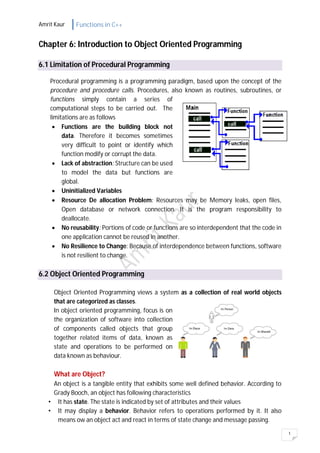
Object oriented programming views a system as a collection of objects that contain both data (state) and behaviors (operations). An object has an identity, state, and behavior. Classes are sets of similar objects that share common attributes and behaviors. The key characteristics of object oriented programming are abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Abstraction involves hiding non-essential details and focusing on essential characteristics. Encapsulation implements abstraction by hiding implementation details within an object. Inheritance allows new classes to inherit and modify attributes and behaviors from existing classes. Polymorphism means an object can behave differently under different circumstances.