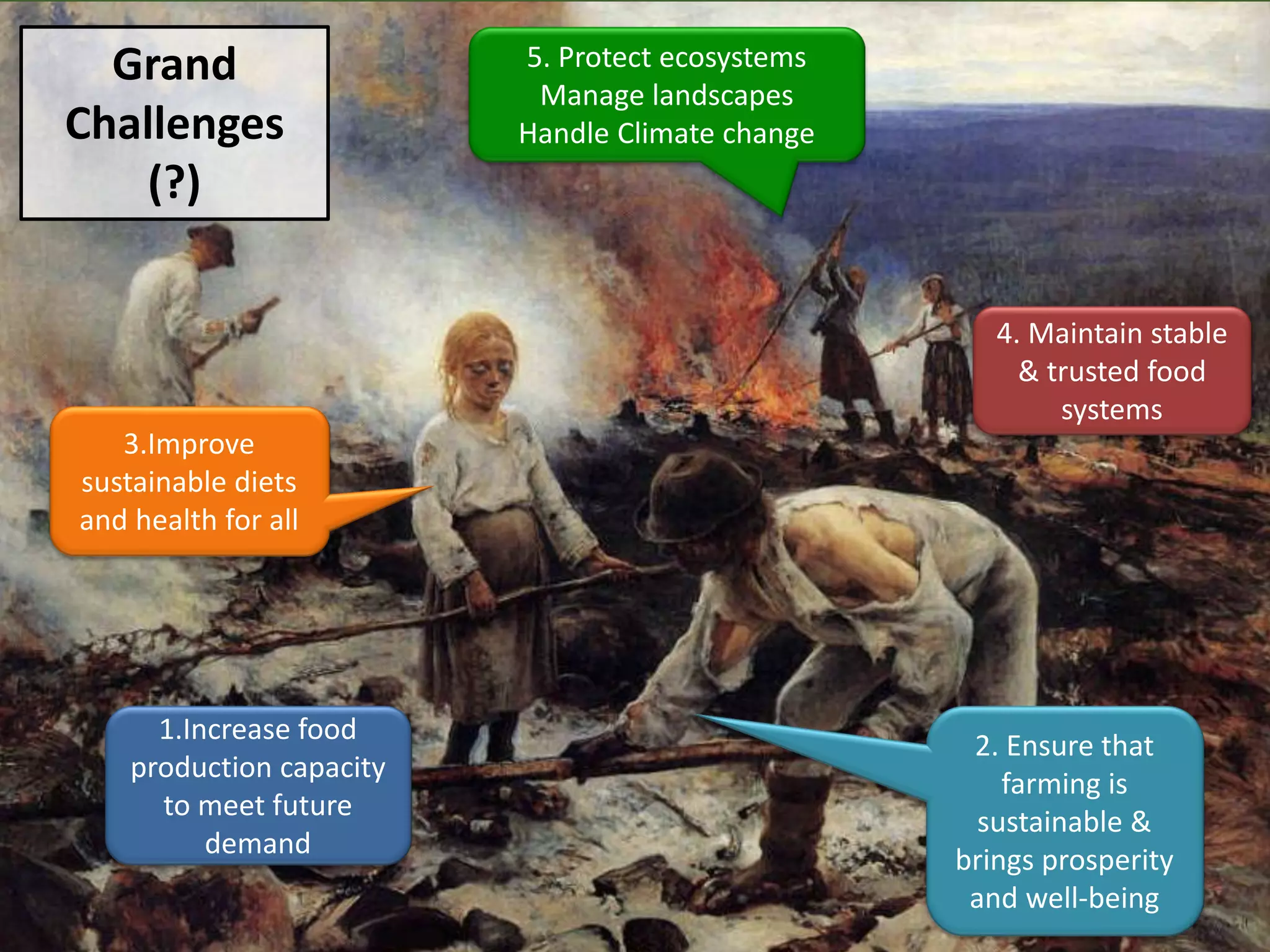
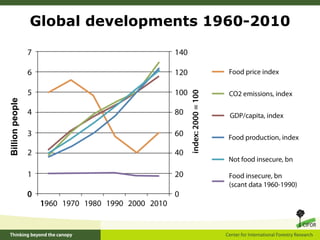
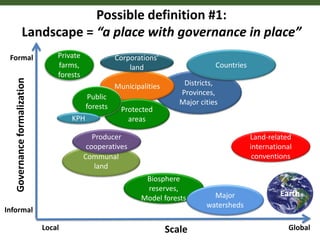
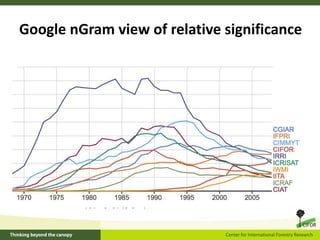
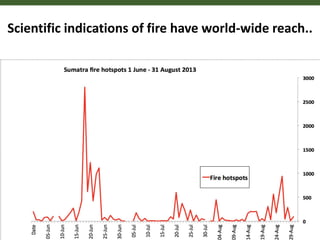
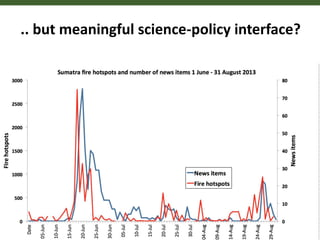
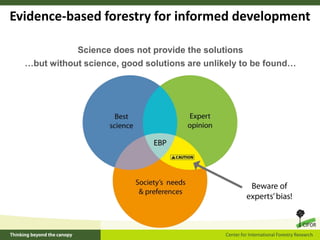
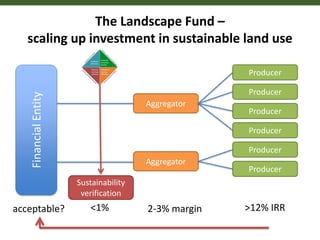
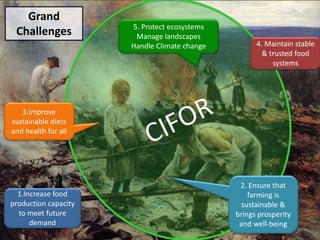
This document outlines 5 grand challenges for ensuring global food security and environmental sustainability: 1) Increase food production capacity, 2) Ensure sustainable and prosperous farming, 3) Improve healthy diets for all, 4) Maintain stable food systems, and 5) Protect ecosystems by managing landscapes and addressing climate change. It also provides context on expected global population growth, consumption patterns, and increased climate variability, emphasizing the need to create a planet with healthy landscapes to meet these challenges.