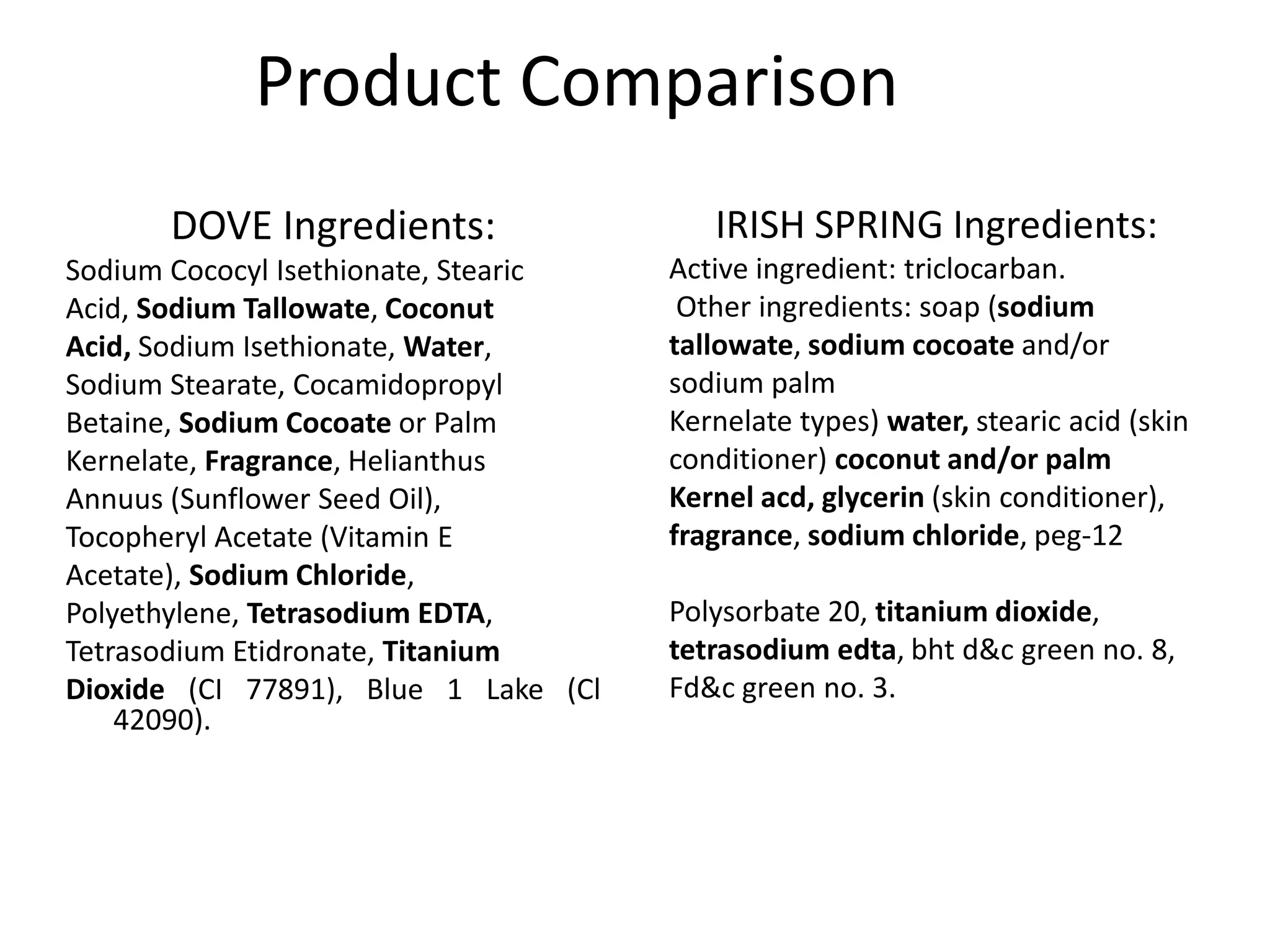
The document provides a history of soap and compares three popular bar soap brands: Dove, Irish Spring, and Zest. It discusses the origins of soap in ancient Babylon and Rome. It also outlines the key ingredients in each brand and how they differ. Dove contains more moisturizing oils, making it the most expensive. Irish Spring relies on fragrance with drying ingredients. Zest dissolves quickly with no special properties. The document concludes different soaps suit different preferences but notes environmental and health concerns with traditional hard soaps.






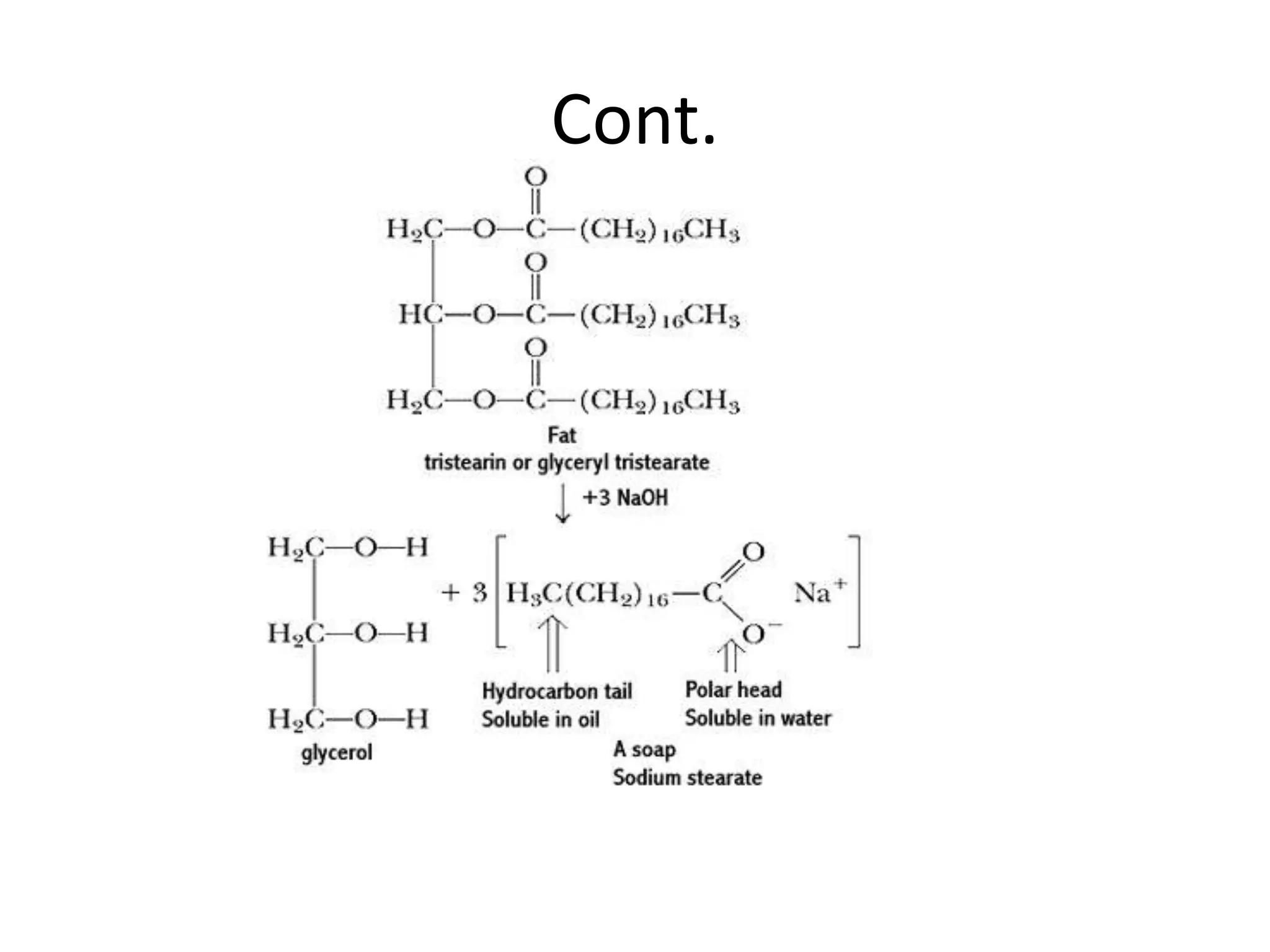
![Chemical structure
• Most soaps are soluble sodium or potassium salts of
carboxylic acids. The most common commercial soap is
sodium stearate, Na[C17H35CO2]. It dissolves in
water, forming the sodium and stearate ions. Even though
most of the stearate ion is a hydrocarbon chain, it dissolves in
water because of the carboxylate group. The carboxylate end
is called hydrophilic (water-loving), and the hydrocarbon tail is
called hydrophobic (water-fearing).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalcomparisonppt-120126113031-phpapp02/75/Chemical-comparison-ppt-7-2048.jpg)