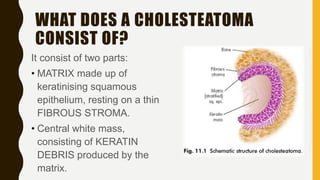
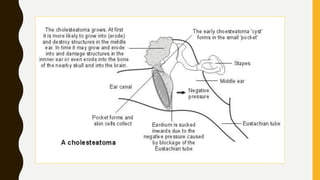
1. A cholesteatoma is a cyst-like sac in the middle ear that is lined with keratinizing squamous epithelium and contains desquamated keratin. It is not a tumor and does not contain cholesterol.
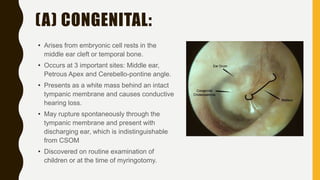
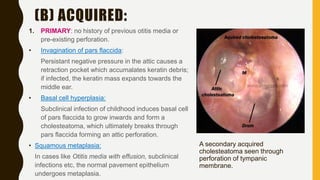
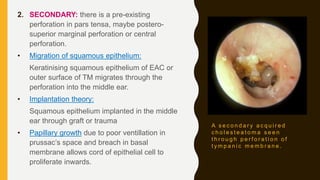
2. Cholesteatomas can be congenital, arising from embryonic cell rests, or acquired through retraction pockets, squamous metaplasia, or migration of epithelium through a perforated eardrum.
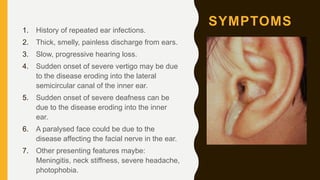
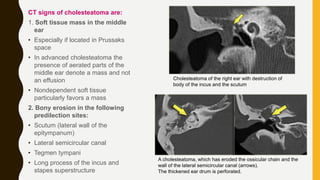
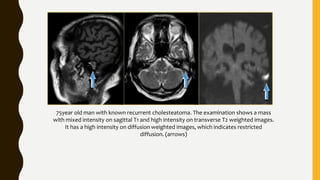
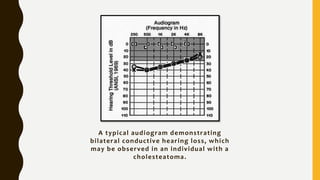
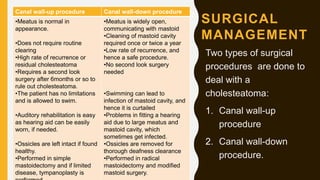
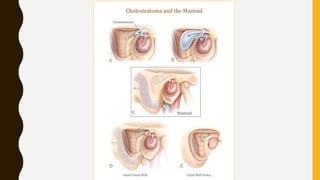
3. It expands through bone erosion using enzymes produced by the epithelial lining and inflammatory cells, and can cause hearing loss, facial paralysis, and other complications if left untreated.