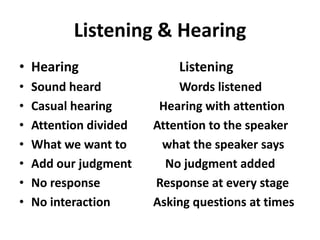
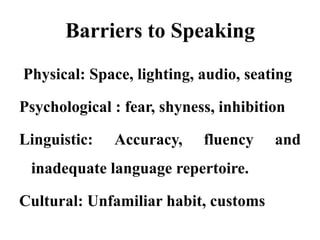
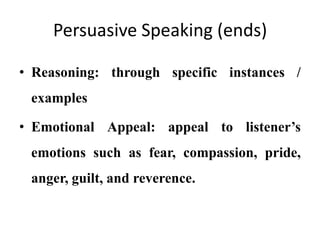
This document discusses effective speaking and listening. It covers various modes and types of listening like active listening, empathetic listening, and barriers to listening. It also discusses types of conversations, paralinguistic features that affect speaking, confidence and clarity in speaking, types of speaking like persuasive speaking, and public speaking. The key aspects of persuasive speaking discussed are credibility, evidence, emotional appeal, and reasoning. Tips are provided for effective conversation, telephone etiquette, writing dialogues, and overcoming barriers to speaking.