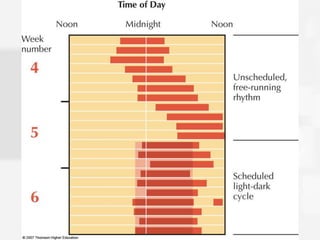
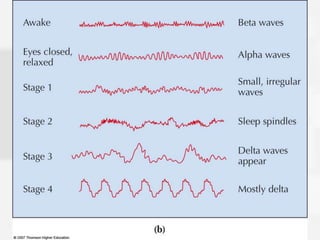
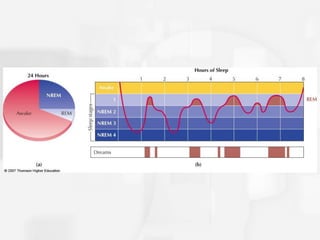
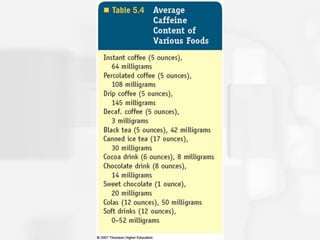
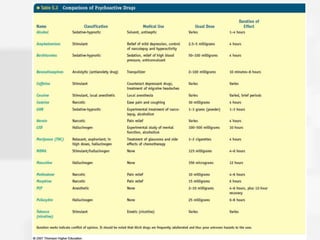
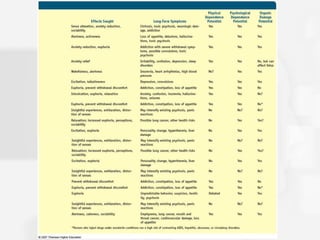
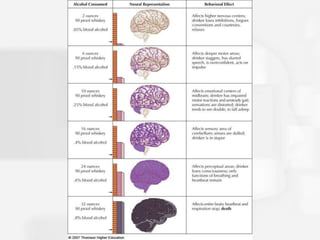
Chapter 5 discusses states of consciousness, emphasizing the distinction between waking consciousness and altered states, such as sleep and hypnosis. It covers various sleep stages, disorders, and the effects of psychoactive drugs, detailing the physiological and psychological aspects of addiction. Additionally, it examines the nature of dreams, the practice of meditation, and the implications of drug use on health.