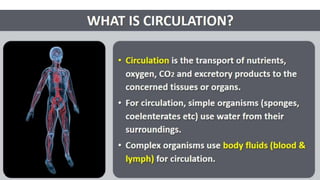
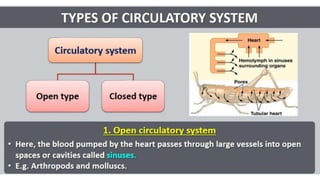
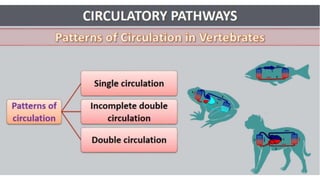
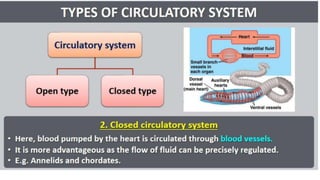
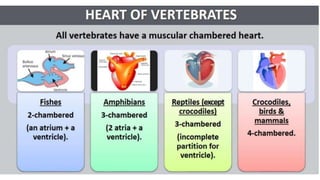
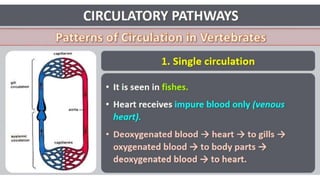
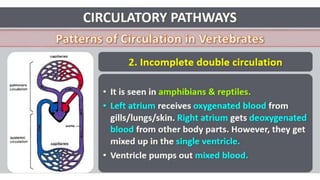
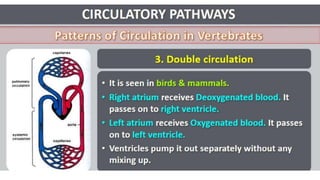
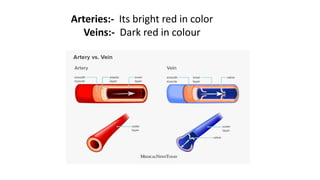
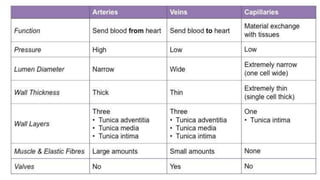
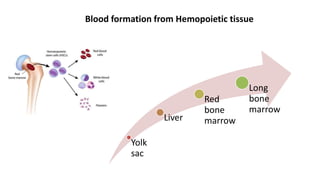
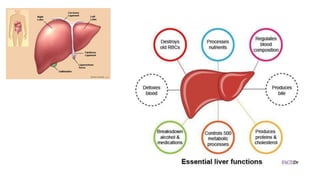
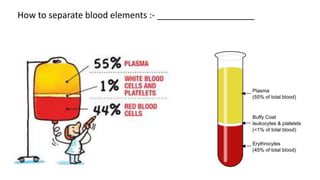
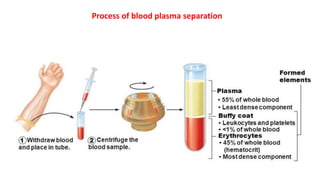
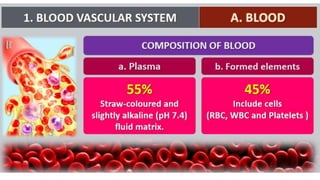
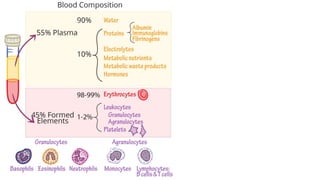
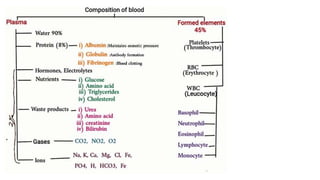
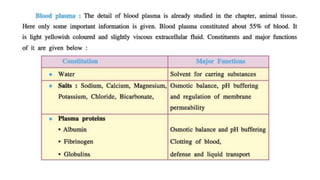
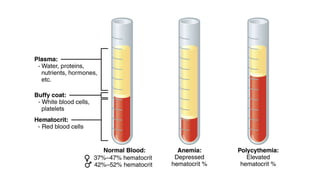
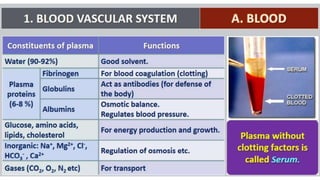
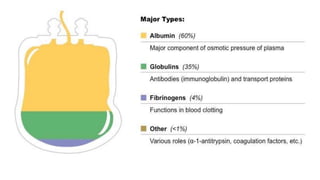
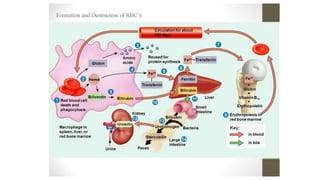
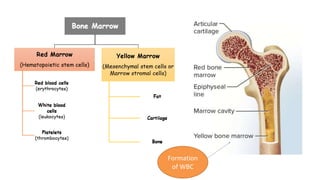
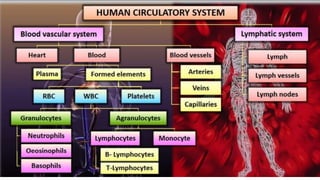
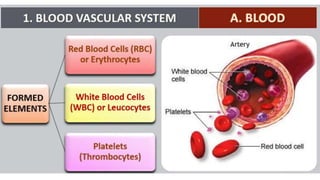
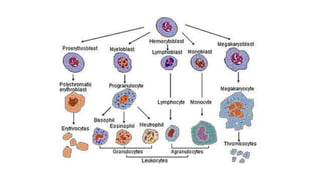
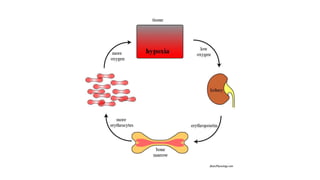
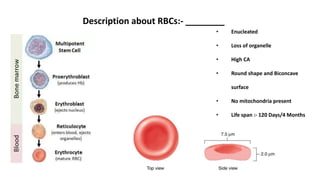
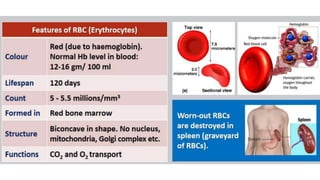
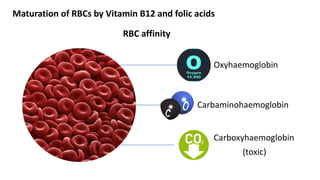
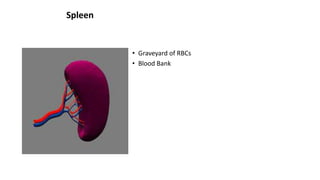
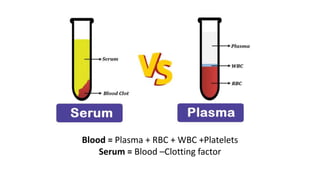
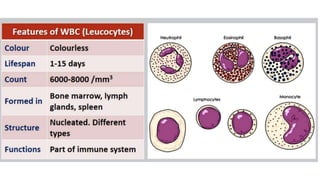
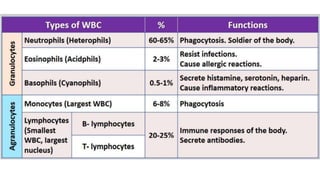
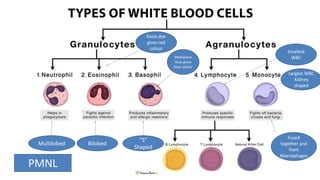
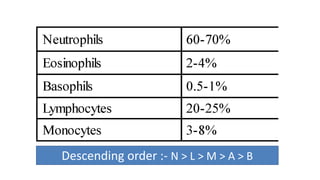
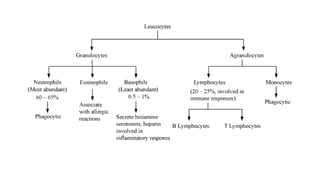
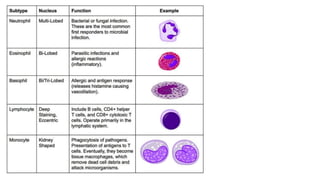
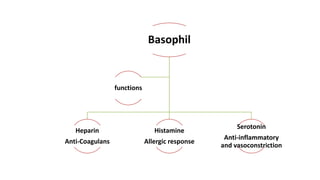
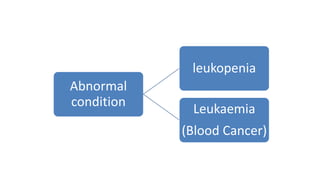
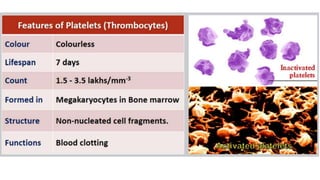
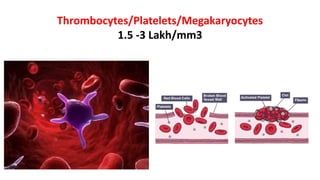
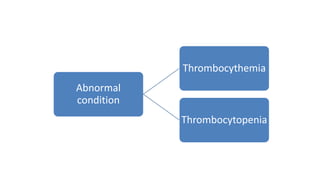
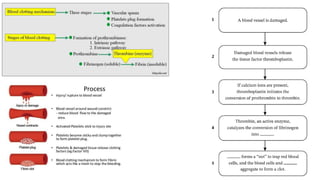
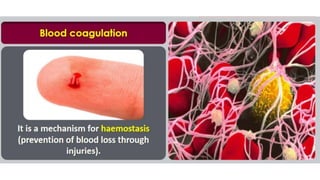
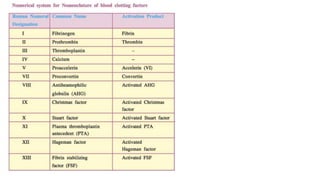
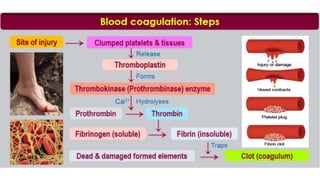
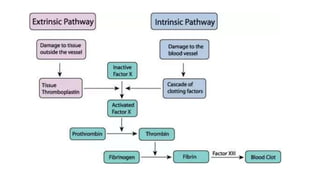
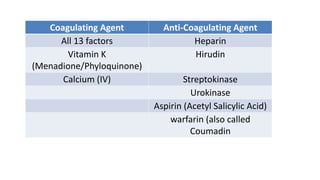
This document discusses body fluids and circulation. It defines terms related to hematology and blood vessels. It describes the formation of blood from hemopoietic tissue in the yolk sac, liver, red bone marrow, and long bone marrow. The document outlines the process of separating blood elements and forming plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It provides details on characteristics of red blood cells, diseases related to red blood cells, and maturation of red blood cells through vitamins. The document also describes types of white blood cells, platelet functions, and abnormal blood conditions. It concludes with lists of coagulating and anti-coagulating agents in the blood.