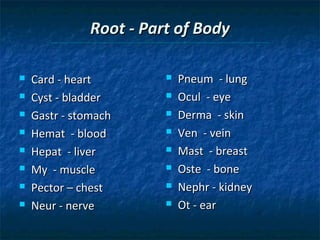
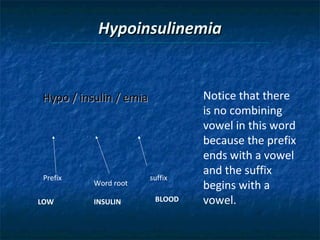
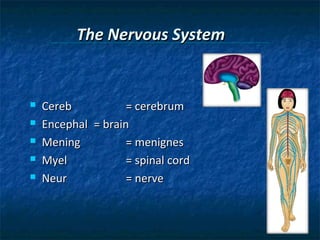
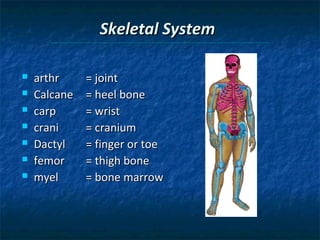
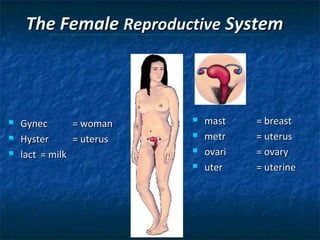
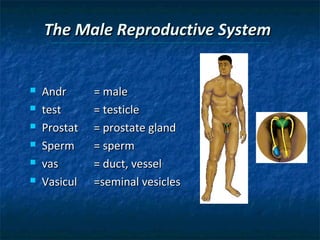
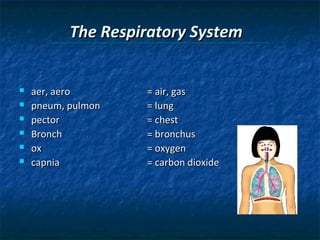
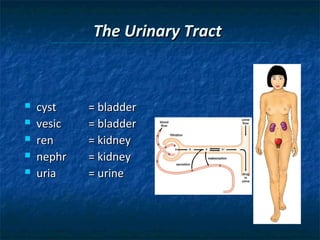
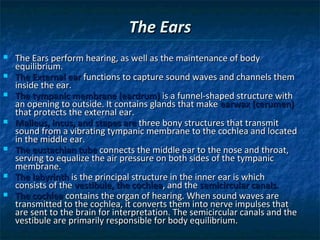
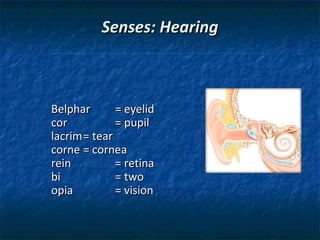
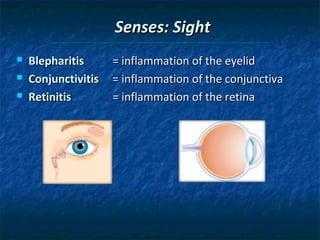
The document provides an overview of medical terminology by discussing the basic elements of medical words, including word roots, combining forms, suffixes, and prefixes. It then summarizes several body systems, including the cardiovascular, endocrine, gastrointestinal, integumentary, lymphatic, muscular, nervous, skeletal, and reproductive systems. For each system, it identifies key root words and provides examples of medical terms related to that system.