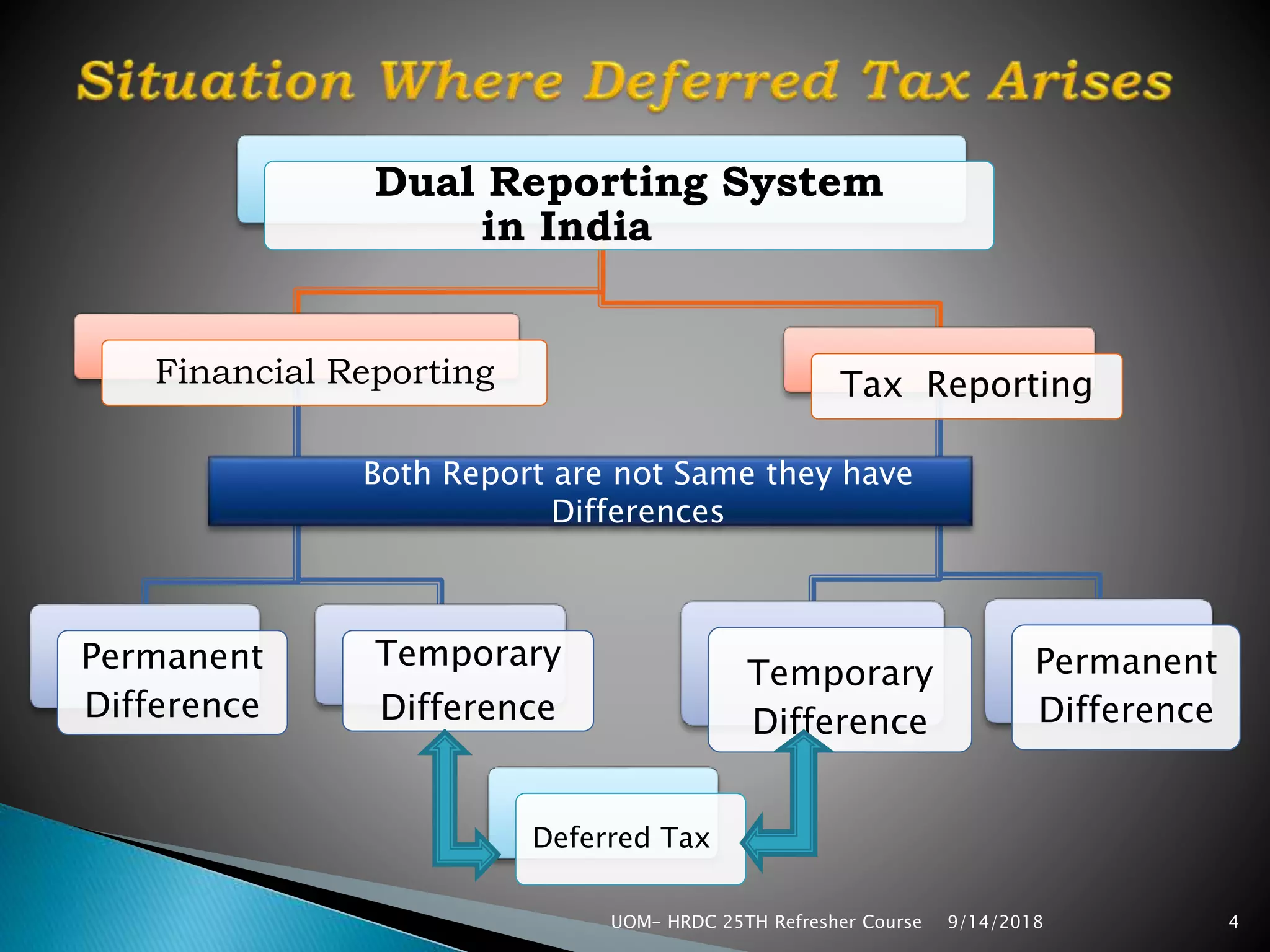
The document discusses dual reporting systems in India for financial and tax reporting. There are often differences between the income reported by companies to investors and that reported for tax assessment. Book income is determined under accounting principles and company law, while taxable income is computed under income tax law.
The concept of matching revenues and expenses over the periods they relate to gives rise to differences in profit/loss calculations under company and tax law. This leads to the concept of deferred tax to account for temporary differences between accounting and taxable income. Accounting standards prescribe deferred tax accounting to recognize the tax effect of these temporary differences over time.





![ The book entries of deferred tax is very simple. We have to
create Deferred Tax liability A/c or Deferred Tax Asset A/c by
debiting or crediting Profit & Loss A/c respectively.
The Deferred Tax is created at normal tax rate.
[1] Profit & Loss A/c Dr
To Deferred Tax Liability A/c
[2] Deferred Tax Asset A/c
To Profit & Loss A/c
Please, note that both the entries are not passed but only liability
or asset is created for net amount of deferred tax.
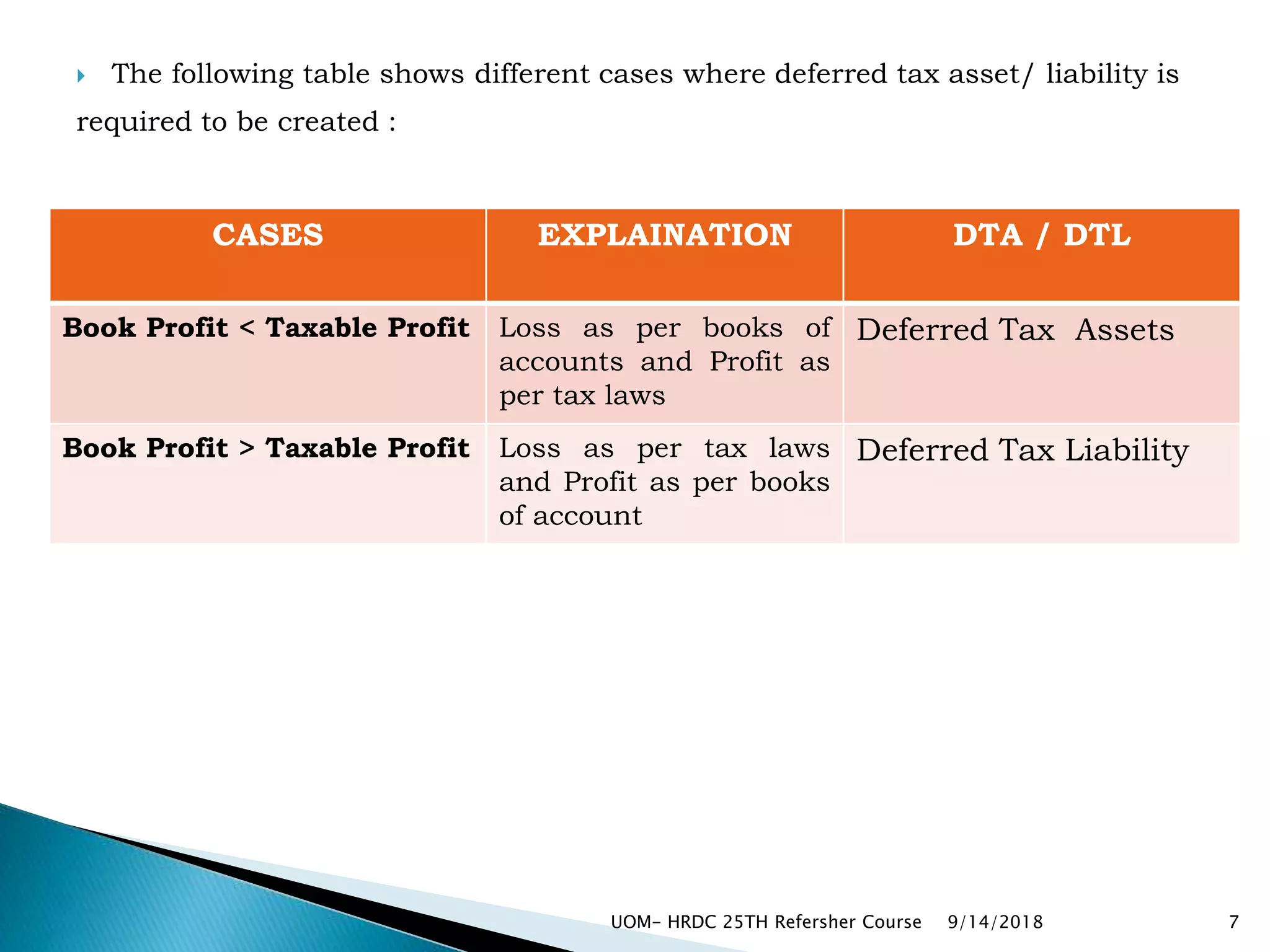
If book profit is greater than taxable profit, create deferred tax
liability.
If book profit is less than taxable profit, create deferred tax
asset.
9/14/2018UOM- HRDC 25TH Refresher Course 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtaanddtl-180914173207/75/Deferred-Tax-Assets-Deferred-Tax-Liability-8-2048.jpg)


