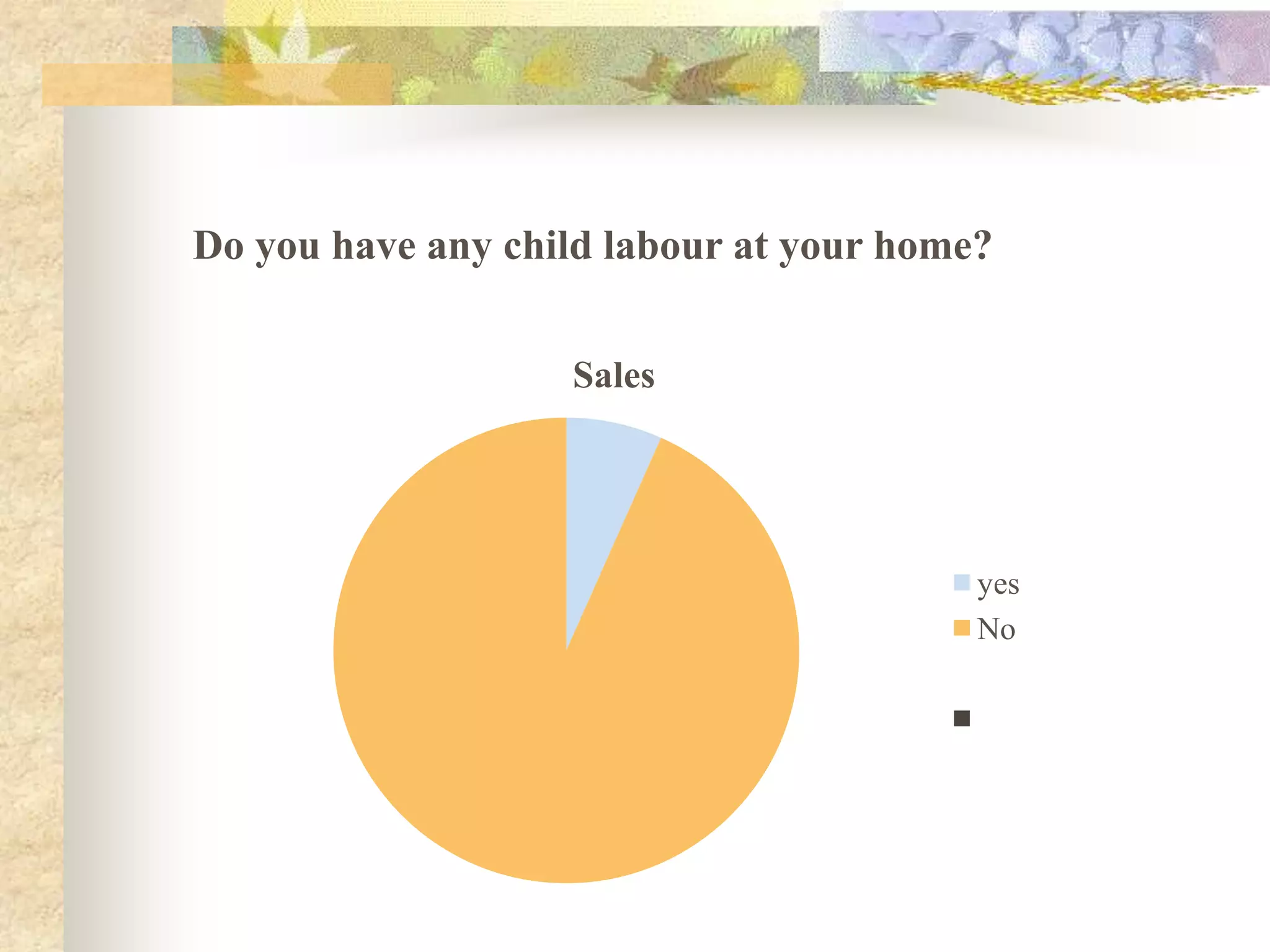
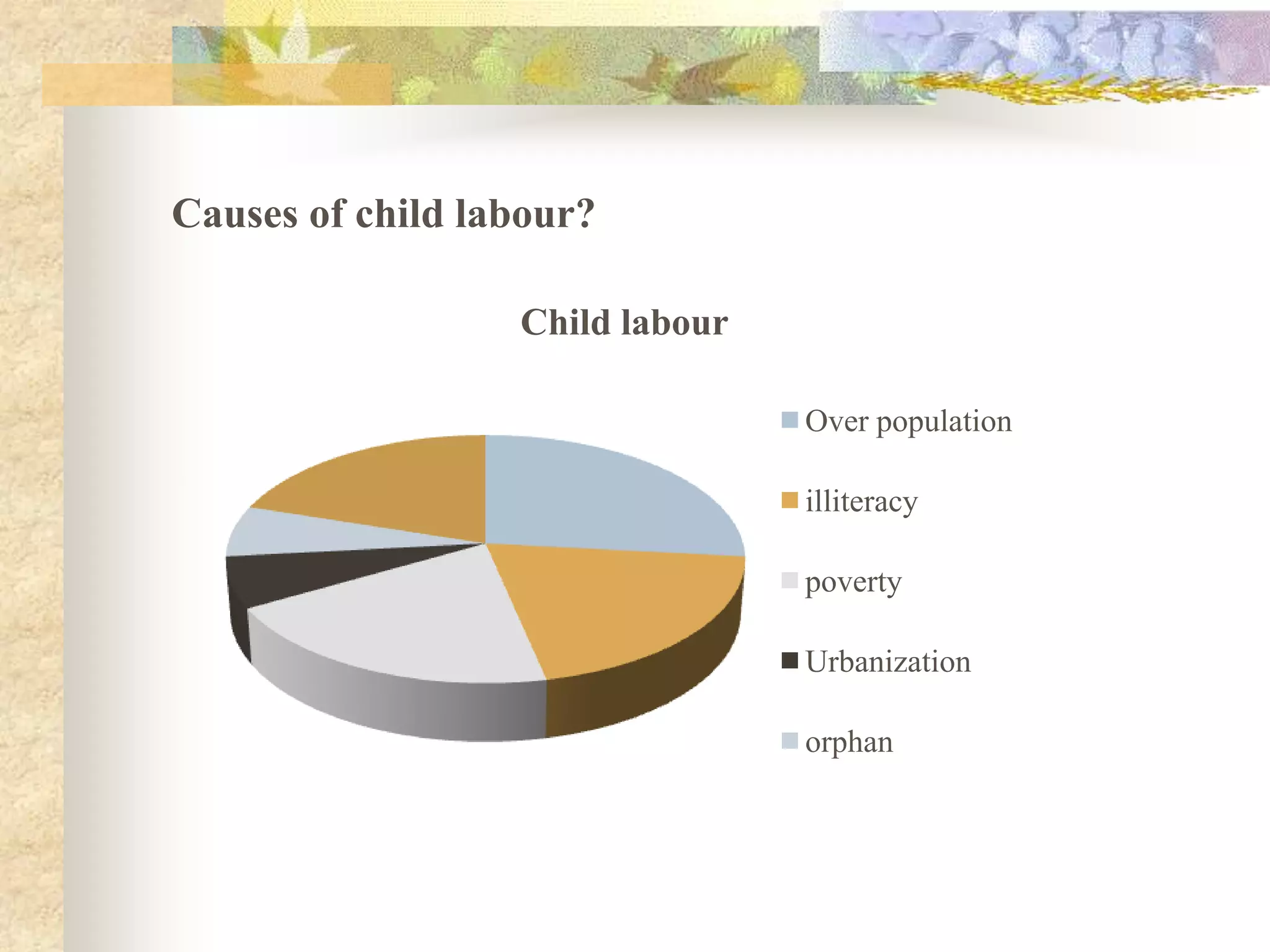
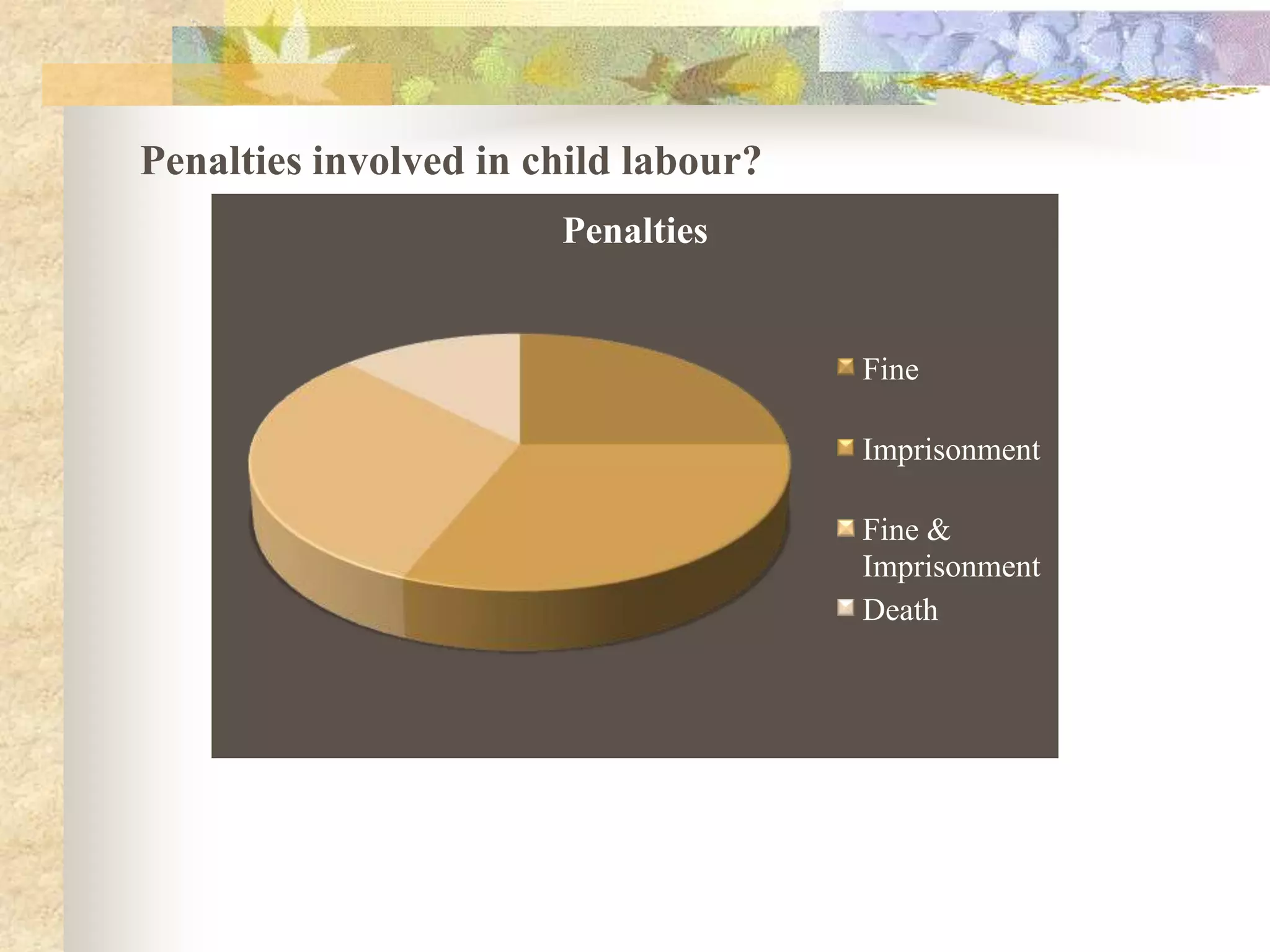
This document discusses child labor in India. It provides statistics on child labor such as 73 million children under 10 years old working and 47 out of 100 children in India enrolled in class I dropping out before class VIII. It discusses causes of child labor like poverty, illiteracy, urbanization, and willingness of others to exploit children. Consequences for children who work include physical injuries, growth deficiencies, and exhaustion. The document also outlines India's Child Labour Act of 1986 which prohibits certain occupations for children under 14 and regulates their work conditions.