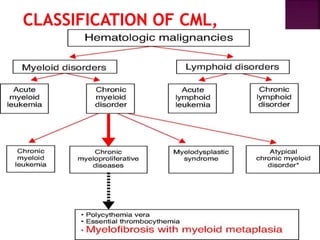
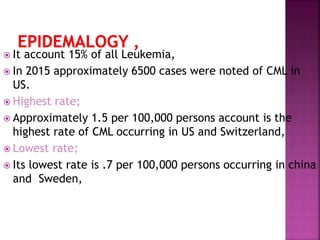
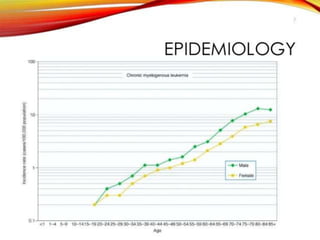
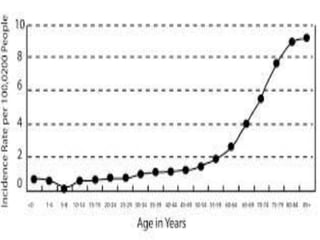
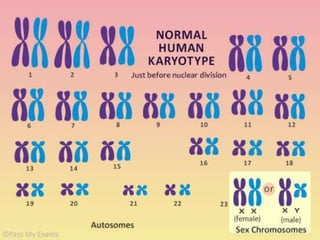
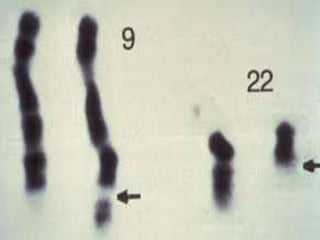
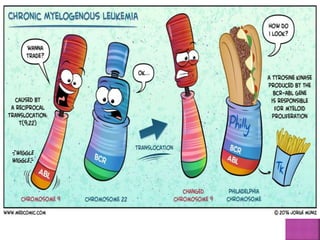
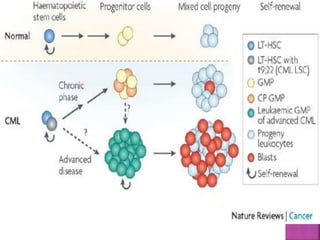
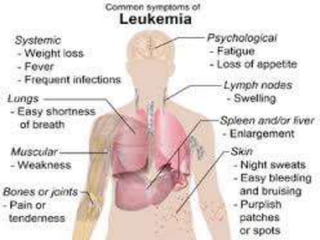
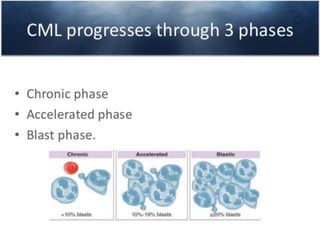
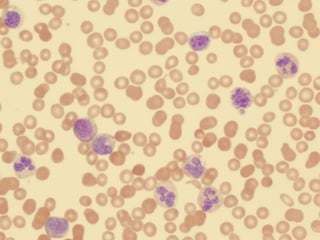
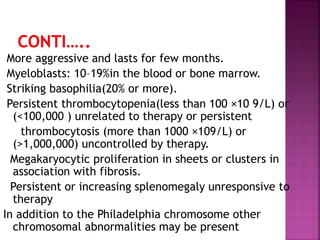
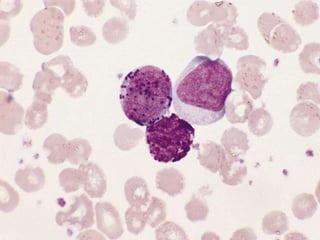
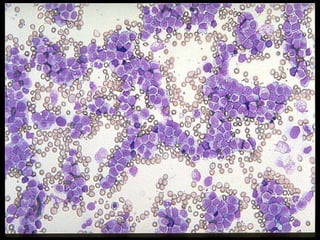
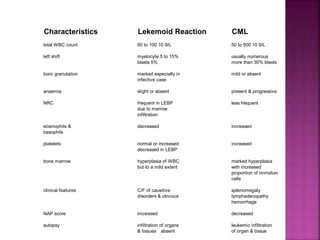
This presentation provides information about chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It begins by outlining 8 learning objectives about CML, including defining it, describing its subtypes and epidemiology, explaining its pathophysiology and genetic alterations, comparing its clinical signs in different phases, and more. Key points covered include that CML is characterized by overproduction of myeloid cells due to the Philadelphia chromosome and BCR-ABL fusion gene. It progresses through chronic, accelerated, and blast crisis phases and is typically diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and genetic testing. Treatment involves targeting the BCR-ABL fusion protein to control symptoms and slow disease progression.