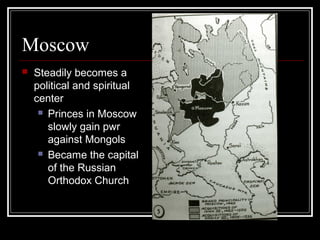
The document provides details about the Byzantine Empire and Eastern Europe. It describes the founding and role of Constantinople as the capital of the Byzantine Empire. It then discusses important figures like Justinian who commissioned constructions like the Hagia Sophia. The document also outlines the rise of Russia through the Kievan Rus period and the impacts of the Mongol invasion, with Moscow emerging as a new center.