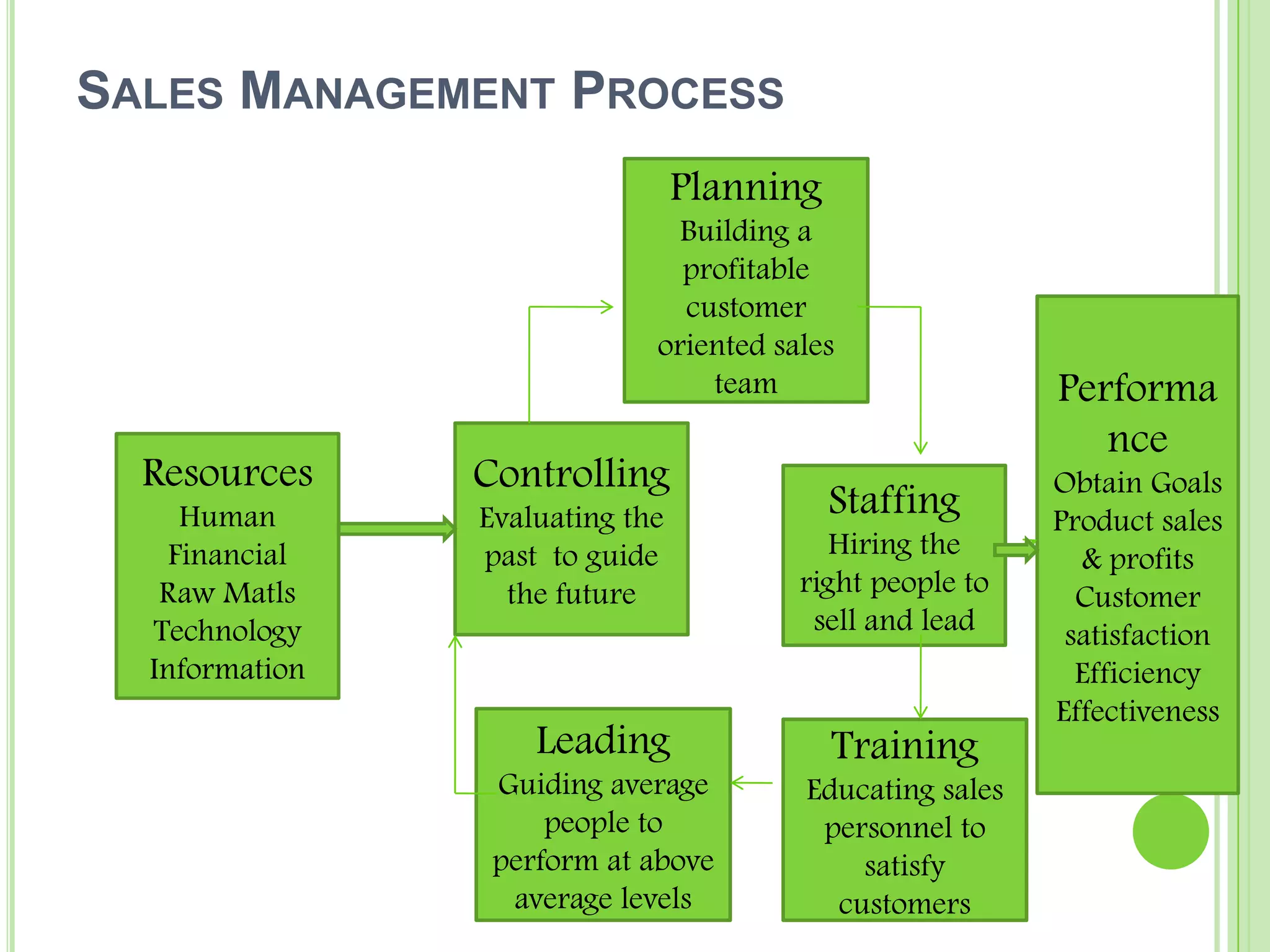
1) Sales management involves planning, directing, and controlling personnel to achieve sales goals and maximize profits. It includes recruiting, training, motivating the sales force.
2) Personal selling is a direct presentation to customers to persuade them to purchase products. It can take different forms like service, developmental, and creative selling depending on the situation.
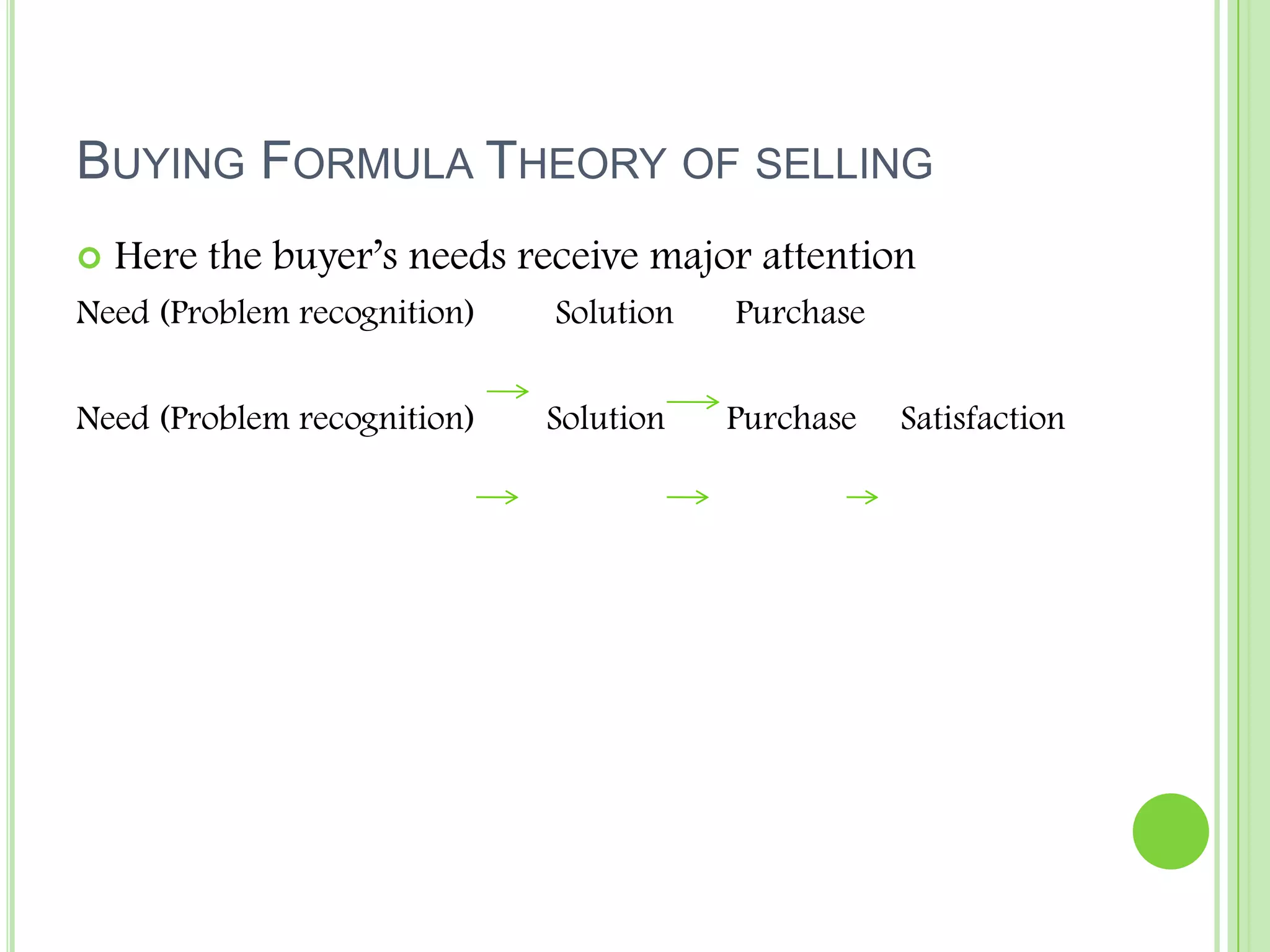
3) Theories of selling include both seller-oriented and buyer-oriented approaches. Seller approaches focus on techniques like AIDA while buyer approaches examine the customer purchase decision process and factors that influence it like needs, solutions, and satisfaction.