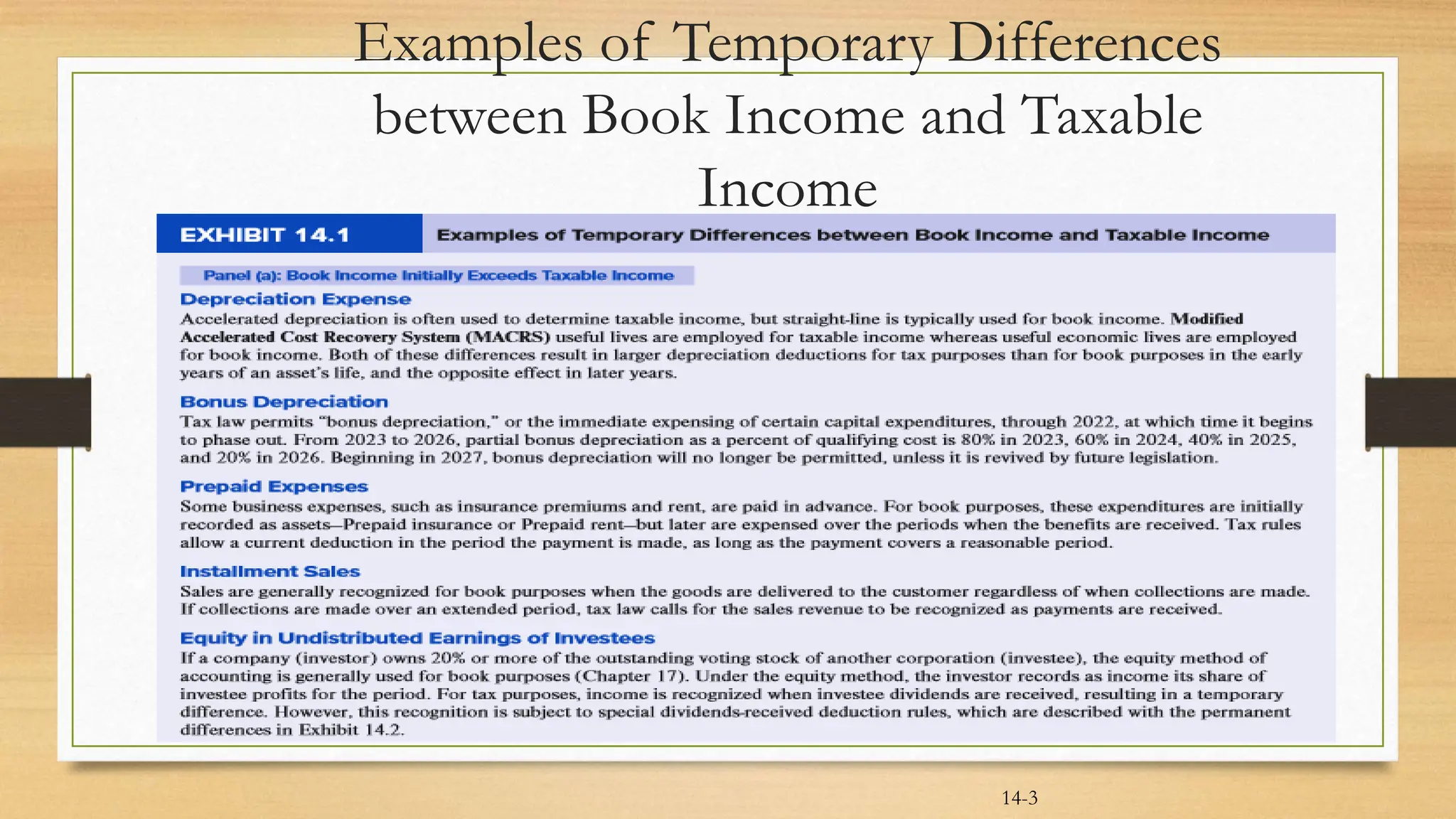
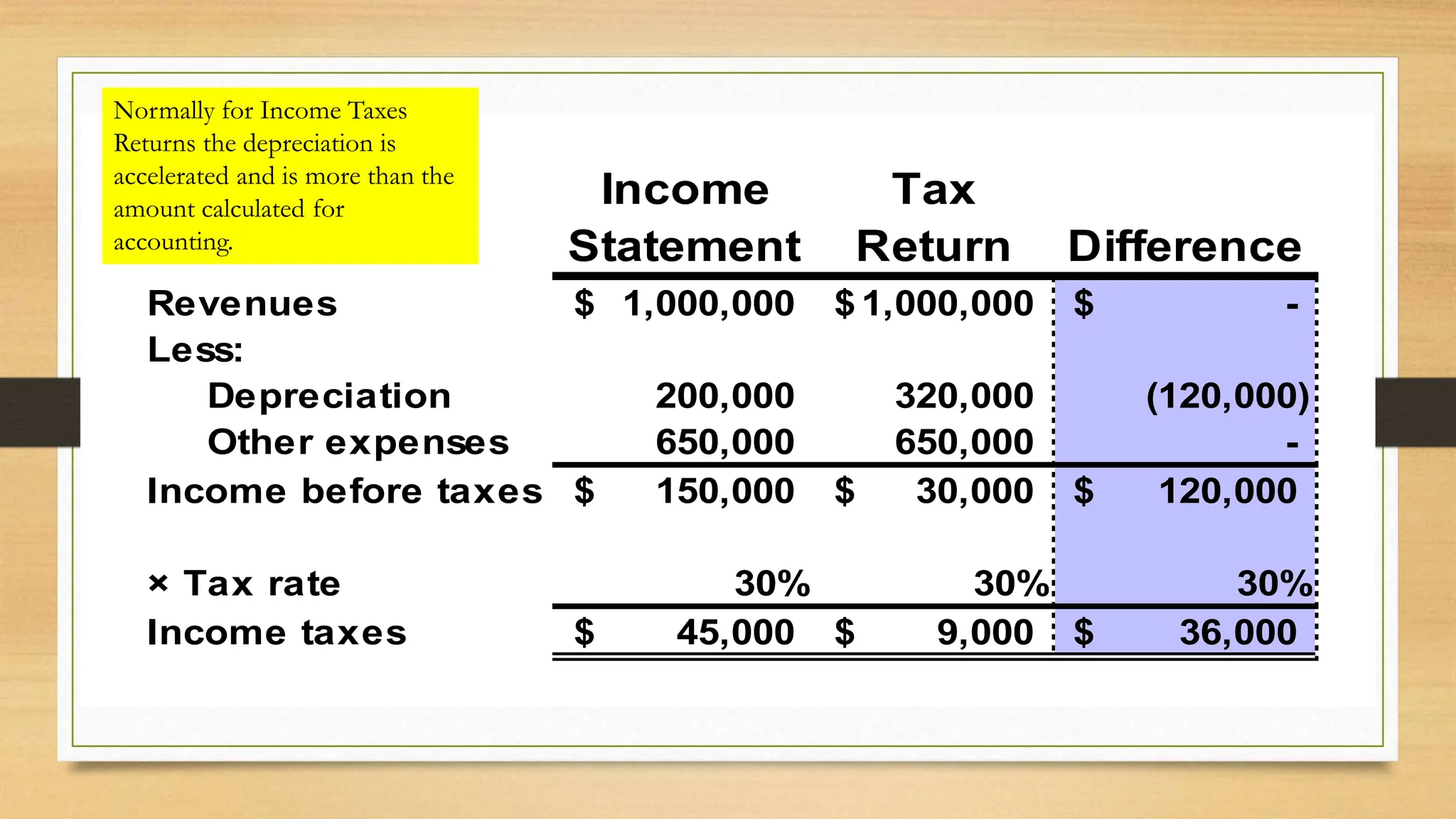
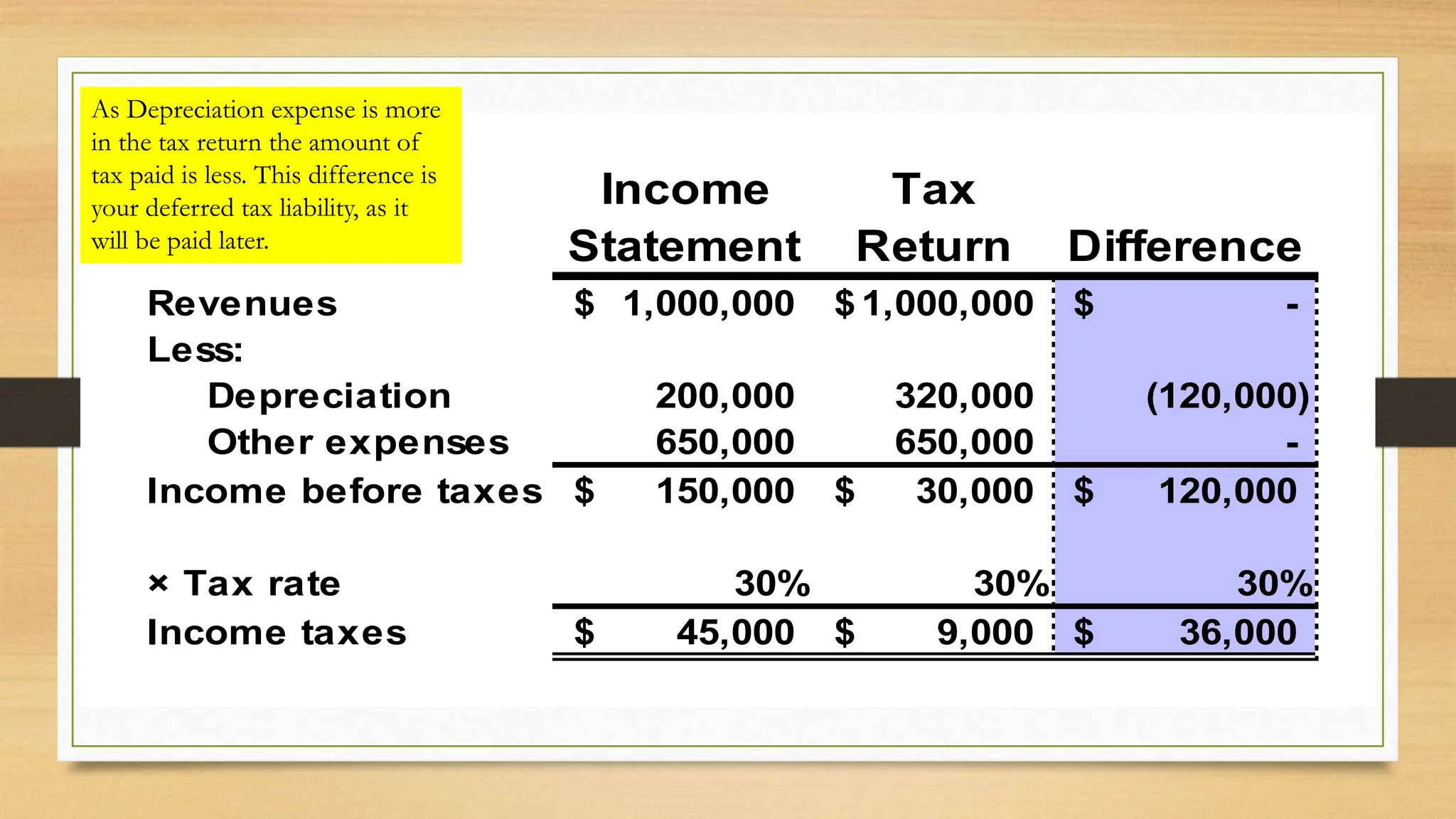
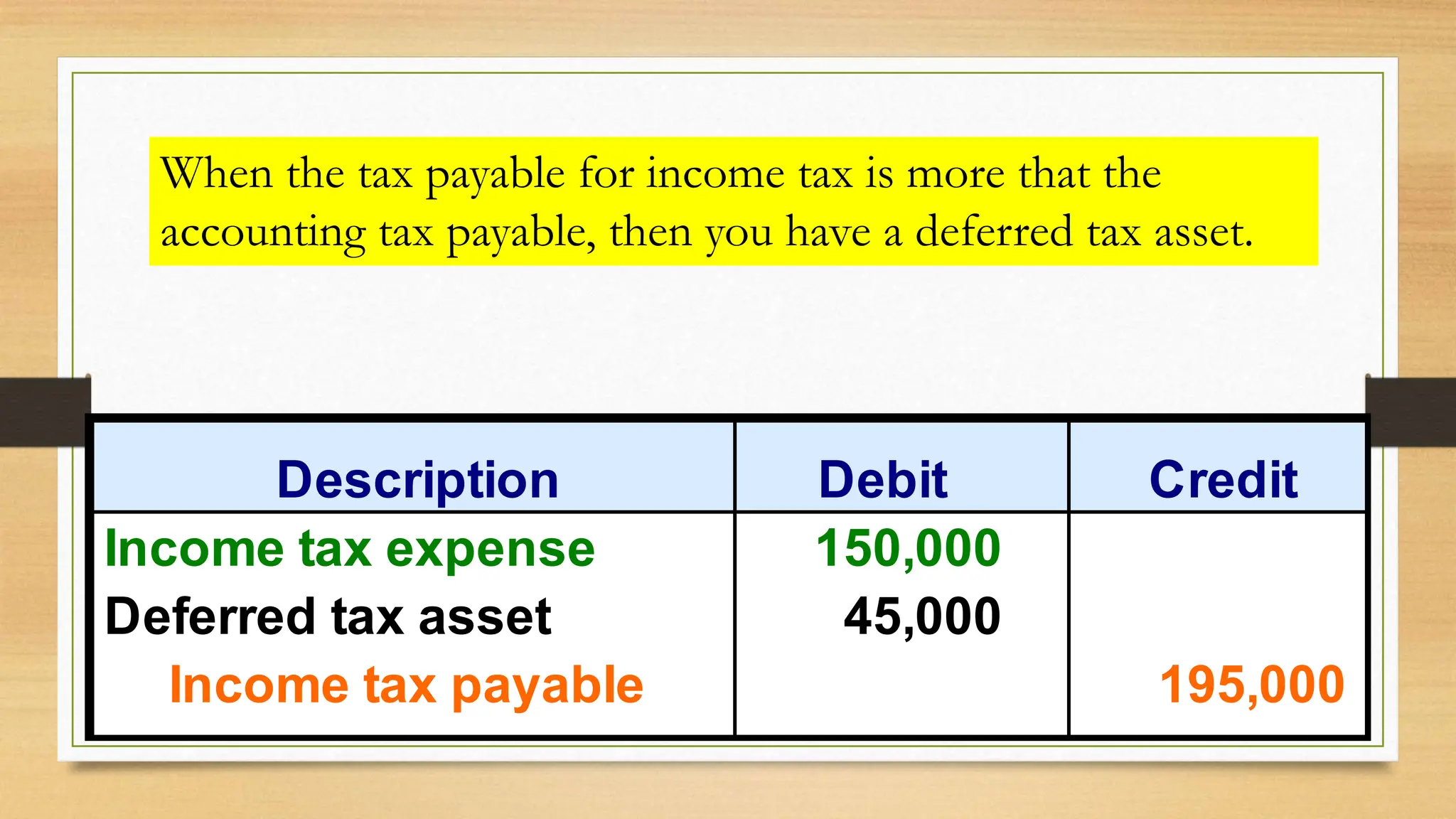
IAS 12 provides guidance on accounting for deferred taxes. A deferred tax liability arises when tax depreciation is higher than book depreciation, resulting in lower current tax expense. A deferred tax asset occurs when tax depreciation is lower than book depreciation, resulting in higher current tax expense. These differences are temporary and will offset over time. The deferred tax amounts are recorded to allocate the tax expense or benefit to the appropriate accounting periods. Examples show calculating deferred tax liability when tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation, resulting in lower current taxes. Deferred tax amounts are presented separately from other assets/liabilities and not classified as current. Tax rate changes use enacted rates when the deferred amount reverses.