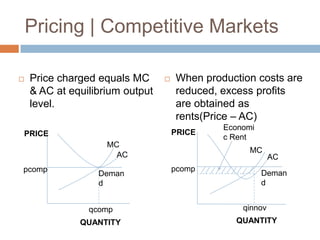
This document discusses the role of pricing and public policy in various market structures, particularly focusing on perfect competition, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. It emphasizes the importance of understanding market imperfections, economies of scale in natural monopolies, and the challenges posed by oligopoly dynamics, including strategic interdependence and the potential for price wars. Overall, it highlights how these factors influence prices and market efficiency, necessitating careful consideration by policymakers.