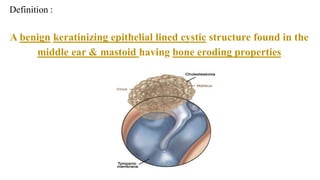
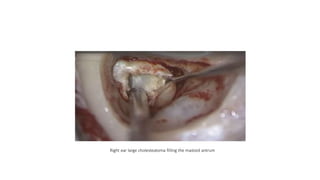
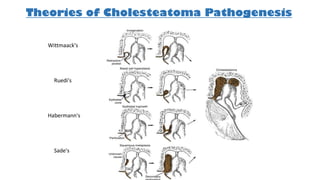
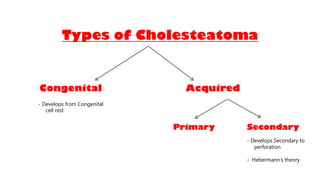
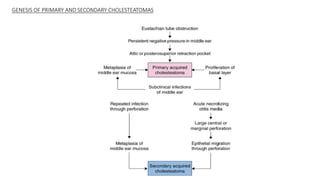
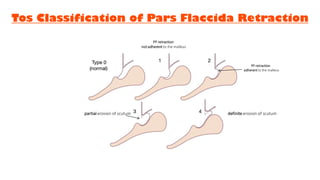
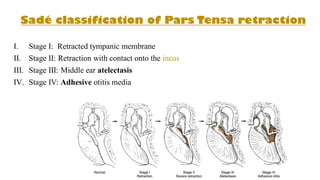
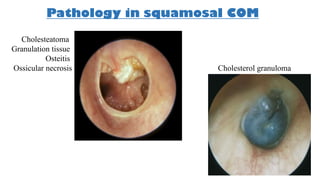
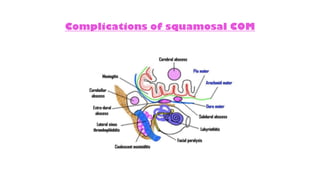
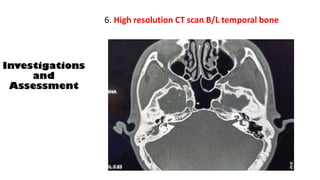
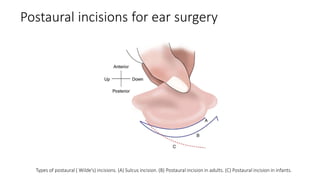
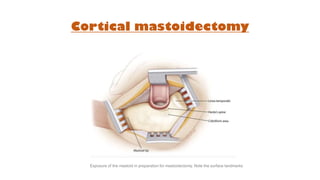
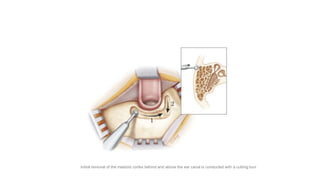
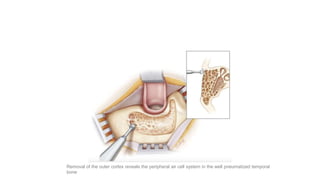
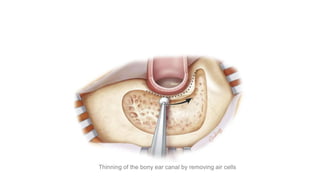
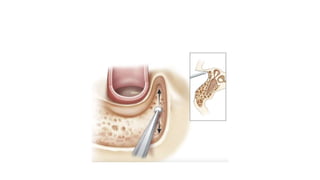
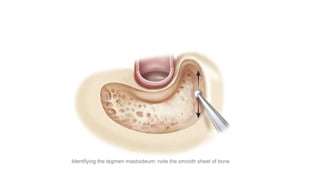
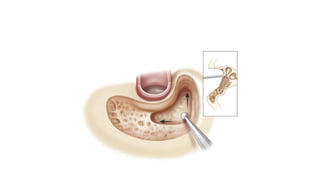
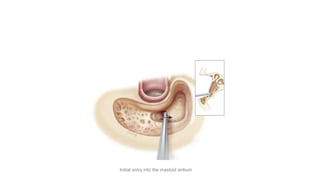
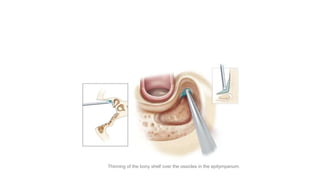
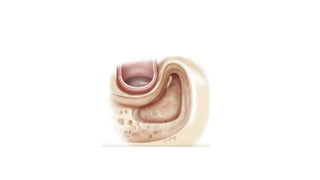
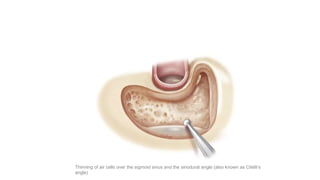
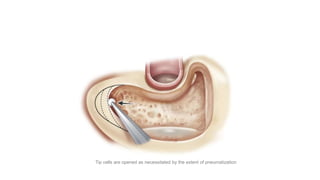
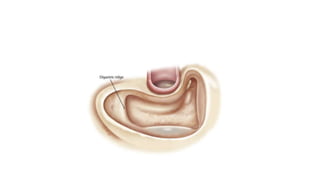
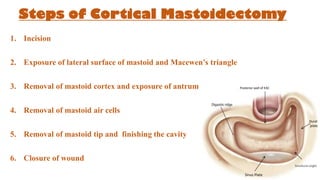
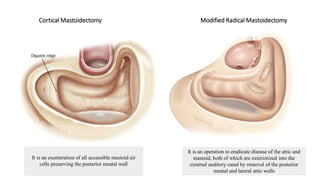
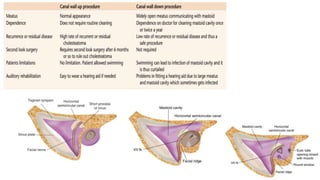
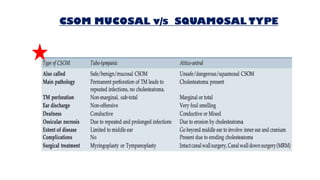
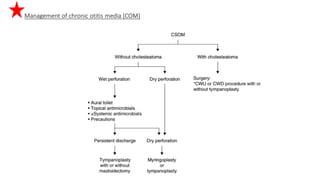
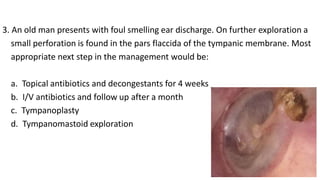
Cholesteatoma is a benign, cystic structure in the middle ear characterized by a growth of keratinizing epithelium that can erode bone and lead to various complications, primarily presenting with persistent foul-smelling discharge and conductive hearing loss. Treatment mainly involves surgical intervention, with options including mastoid exploration and different types of mastoid surgeries aimed at eradicating the disease and reconstructing hearing mechanisms. Postoperative complications may include facial nerve injury and infections.