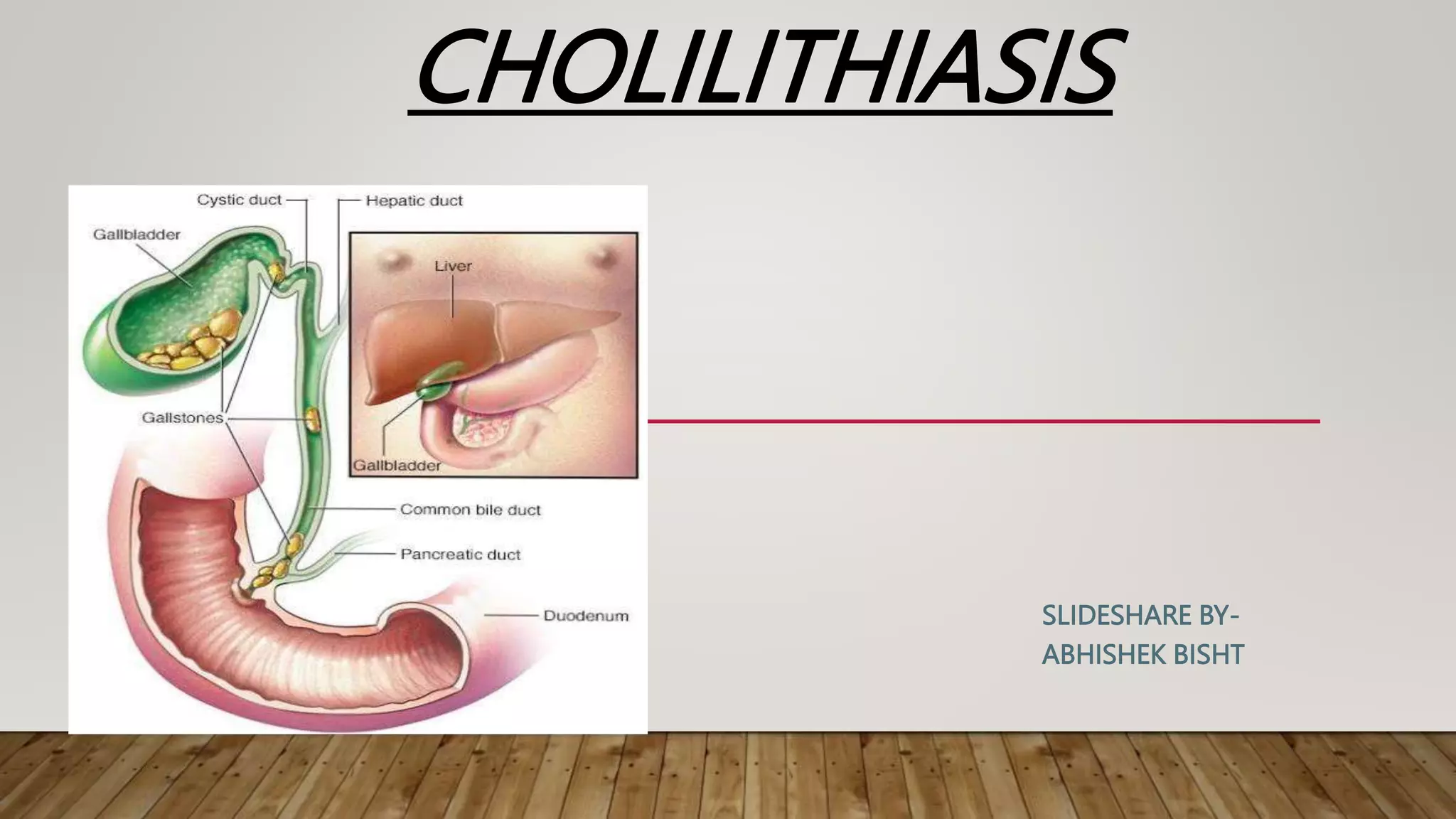
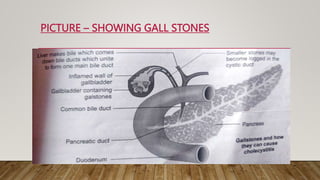
Cholilithiasis refers to the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder. Gallstones are crystalline formations that develop from the accumulation of bile components. There are three main types of gallstones: cholesterol stones, pigment stones, and mixed stones. Risk factors for developing gallstones include female gender, family history, obesity, diet high in fat and cholesterol, older age, and certain medical conditions or drugs. Symptoms include pain in the right upper abdomen or under the right shoulder, nausea and vomiting, and clay-colored stools. Gallstones are diagnosed through imaging tests, blood tests, or endoscopic procedures and can be managed through medications, surgery, shockwave lithotripsy, or diet and lifestyle changes