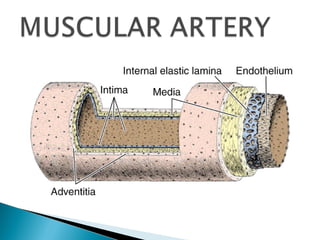
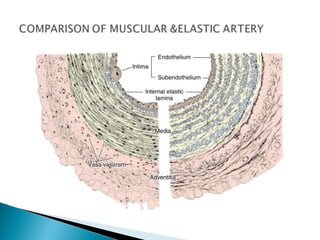
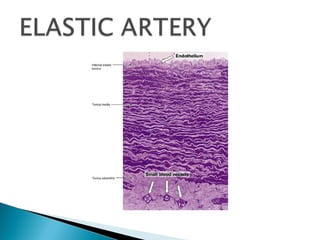
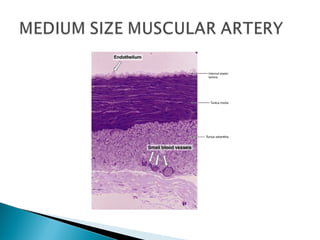
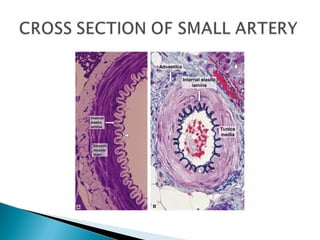
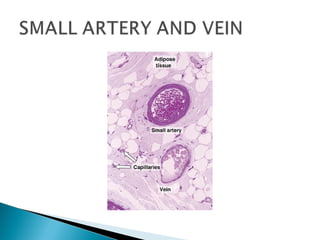
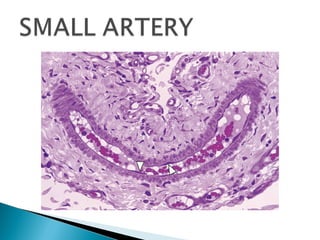
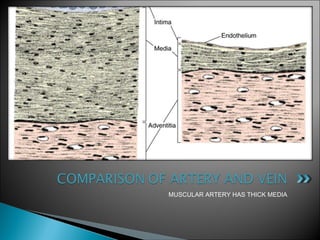
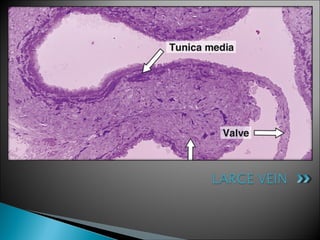
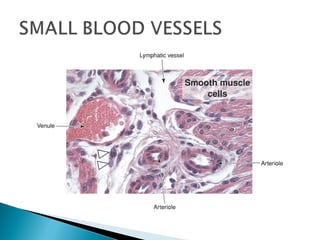
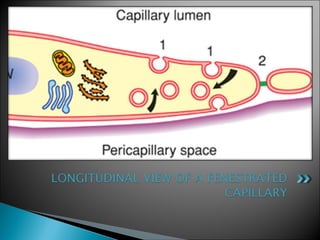
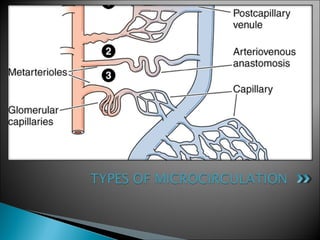
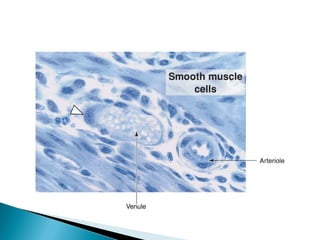
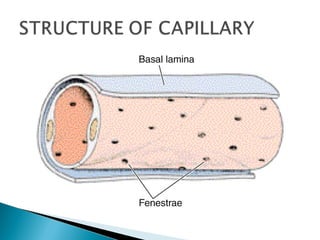
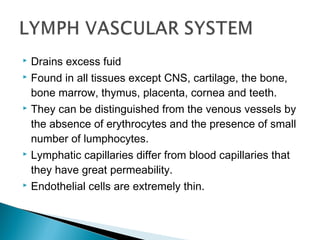
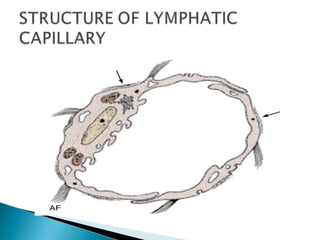
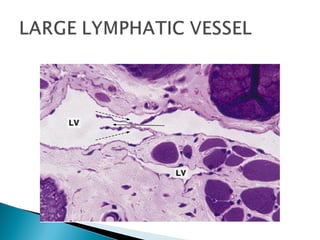
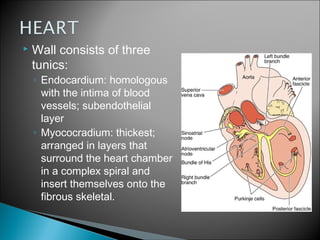
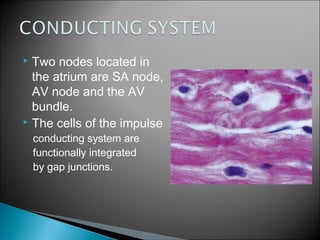
The document discusses the structure and function of lymphatic vessels and the heart. Lymphatic vessels drain excess fluid from tissues and have thin endothelial walls lacking basement membrane and pericytes. The heart has three layers - endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium. The myocardium is the thickest layer and contains specialized conduction system nodes that coordinate heart contractions.