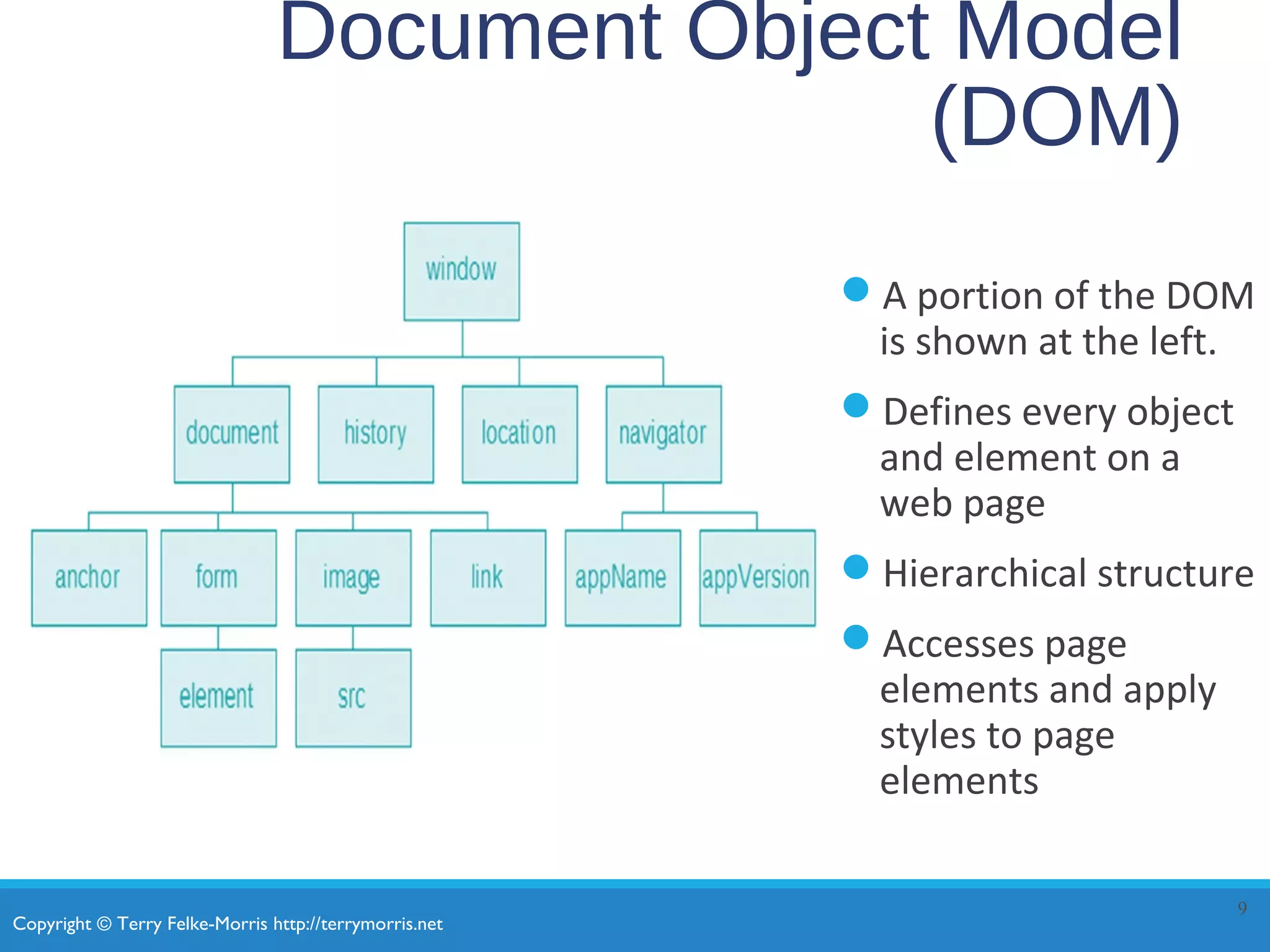
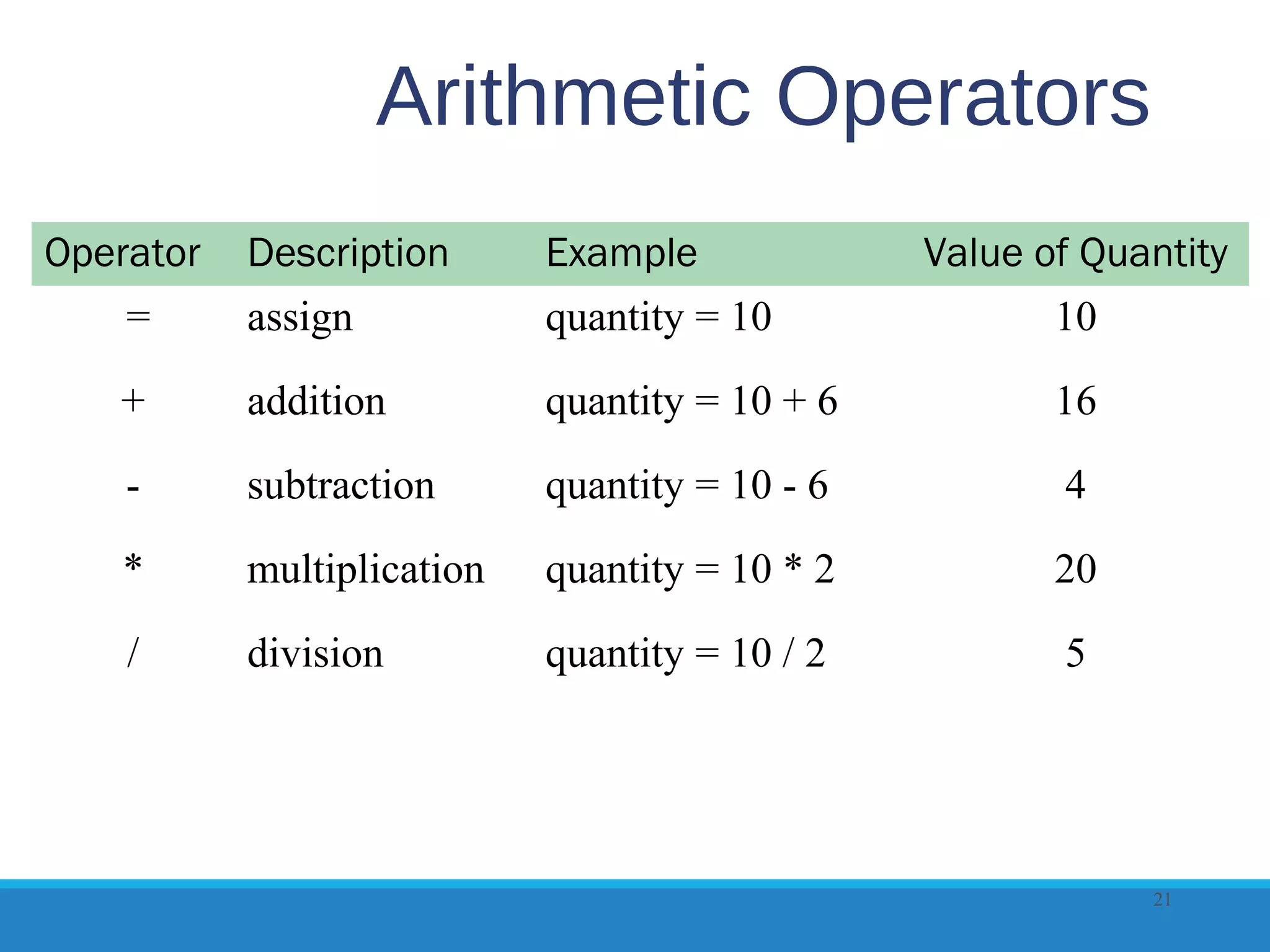
This document provides an overview of JavaScript and jQuery concepts for dynamic web development. It begins by listing learning outcomes which include describing common JavaScript uses, the Document Object Model, basic JavaScript syntax, variables, operators, and form validation. It also covers obtaining and using jQuery, selectors, methods, and plugins. Key topics are JavaScript debugging, functions, events, and ensuring accessibility without JavaScript. The document provides examples and checkpoints to reinforce understanding.























![Copyright © Terry Felke-Morris http://terrymorris.net
Validating Form Fields
Use the "" or null to check to determine if a form
field has information
if (document.forms[0].userName.value == "" ) {
alert("Name field cannot be empty.");
return false;
} // end if
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter14-170108213128/75/Chapter14-28-2048.jpg)