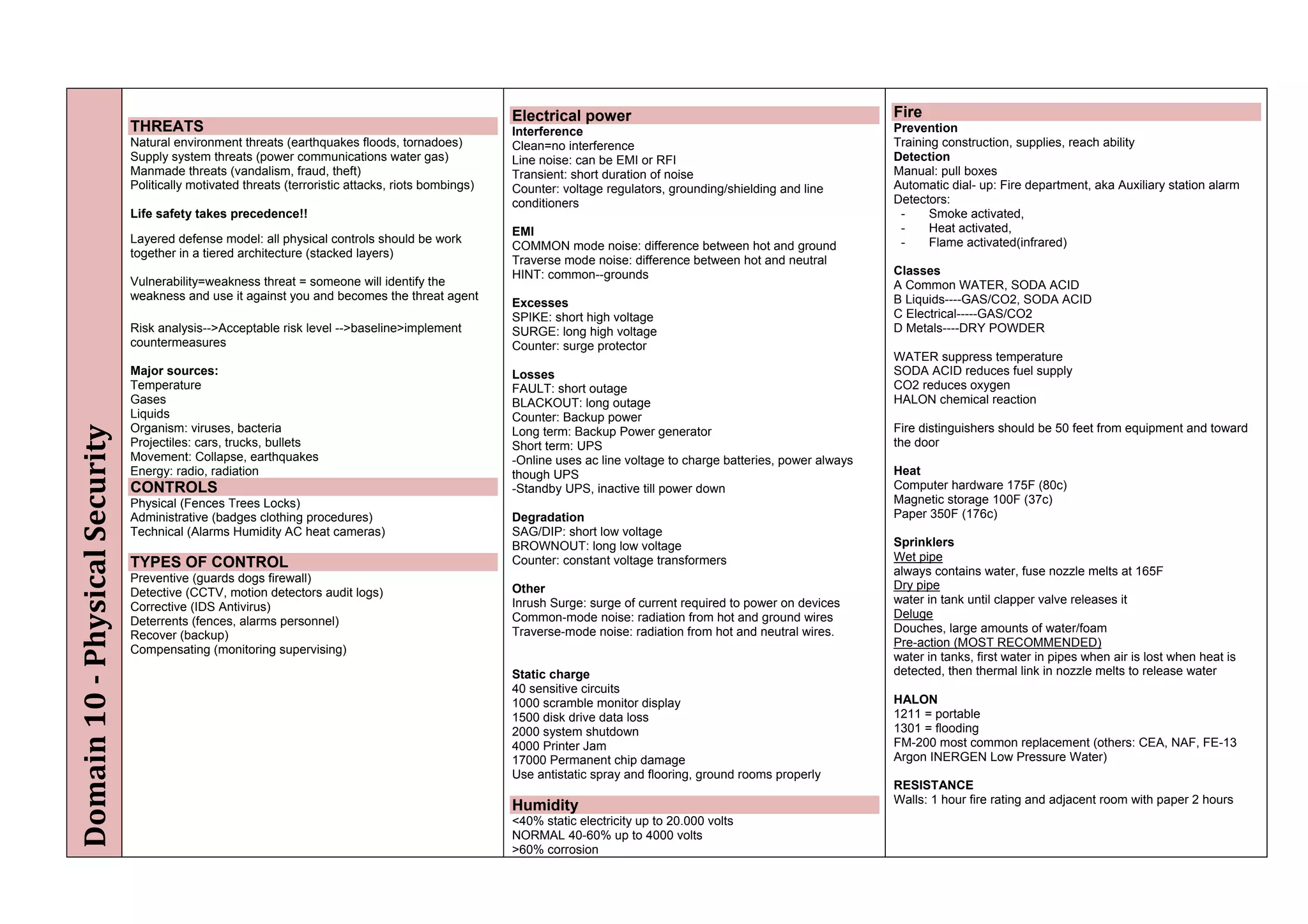
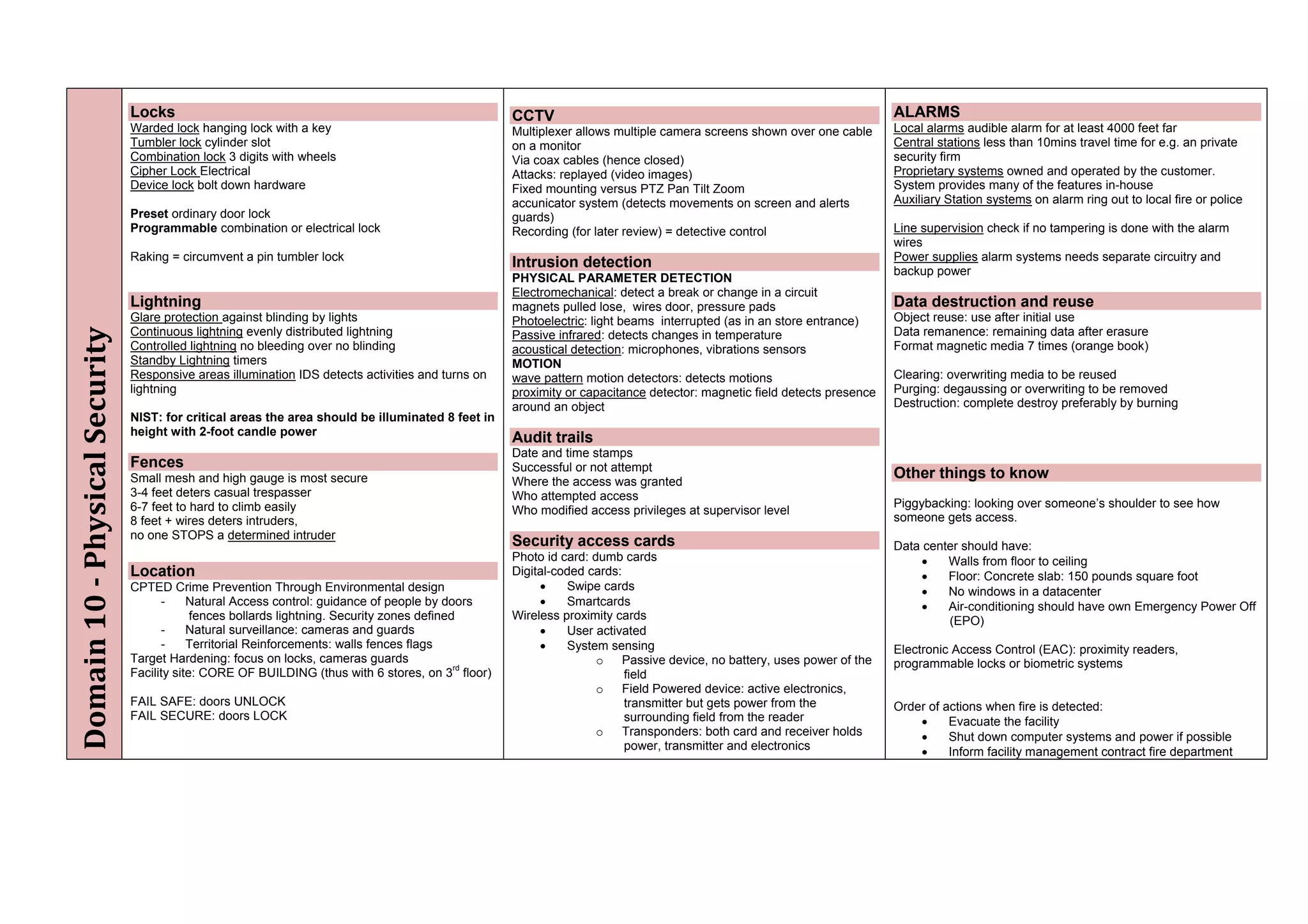
The document provides an overview of security policies, standards, and guidelines within information security, emphasizing the importance of management commitment, user identity authentication, and risk management strategies. It discusses various access control models, biometric authentication, and the roles of directory services and identity management in maintaining security. The document also outlines threats, vulnerabilities, and control measures necessary to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulations.