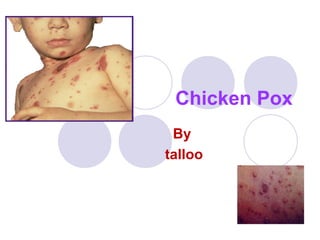
Chicken pox is caused by the varicella zoster virus and is highly contagious, usually occurring in children ages 5-9. It spreads through direct contact or respiratory droplets from infected individuals. After an incubation period of 2-3 weeks, symptoms include a slight fever and rash that begins on the trunk and spreads, with blisters forming scabs within a few days. While there is no cure, treatments can relieve itching and fever, and isolation is required until lesions have healed to prevent spread.