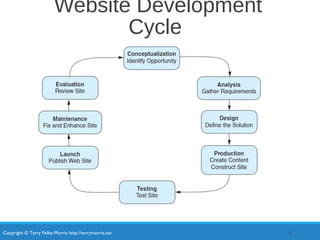
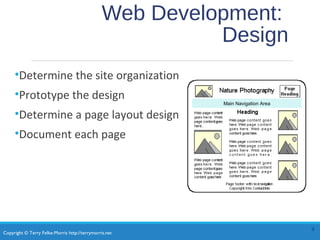
This chapter discusses the system development life cycle for web development projects. It describes the various roles needed for successful large and small-scale projects. These roles include project managers, designers, developers, and administrators. It also outlines the stages of the development cycle, including conceptualization, analysis, design, production, testing, launch, and maintenance. Finally, it covers how to choose a domain name and web hosting provider.