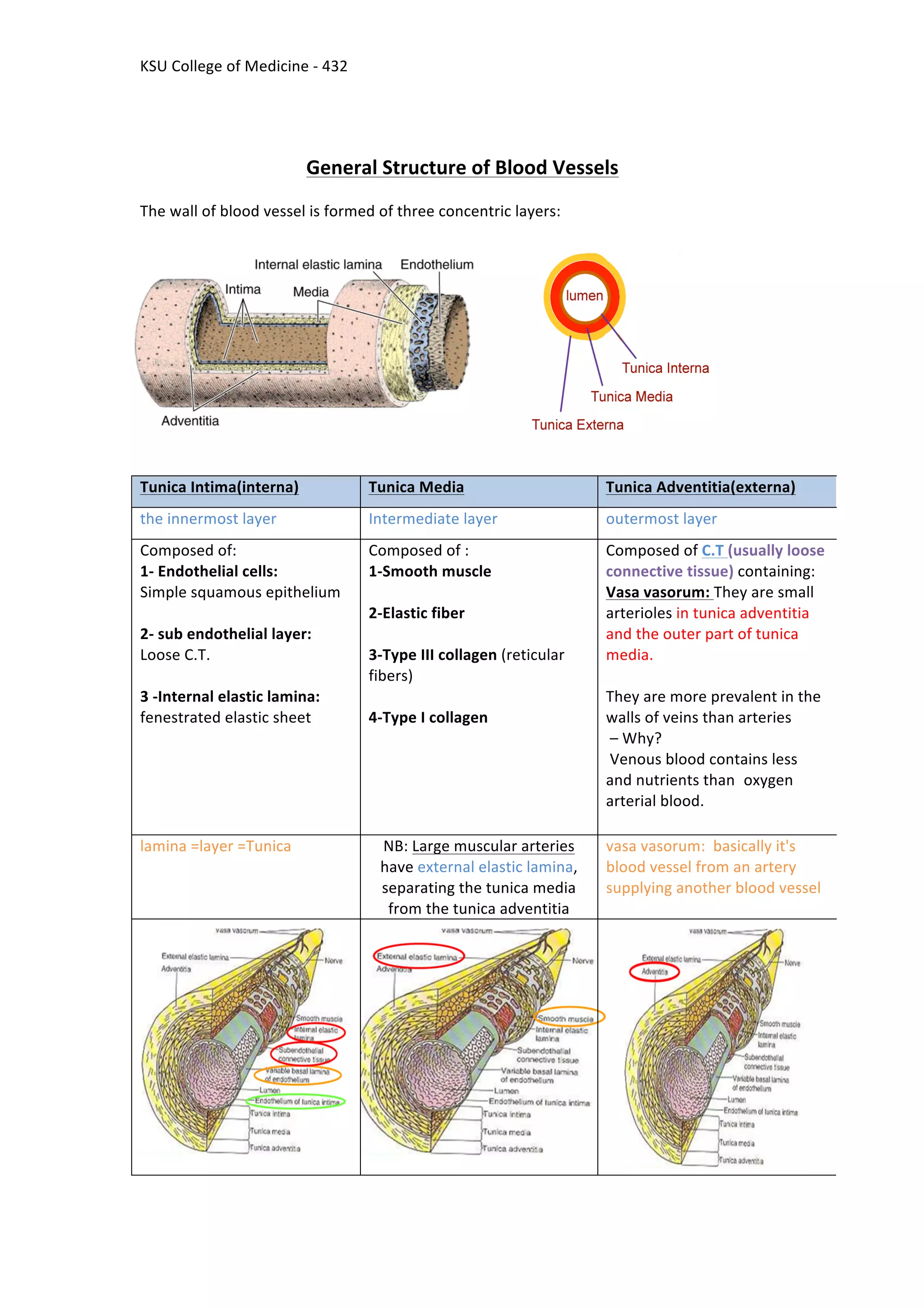
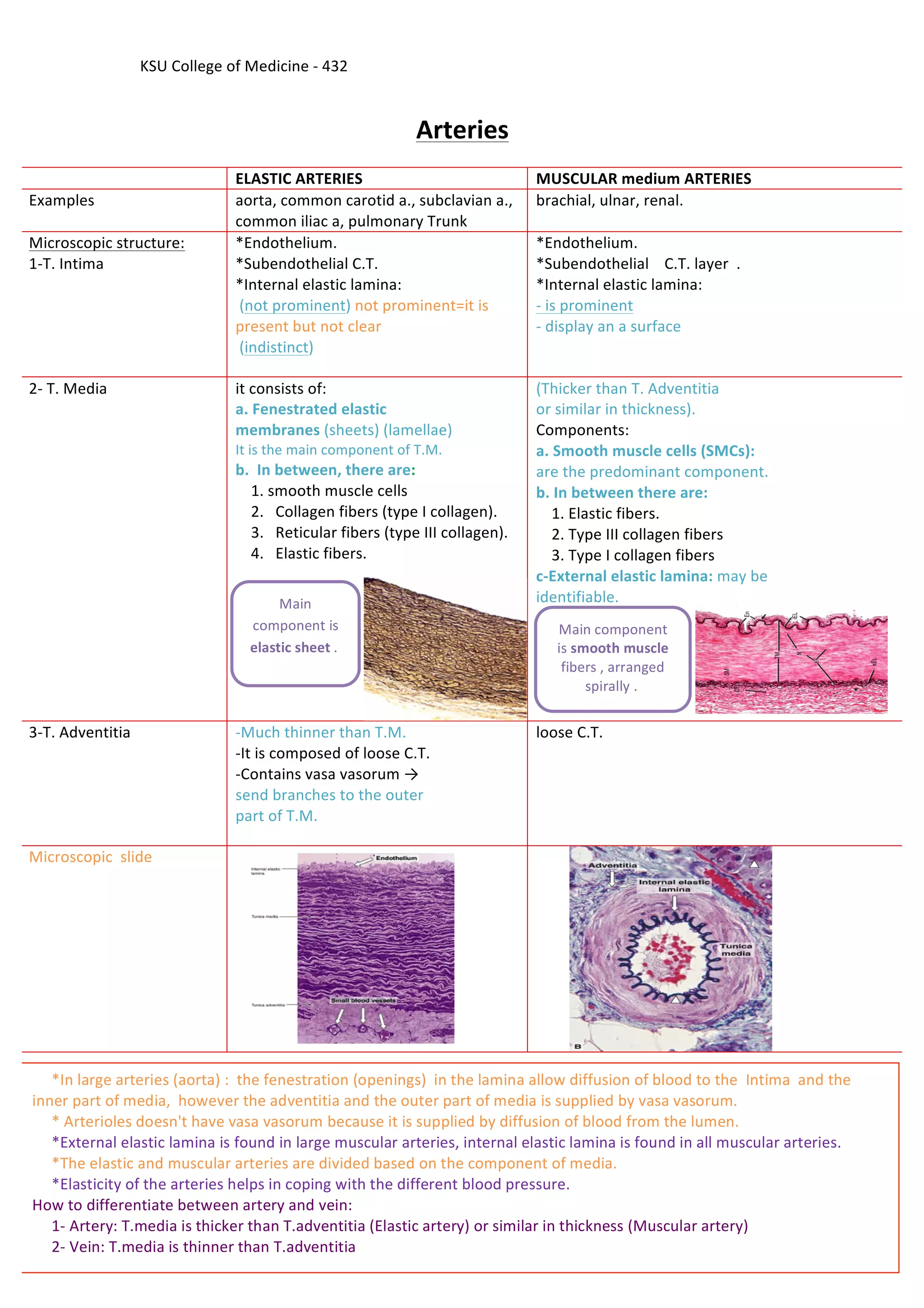
This document provides an overview of the histology of blood vessels, including arteries and veins. It begins by stating the learning objectives of identifying and describing the microscopic structures of elastic arteries, muscular arteries, medium-sized veins, and blood capillaries. The document then provides detailed descriptions of the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia layers and their components in different blood vessel types. Key differences between arteries and veins are highlighted, such as arteries having a thicker tunica media than adventitia, while veins have a thinner tunica media. Examples of elastic and muscular arteries are given along with diagrams and microscopic slides.