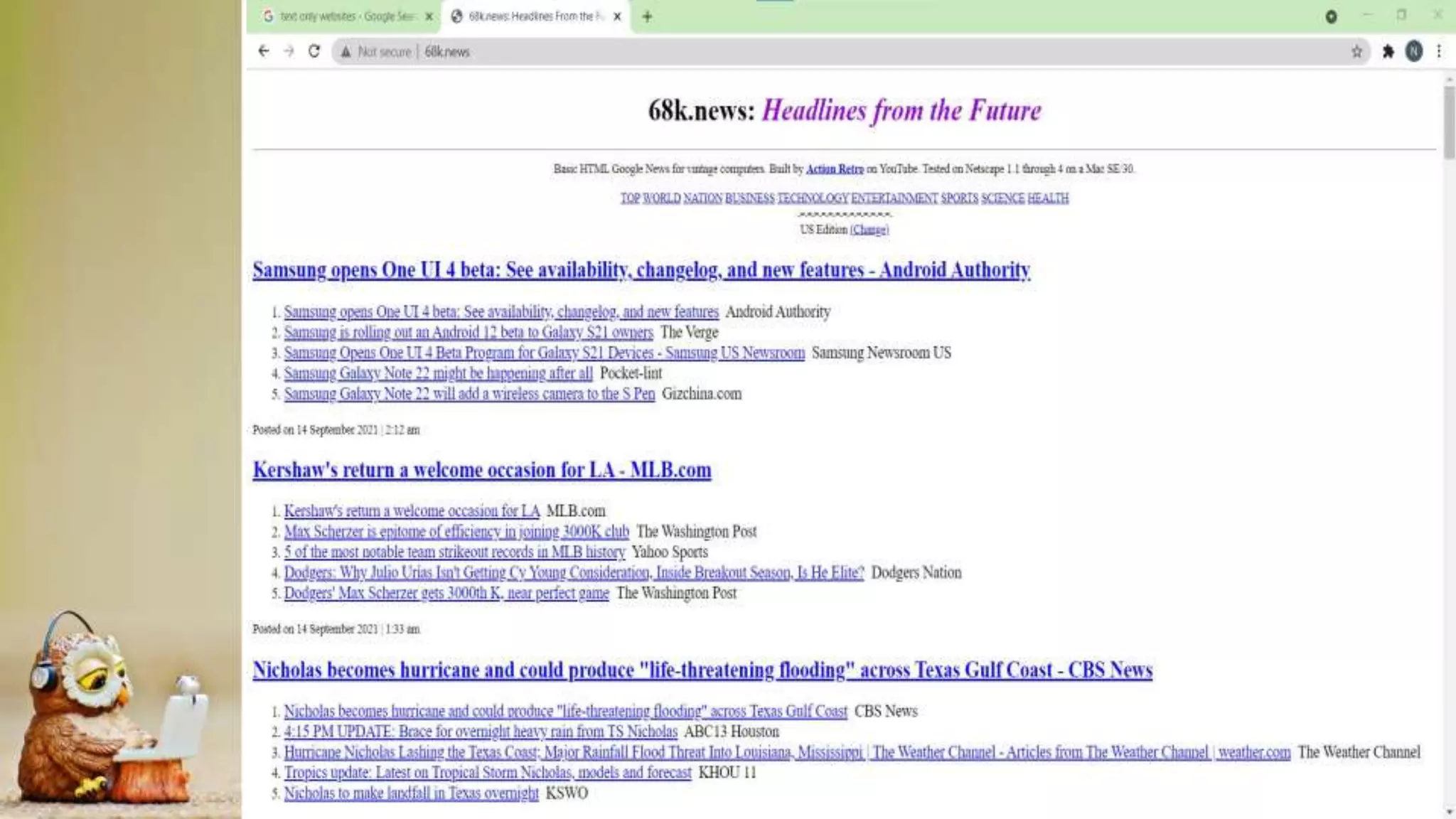
This document discusses the evolution of the World Wide Web and technologies. It describes Web 1.0 as the original static web with read-only pages. Web 2.0 enabled user interaction and sharing through social media. Web 3.0 aims to be more personalized through semantic technologies and machine learning. The document also outlines trends in information and communication technologies including convergence, social media, mobile technologies, assistive media, and cloud computing.