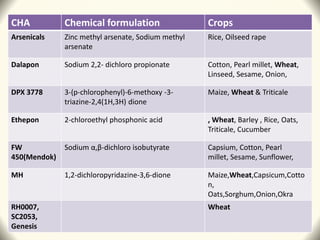
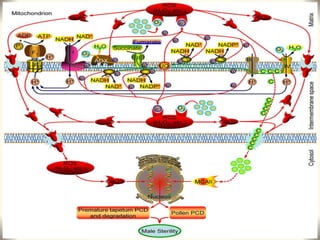
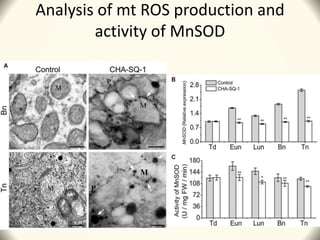
1) The document discusses the use of the chemical hybridization agent SQ-1 to induce male sterility in wheat plants. It investigates the effects of SQ-1 on anther and microspore development, flag leaf morphology, and mitochondrial function.
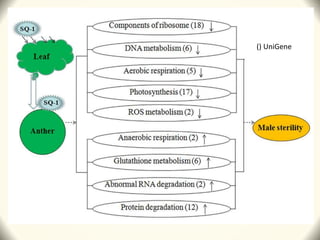
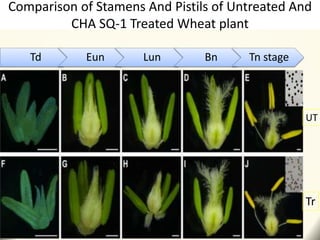
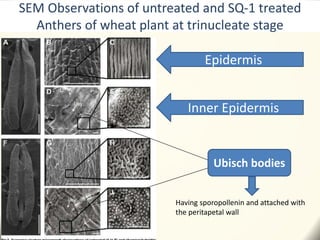
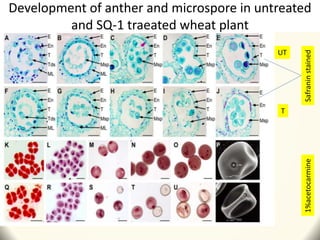
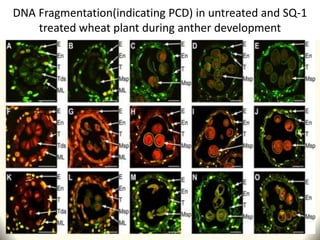
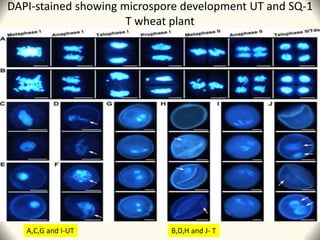
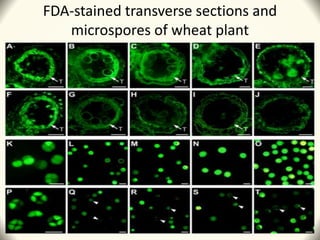
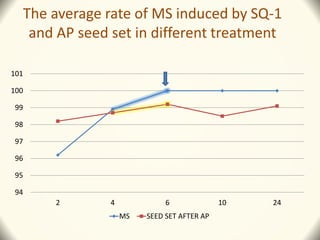
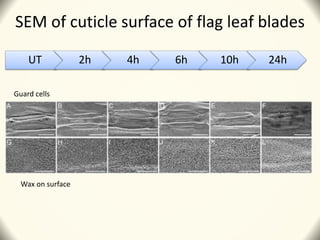
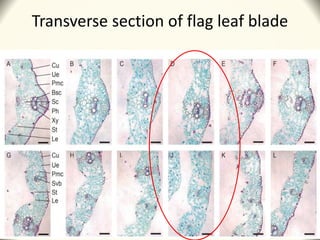
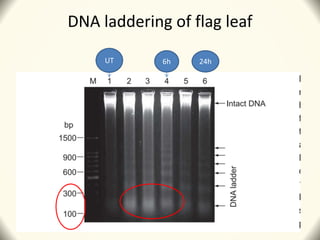
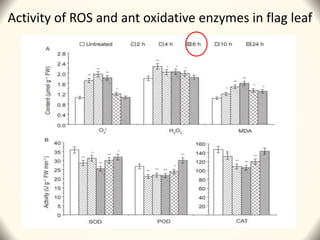
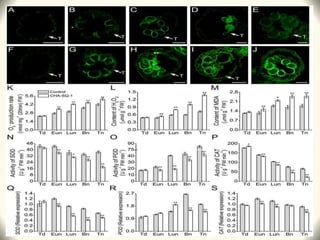
2) Application of SQ-1 led to abnormal tapetum and microspore development, DNA fragmentation in anthers, and oxidative stress responses in both anthers and flag leaves. This caused pollen abortion and full male sterility.
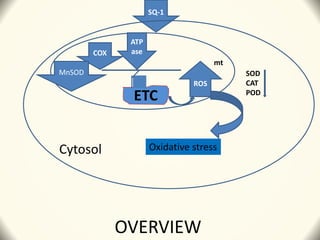
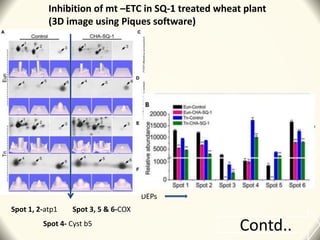
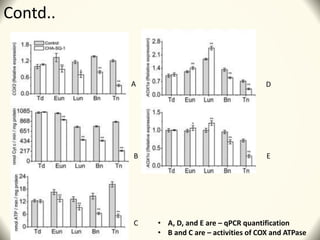
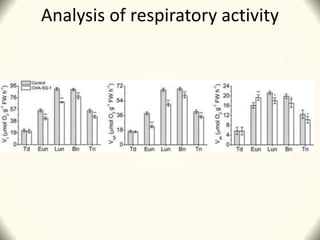
3) The study found that SQ-1 inhibits the mitochondrial electron transport chain, increasing reactive oxygen species in mitochondria. This mitochondrial dysfunction appears to cause tapetal apoptosis and lead to male sterility through