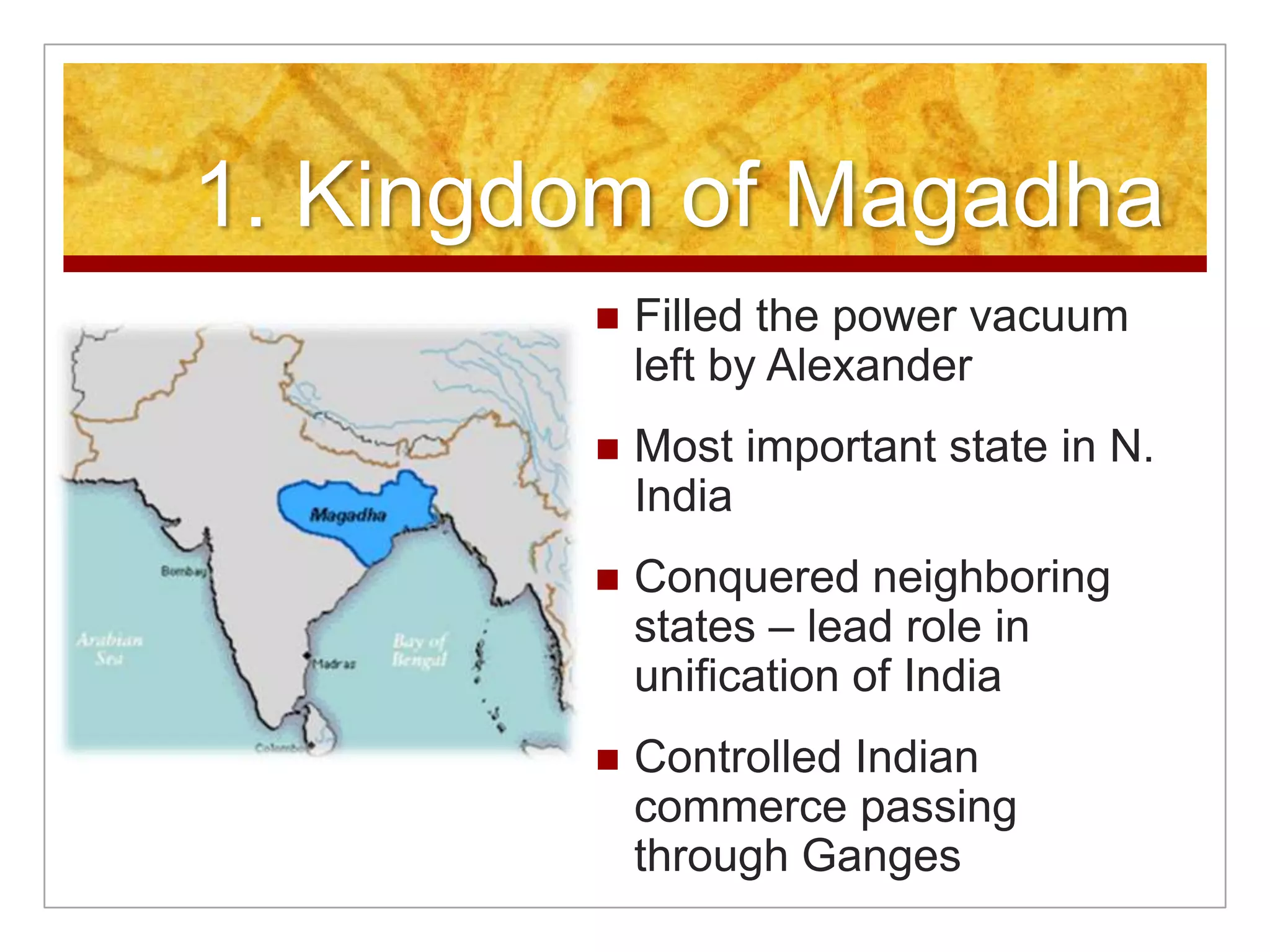
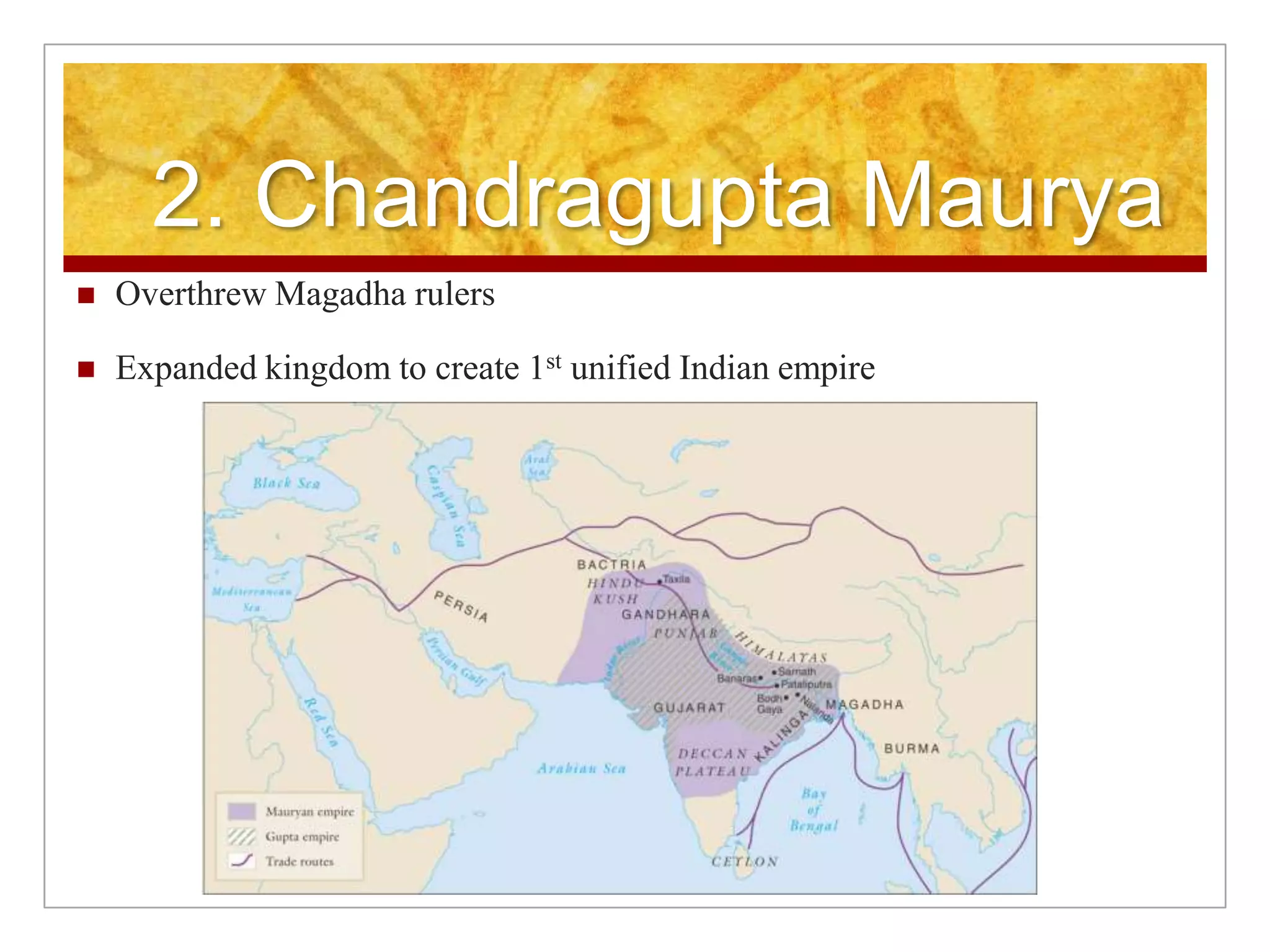
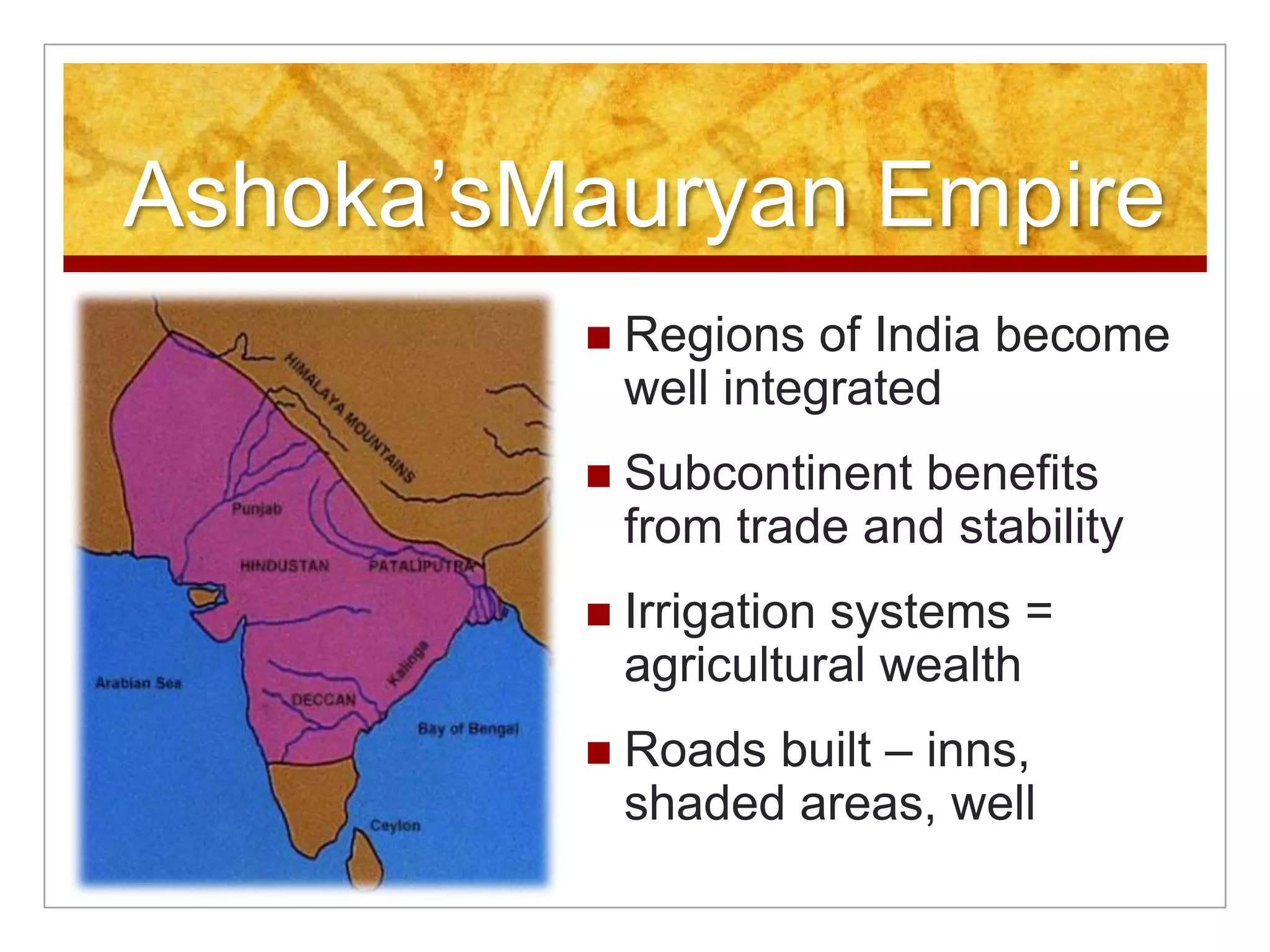
1. The Mauryan Empire briefly unified India under Chandragupta Maurya in the 4th century BCE using an advanced administrative system, but declined after Ashoka's death due to economic and military issues.
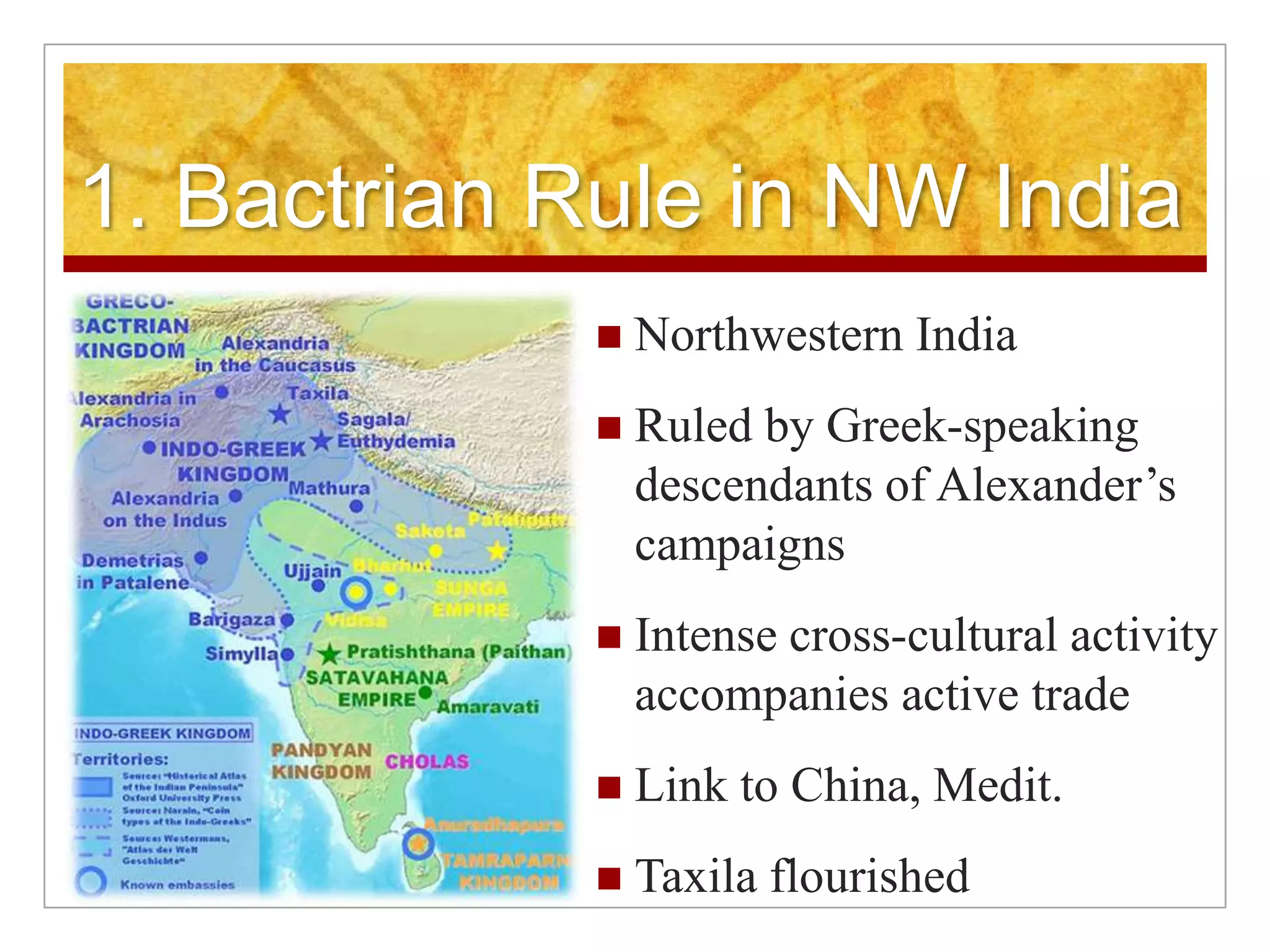
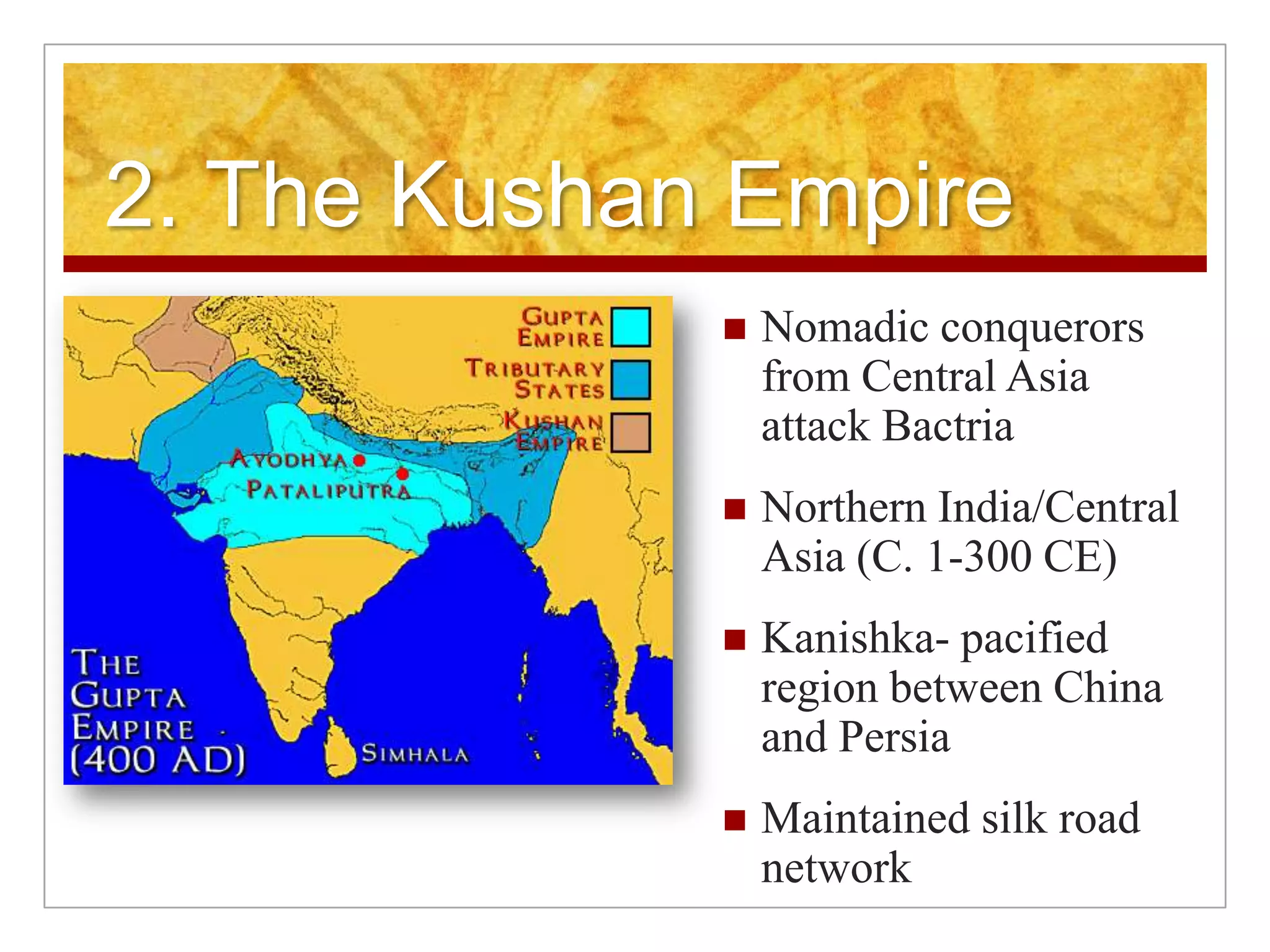
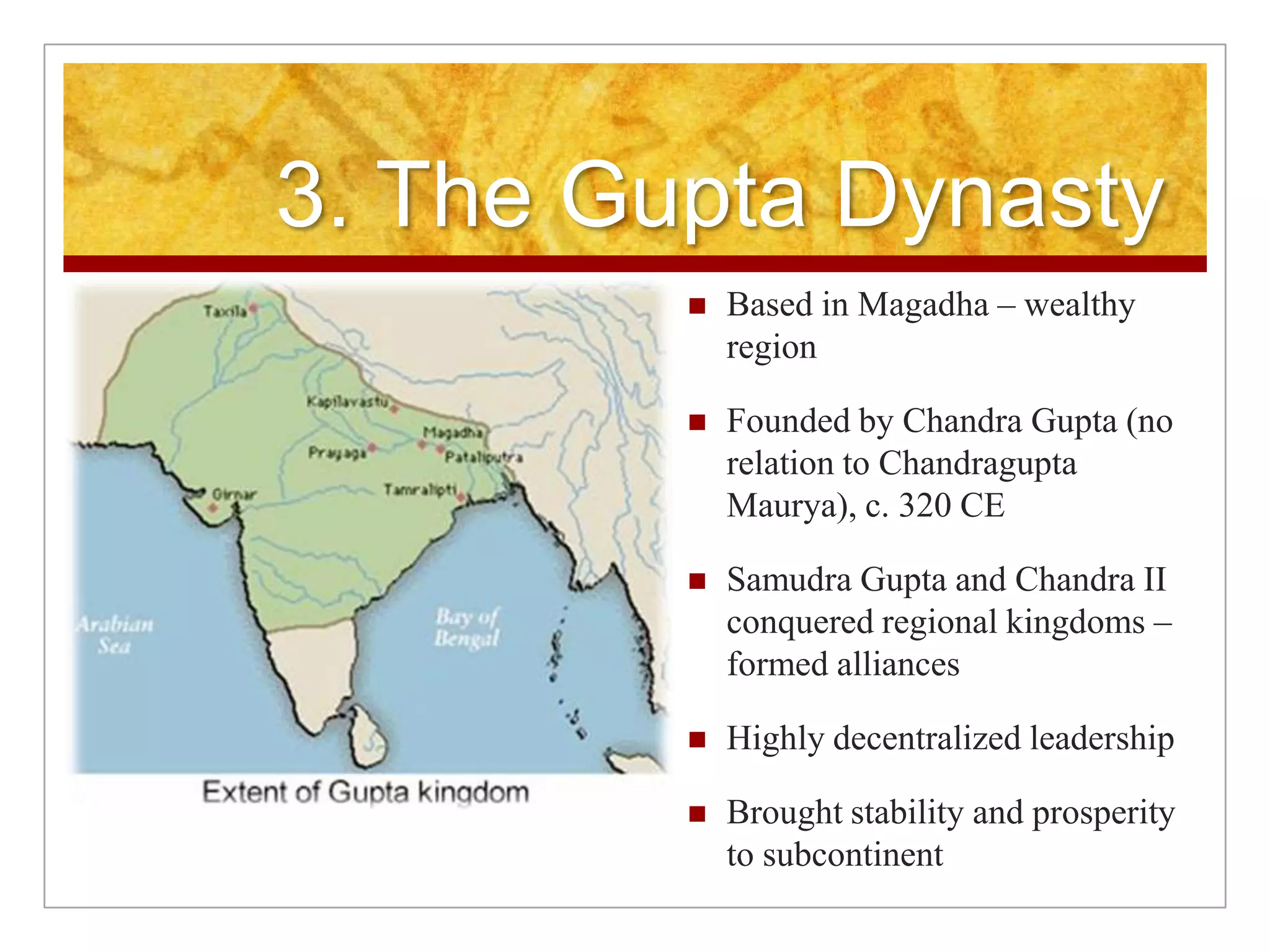
2. Regional kingdoms emerged including the Kushans in the north and the Guptas in the 4th century CE who brought stability, but were later invaded by Huns.
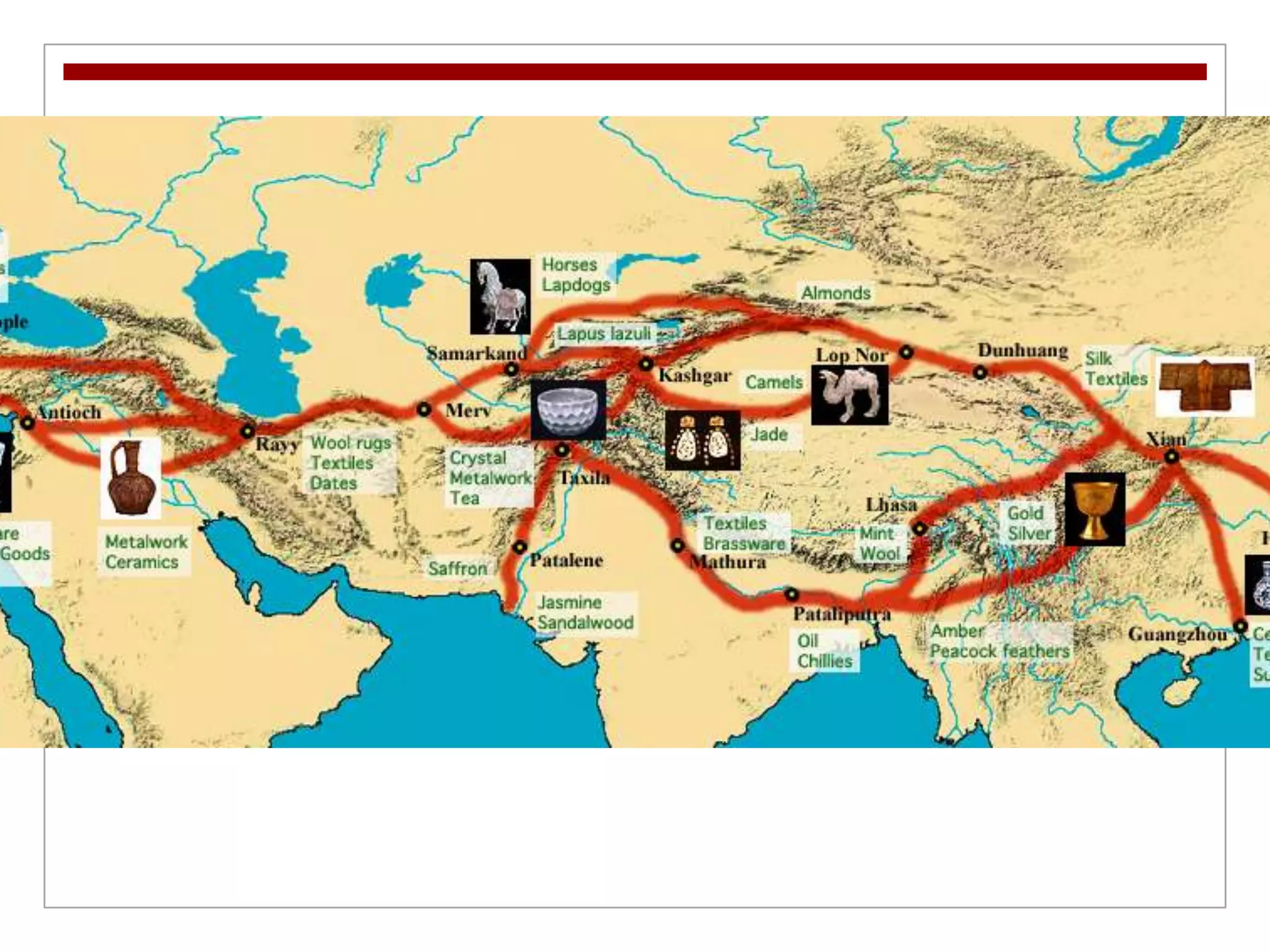
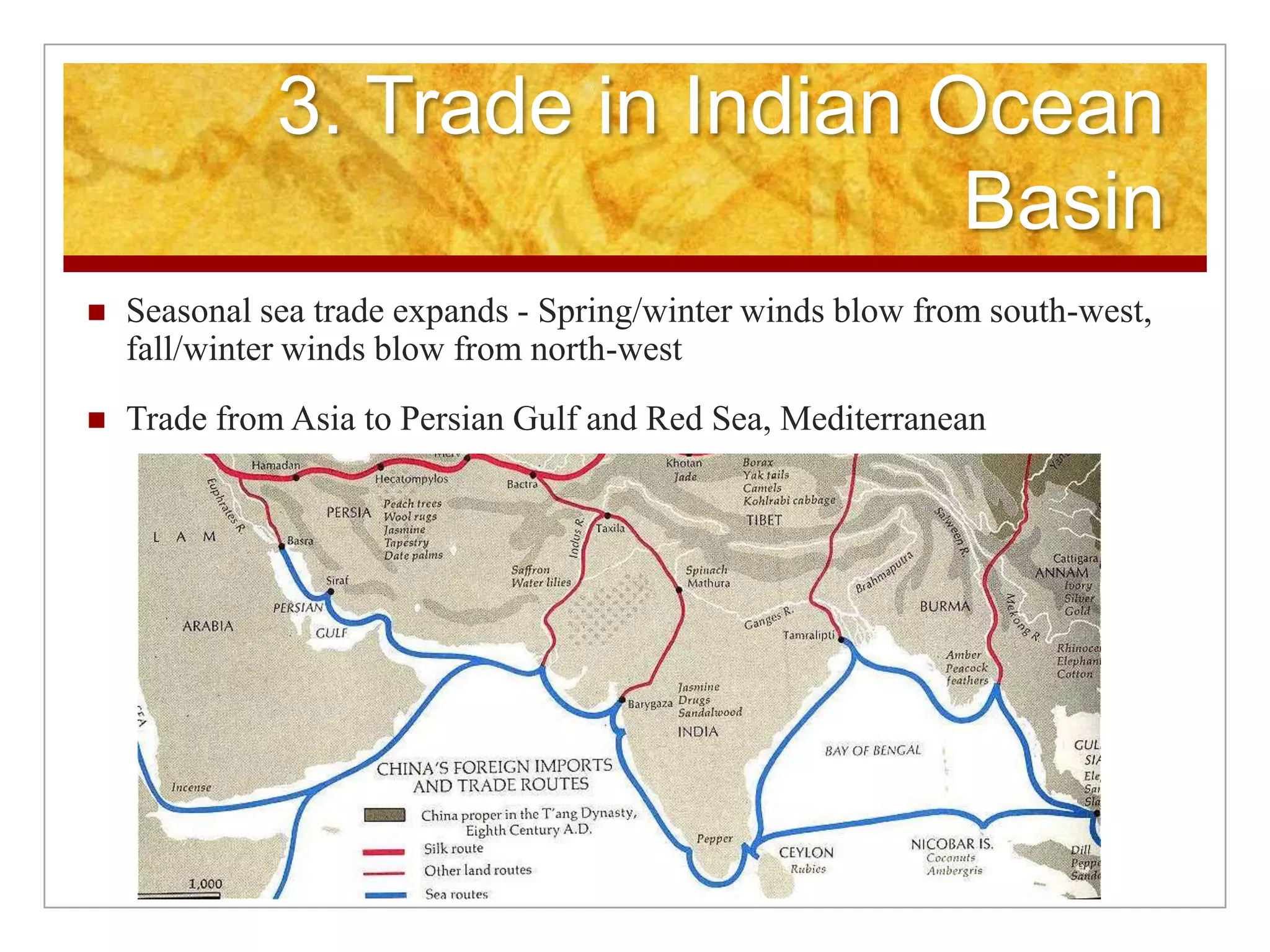
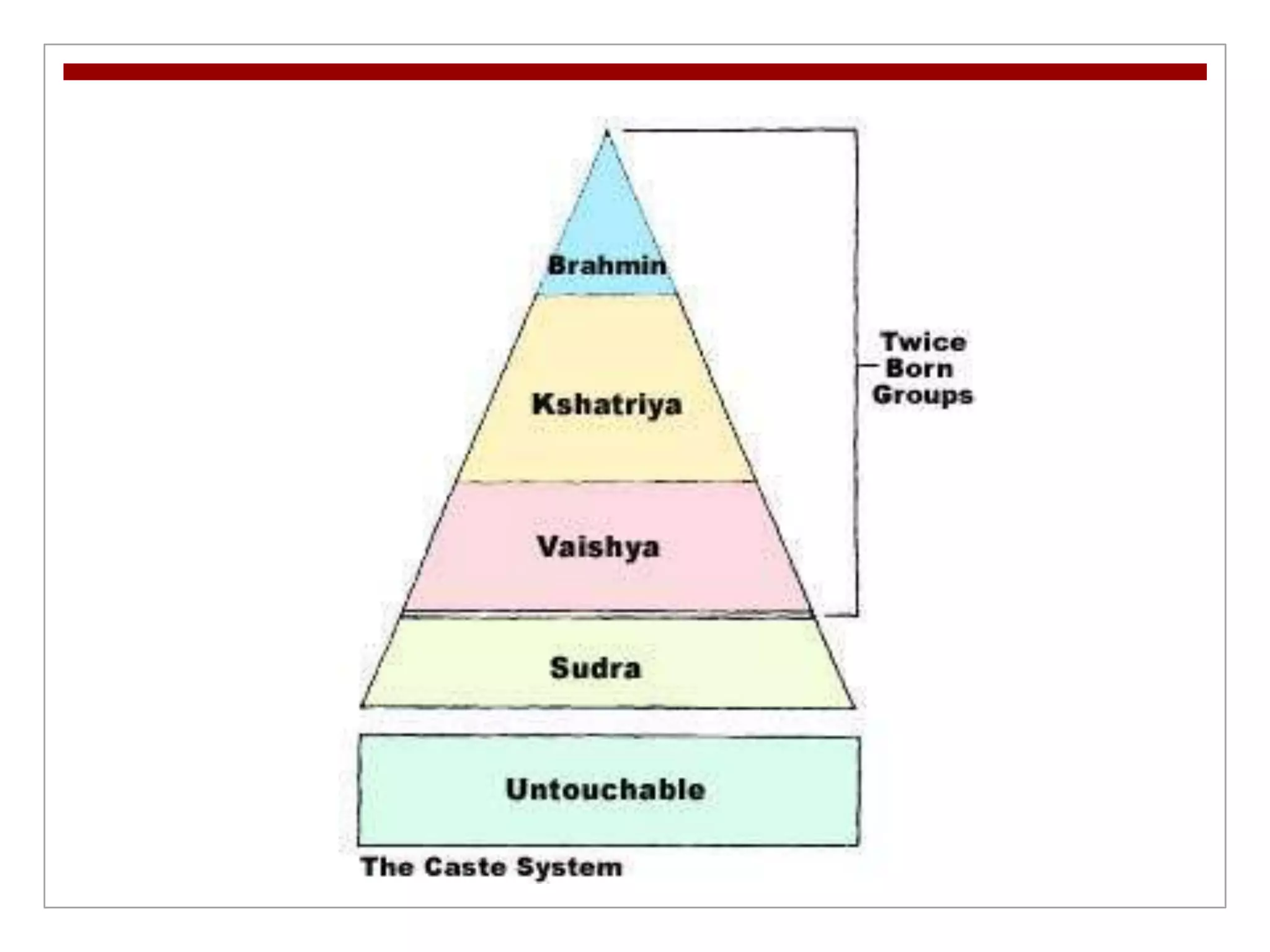
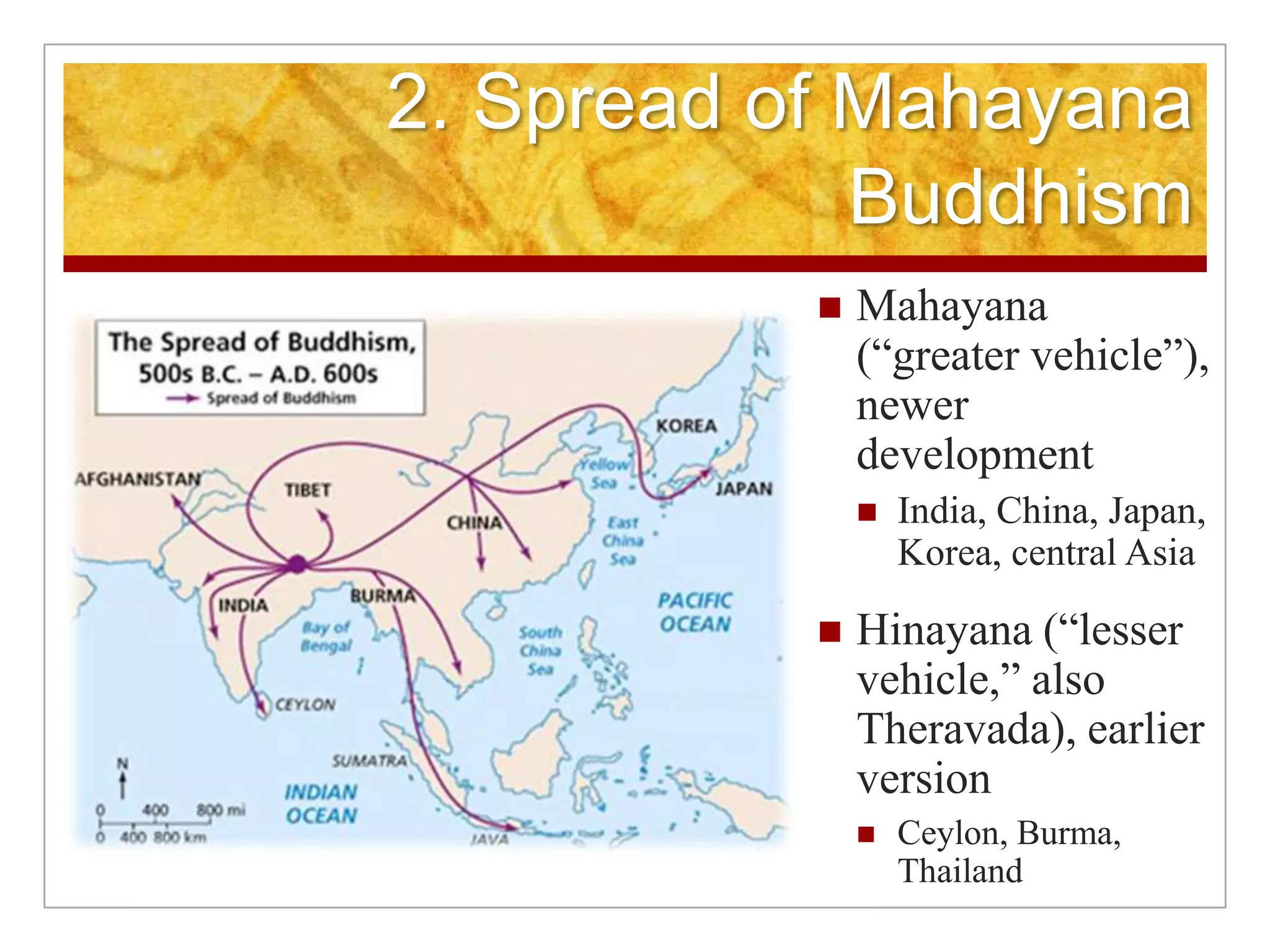
3. A complex social hierarchy developed around castes and guilds as trade grew, challenging traditional values, while religions like Buddhism and new forms of Hinduism appealed to more social classes and spread across India.