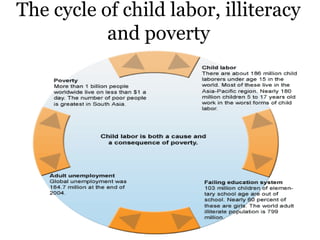
Child labour refers to the employment of children below a certain age, usually considered illegal. Historically, child labour first appeared in agriculture and later in industries such as coal mining. The causes of child labour include overpopulation, poverty, illiteracy, and the willingness to exploit children. Common areas where child labour is practiced include fireworks manufacturing, mining, domestic work, and cocoa production. The consequences are stunted growth, increased illiteracy, perpetuation of poverty, and abuse of children. Several laws and acts have been implemented by governments and non-profits worldwide to prohibit child labour.