The document provides an overview of the history and evolution of pharmacy. Some key points:
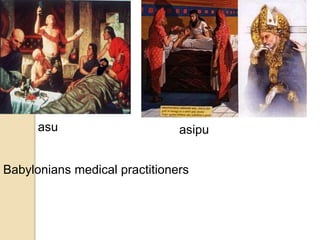
- Pharmacy has its origins in ancient civilizations where herbalists and healers developed early medicines and remedies. It evolved through Greek, Roman, Islamic and European traditions.
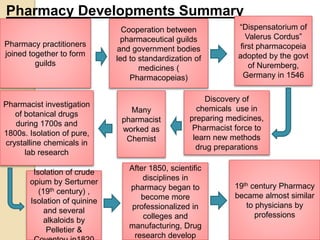
- Modern pharmacy emerged in the 19th century with the development of pharmaceutical sciences, standardized drug production, and pharmacy education in universities.
- The document then summarizes the history of pharmacy in the Philippines, from traditional herbal medicine practices, to its establishment as a university program at the University of Santo Tomas, and its further development under Spanish and American rule.