Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a new programming paradigm that views computation as objects interacting by sending messages to one another. Key elements of OOP include objects performing computation by making requests of each other through message passing, with every object having its own memory consisting of other objects. Classes group similar objects and define their common behaviors. Classes are organized into an inheritance hierarchy to allow subclasses to inherit and override behaviors. OOP aims to help programmers cope with complexity by providing abstraction and modularity.



![A New Paradigm
We start by considering the definition of the term ``paradigm'':
Par a digm n. 1. A list of all the inflectional forms of a word taken as
illustrative example of the conjugation or declension to which it belongs.
An example or model. [Late Latein paradigma, from Greek paradeigma,
modern paradeiknunai, to compare, exhibit.]
OO programming is a new paradigm
• New way of thinking about what it means to compute, and about what we
can structure information inside a computer
Let’s first see the relationship between languages and thoughts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopconcept-130419121756-phpapp02/75/Oop-concept-4-2048.jpg)

![An Example from Computer Languages
The programming language chosen to solve a problem will decide
fundamentally the way in which an algorithm is developed
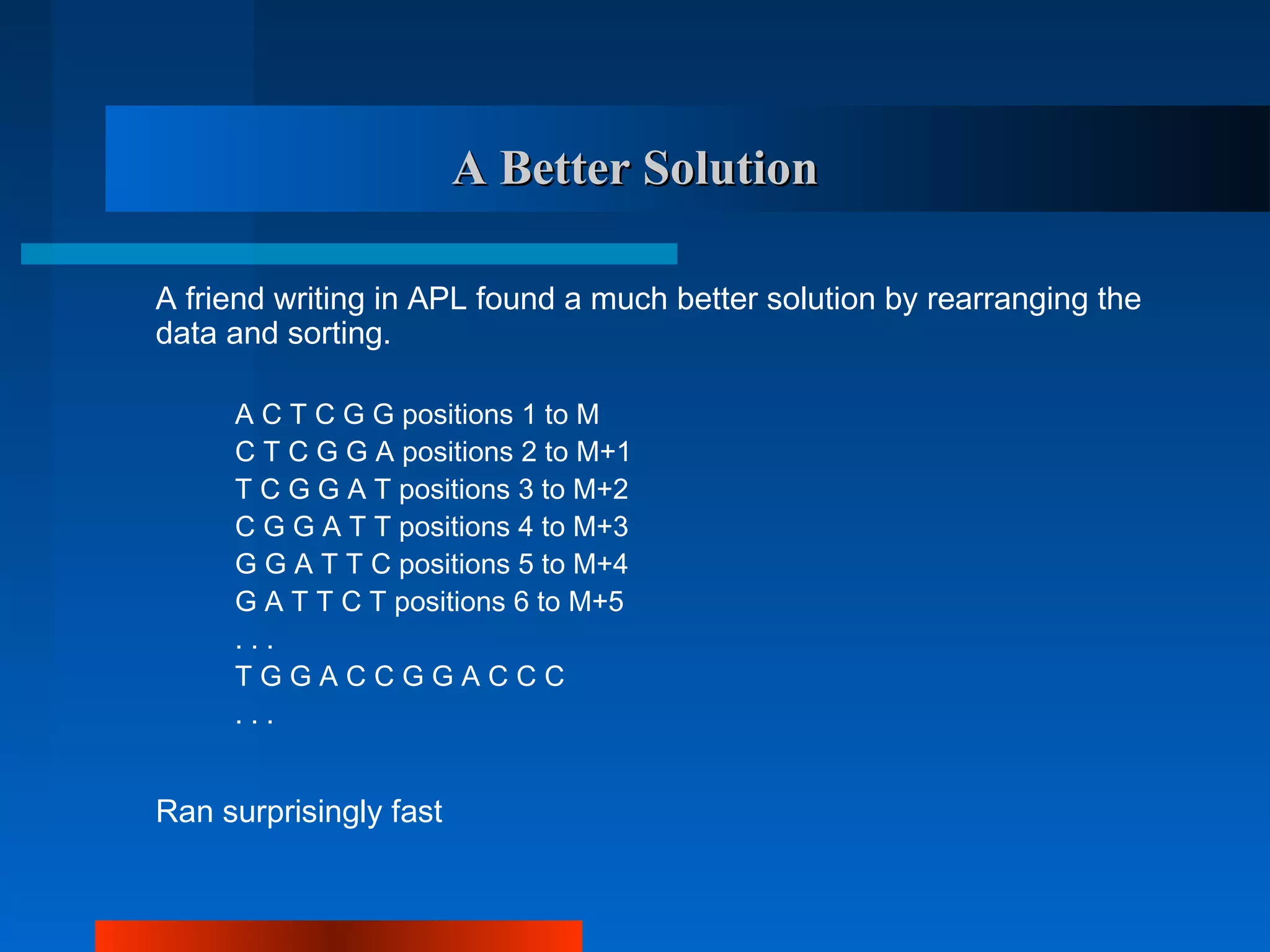
– A student working in DNA research had the task of finding repeated
sequences of M values in a long sequence of values:
ACTCGGATCTTGCATTTCGGCAATTGGACCCTGACTTGGCCA ...
Wrote the simplest (and therefore, most efficient?) Fortran program :
DO 10 I = 1, N-M
DO 10 J = I+1, N-M
FOUND = .TRUE.
DO 20 K = 1, M
20 IF X[I+K-1] .NE. X[J+K-1] THEN FOUND = .FALSE.
IF FOUND THEN ...
10 CONTINUE
Took a depressingly long time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopconcept-130419121756-phpapp02/75/Oop-concept-6-2048.jpg)
























![The Problem of Stacks
int datastack[100];
int datatop = 0;
void init() // initialize the stack
{ datatop = 0; }
void push(int val) // push a value on to the stack
{ if (datatop < 100)
datastack [datatop++] = val; }
int top() // get the top of the stack
{ if (datatop > 0)
return datastack [datatop - 1];
return 0; }
int pop() // pop element from the stack
{ if (datatop > 0)
return datastack [--datatop];
return 0; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopconcept-130419121756-phpapp02/75/Oop-concept-33-2048.jpg)
![Block Scoping Didn't Solve the Problem
Problems with previous implementation
– we need to use global variables for the array (no access control)
– method names cannot be used elsewhere
More control over name visibility using block scoping in Algol and Pascal, but
any scope that accesses the four methods can access the data as well
begin
var
datastack : array [ 1 .. 100 ] of integer;
datatop : integer;
procedure init; ...
procedure push(val : integer); ...
function pop : integer; ...
...
end;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopconcept-130419121756-phpapp02/75/Oop-concept-34-2048.jpg)
![Modules
Modules basically provide collections of procedures and data with
import and export statements [Parnas 1972]
– they can distinguish public part that are accessible outside and private part
that are accessible only within the module
– Enforces need-to-know principle
Solves the problem of encapsulation -- but what if your programming
task requires two or more stacks?
– Only one stack can be manipulated with a module
– Need to define a different module for another stack- with what names?
Modules provide information hiding but do not allow instantiation, which
is the ability to make multiple copies of the data area
– need to develop a new concept](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopconcept-130419121756-phpapp02/75/Oop-concept-35-2048.jpg)


