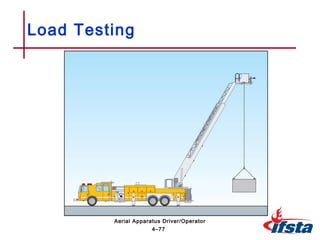
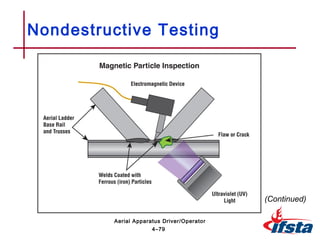
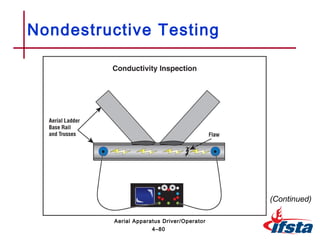
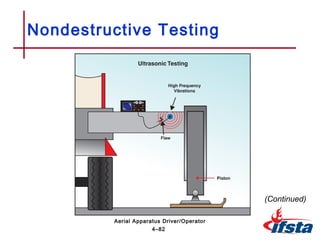
This chapter discusses inspection, maintenance, and testing procedures for aerial fire apparatus. It describes the importance of establishing a systematic maintenance program to dictate responsibilities. Proper procedures are outlined for inspecting and cleaning both the interior and exterior of the apparatus. The chapter also provides detailed guidance on performing walk-around, in-cab, and engine compartment inspections. Finally, it discusses various testing methods for aerial devices, including visual, operational, load, and nondestructive inspections.