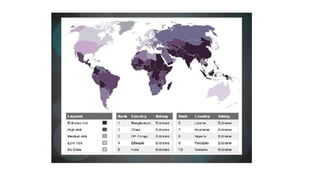
Child labour refers to work done by children that deprives them of their childhood and negatively impacts their health, education, and development. Macroeconomic factors that encourage child labor include poverty, lack of access to schools, growth of the informal economy with low wages, and inflexible labor markets. Consequences of child labor are that it prevents education and proper development, reduces physical health, and has long-term negative impacts on human capital accumulation and economic prosperity. Efforts to reduce child labor include legislation, international initiatives, and increasing access to compulsory education.