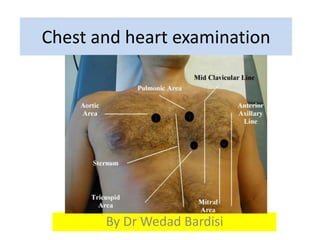
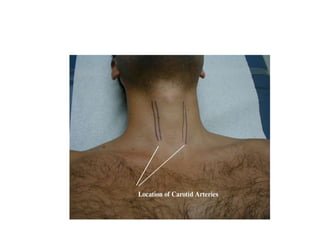
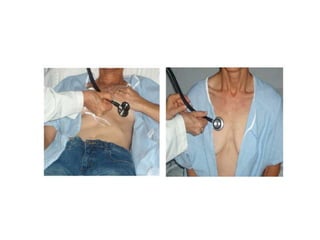
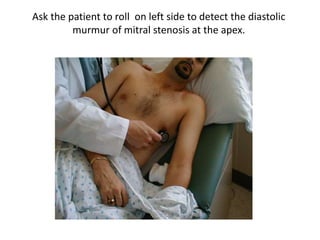
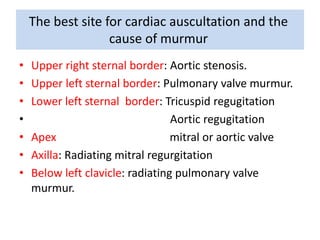
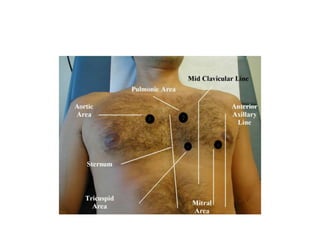
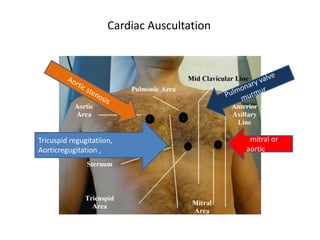
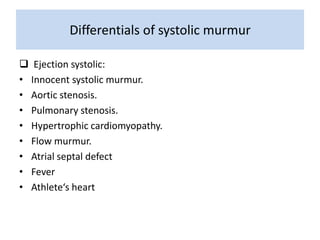
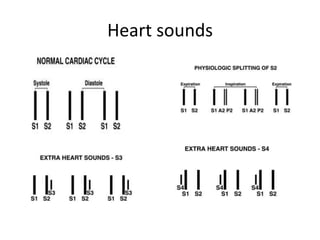
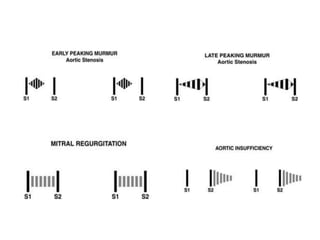
This document outlines the steps for examining the cardiovascular system, including inspection, palpation, auscultation, and percussion of the heart, neck, lungs, abdomen, and limbs. Key steps include assessing pulse and blood pressure, listening to heart sounds and murmurs at different auscultation sites, and differentiating between systolic and diastolic murmurs that may indicate conditions like aortic stenosis, mitral stenosis, or aortic regurgitation. The goal is to perform a thorough routine exam of the cardiovascular system and identify any abnormalities.