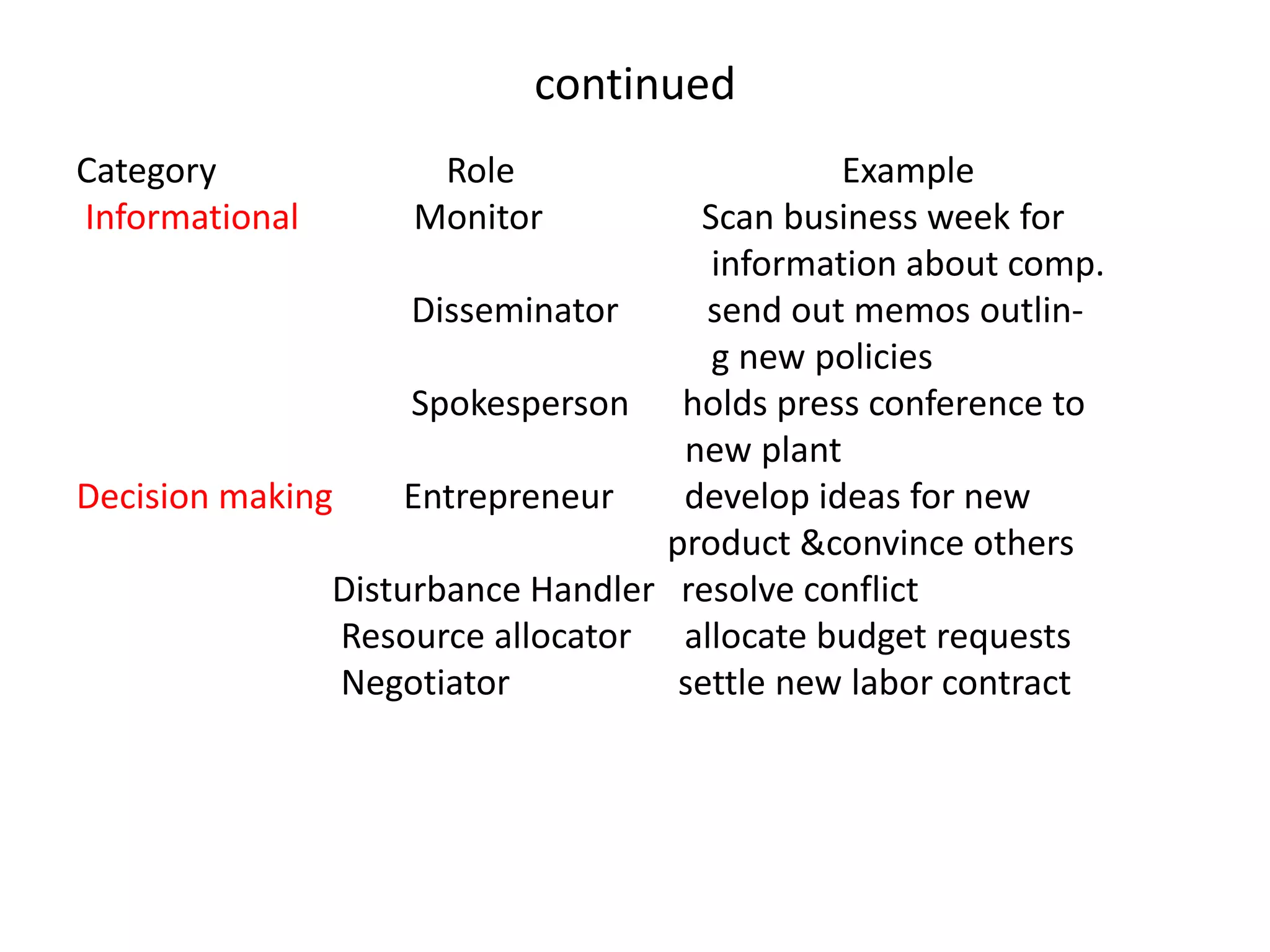
This chapter introduces organizational behavior and management. It defines OB as the study of how individuals, groups, and structure impact behavior in organizations. The goal is to apply this knowledge to improve effectiveness. Management functions include planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Key managerial roles are interpersonal roles like leader and decision-making roles like entrepreneur. Important OB topics are productivity, absenteeism, turnover, job satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior. OB draws from disciplines like psychology, anthropology, political science, and sociology.