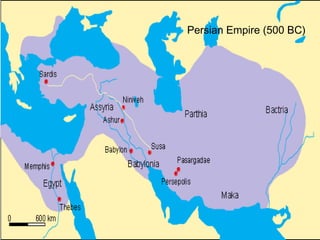
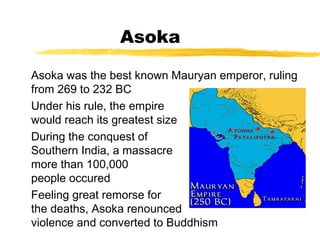
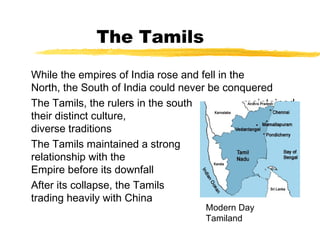
The document summarizes the early empires of India from 512 BC to the Gupta Empire between 320-535 AD. It discusses the Persian and Magadha states in the 6th century BC and the rise of the Maurya Dynasty in the 4th century BC led by Chandragupta Maurya. It then covers the expansion of the Maurya Empire under Ashoka in the 3rd century BC and the spread of Buddhism. Following the decline of the Mauryas, the document outlines the invasions of the Bactrian Greeks and Kushans and their cultural influences. It concludes with the golden age of the Gupta Empire in northern India and the independent kingdom of the Tamils in southern India.