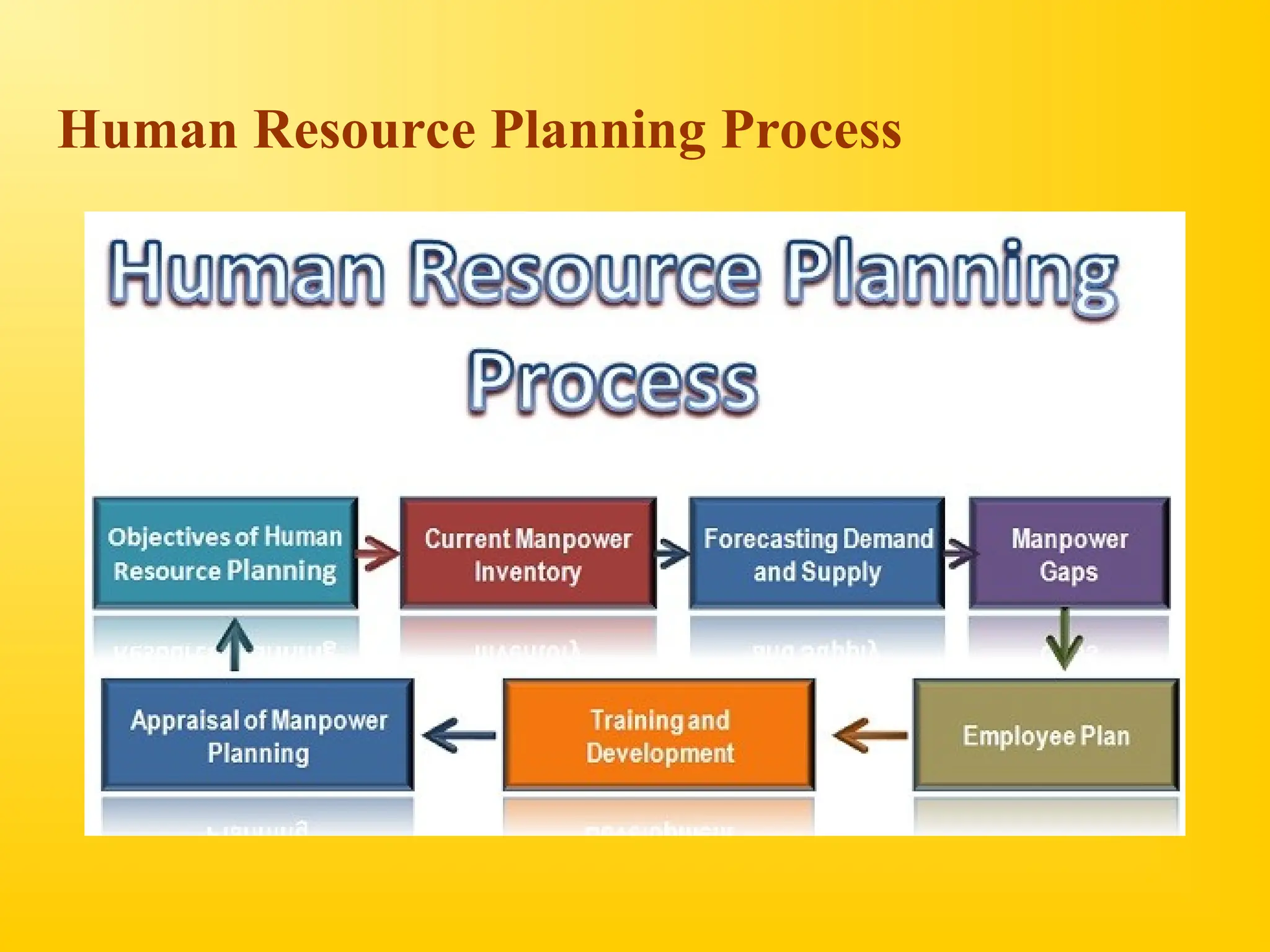
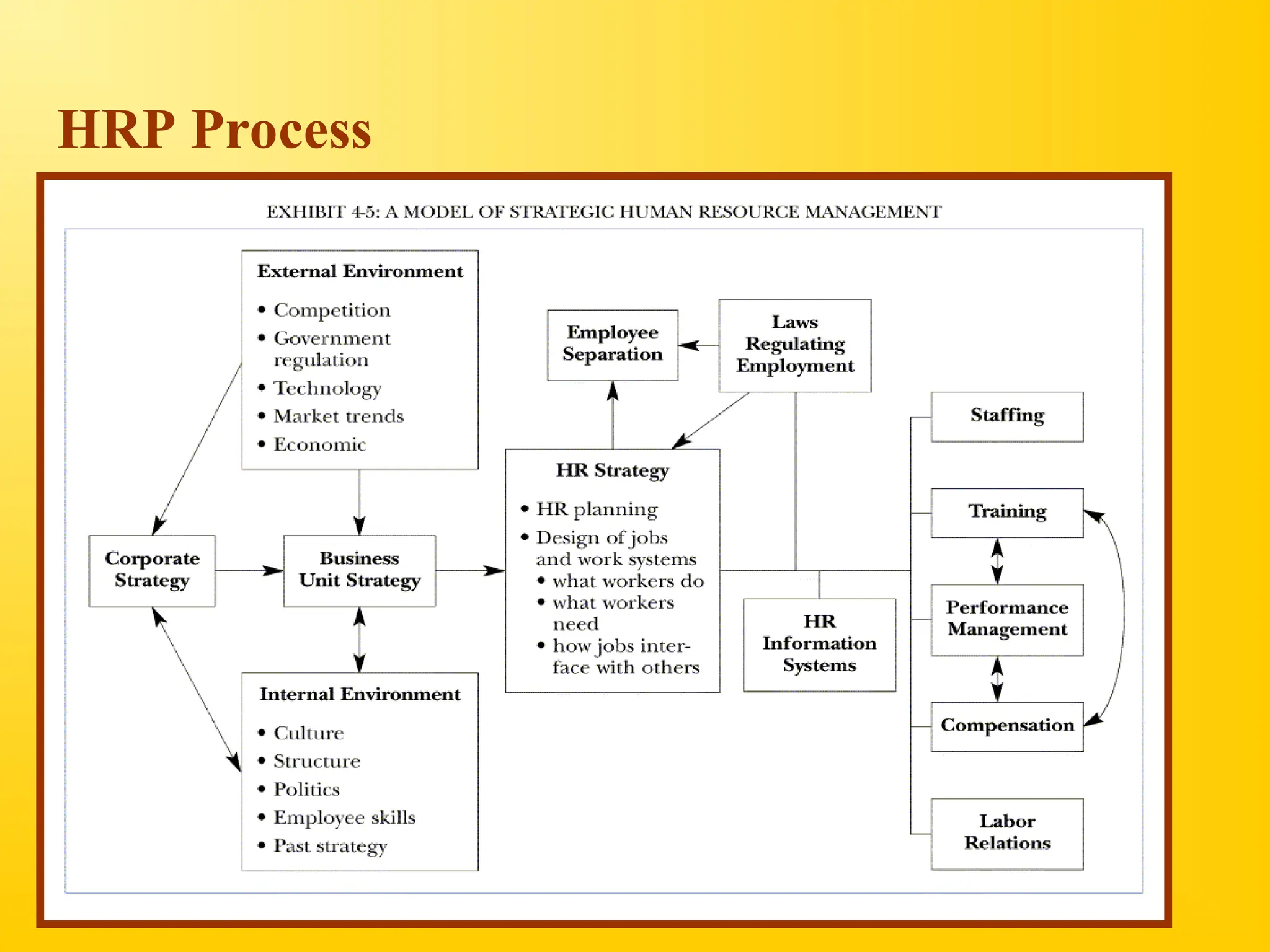
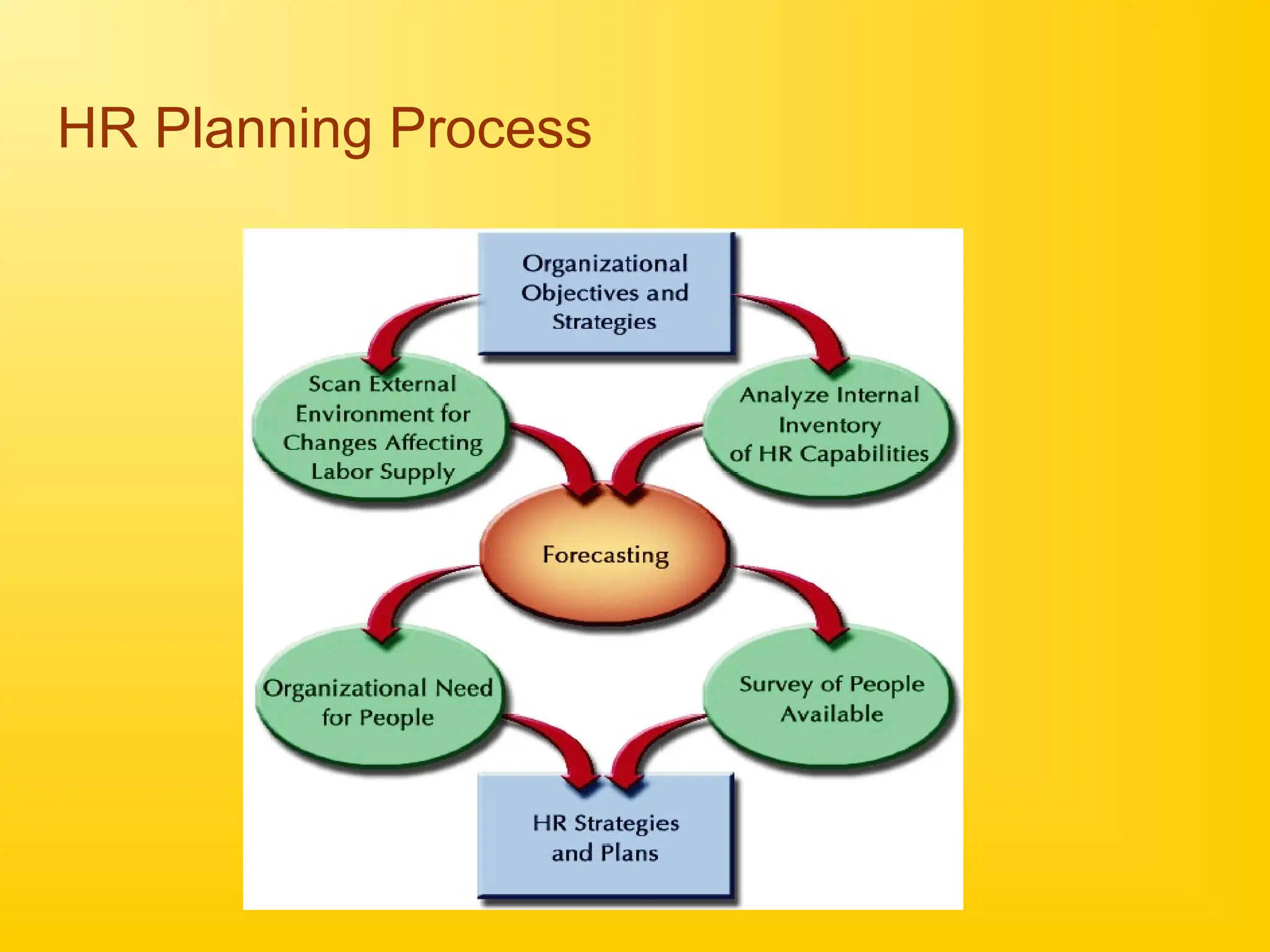
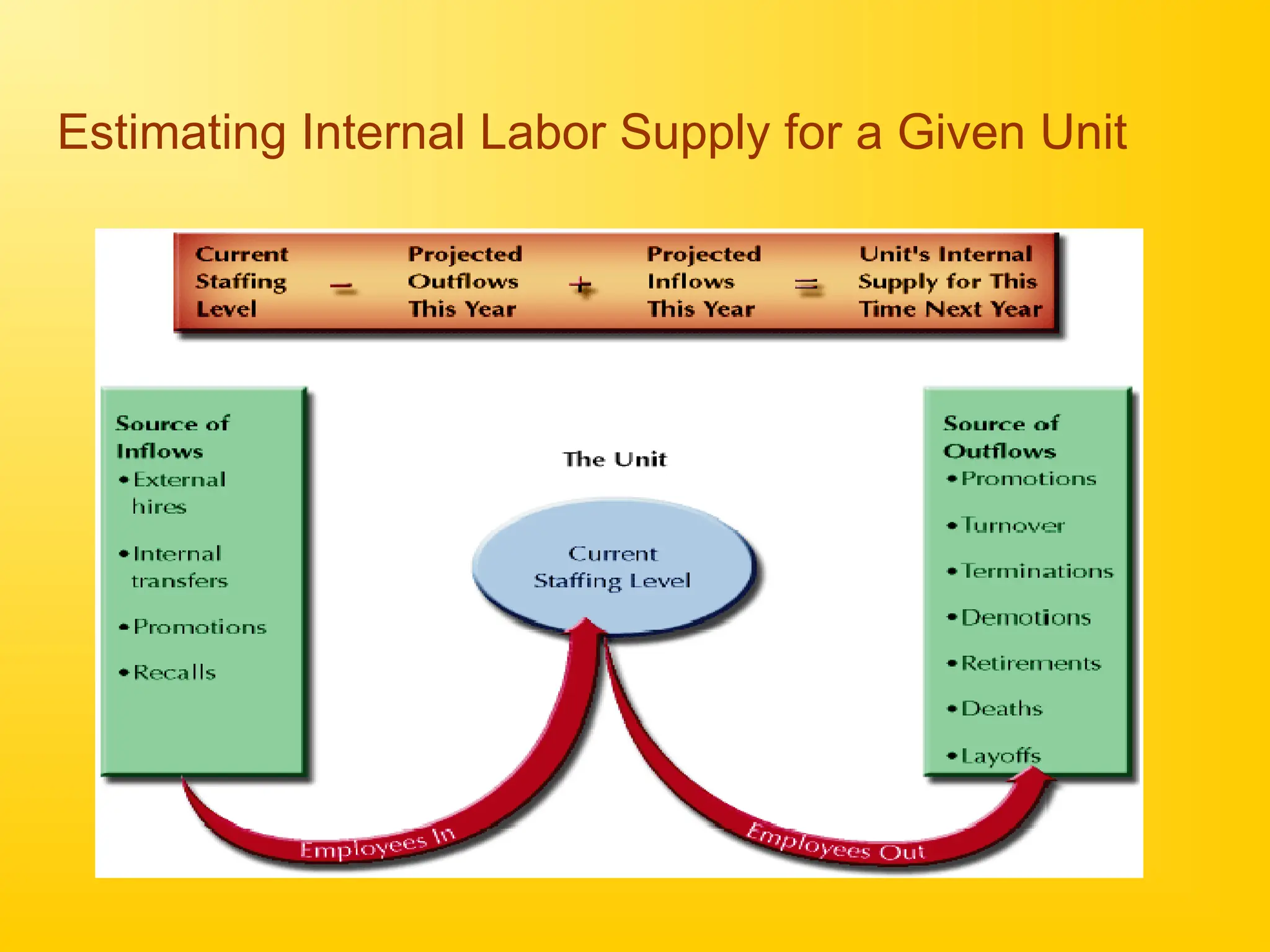
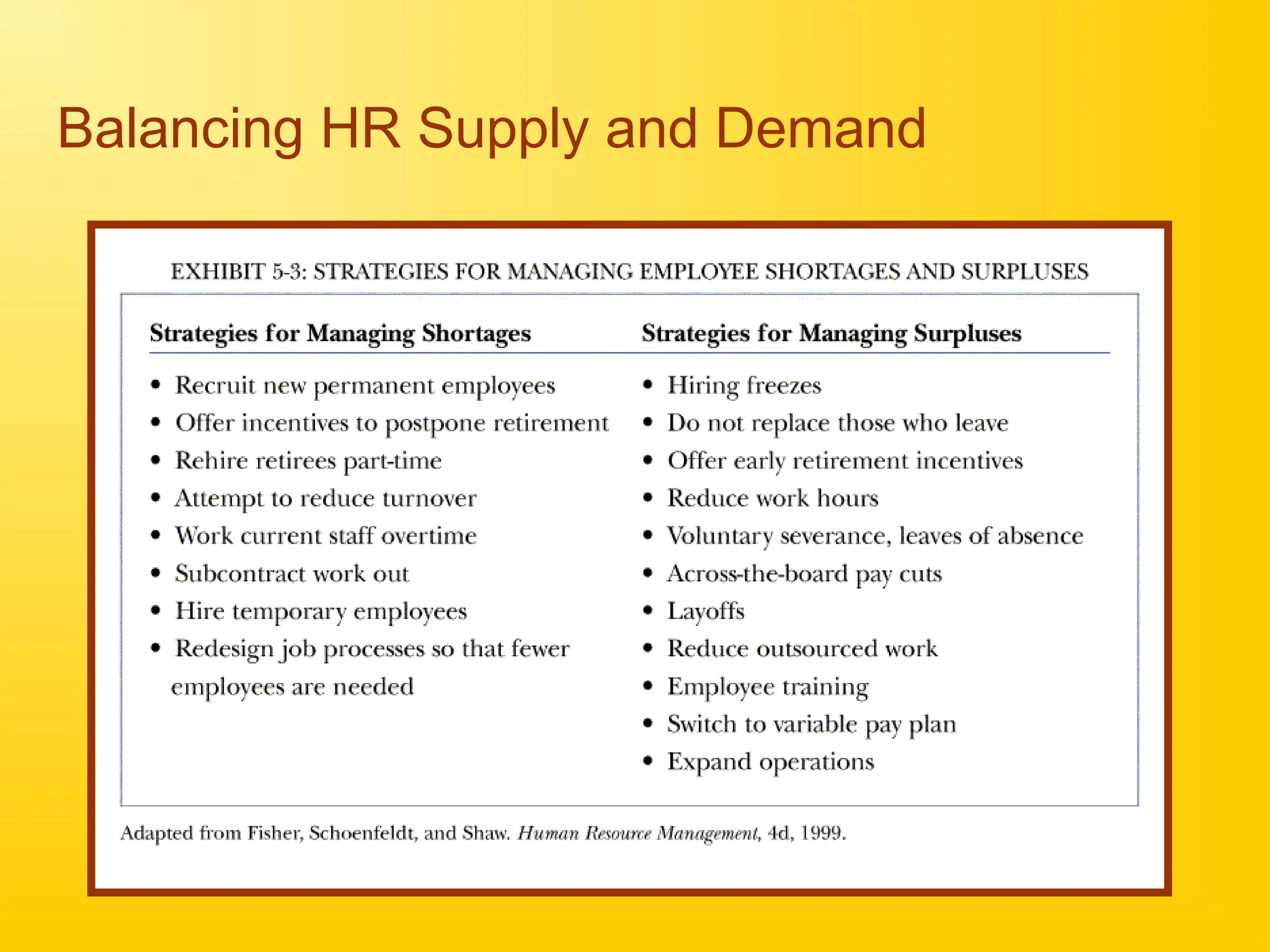
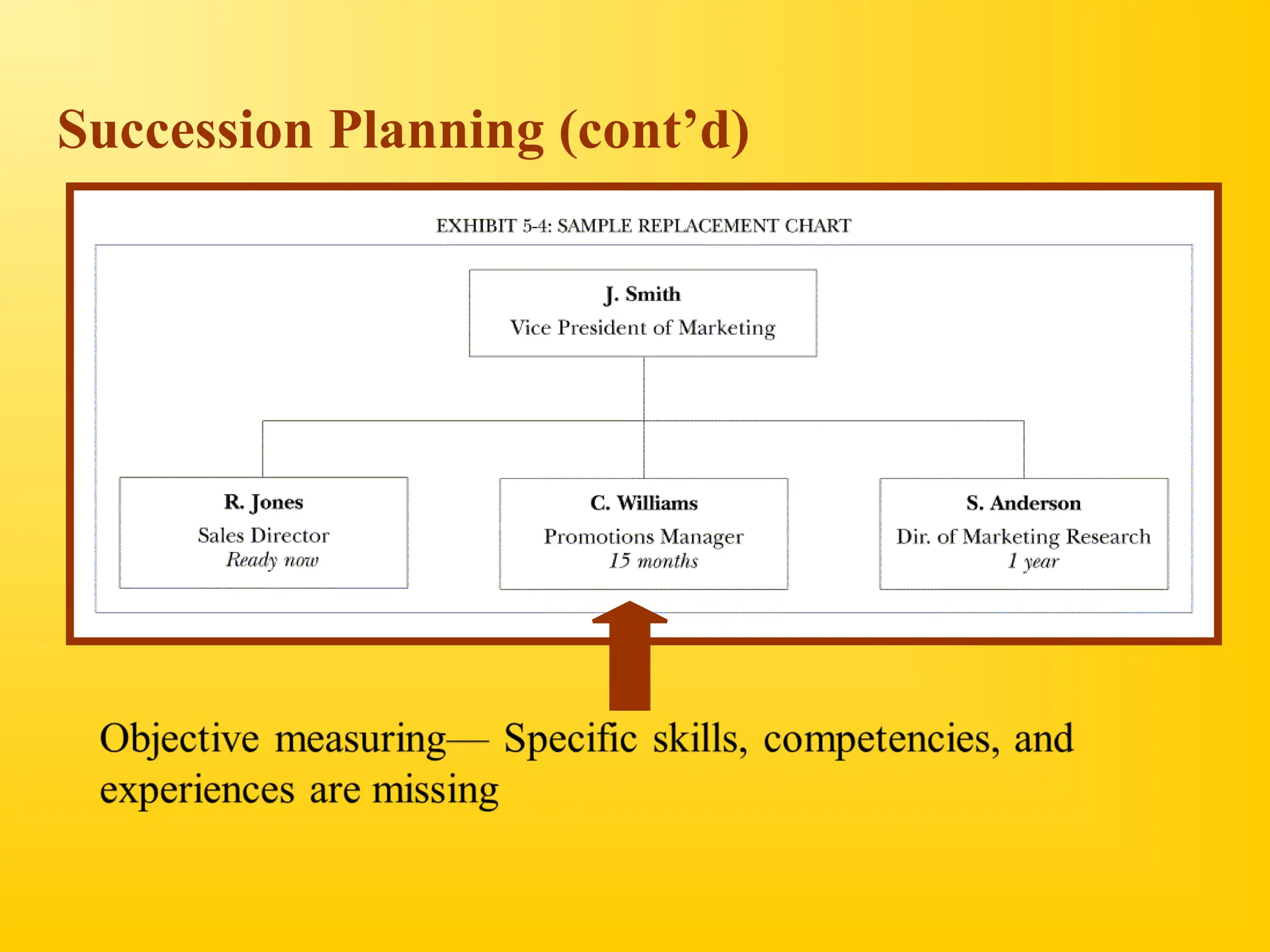
Chapter 4 discusses human resource planning (HRP) as a foundational component of HR management strategy, focusing on anticipating future HR needs based on current capabilities. The document outlines key objectives and methods for forecasting human resources, including techniques like extrapolation and managerial judgment. Additionally, it addresses succession planning, outlining its importance in maintaining organizational continuity and highlighting design shifts for effective implementation.