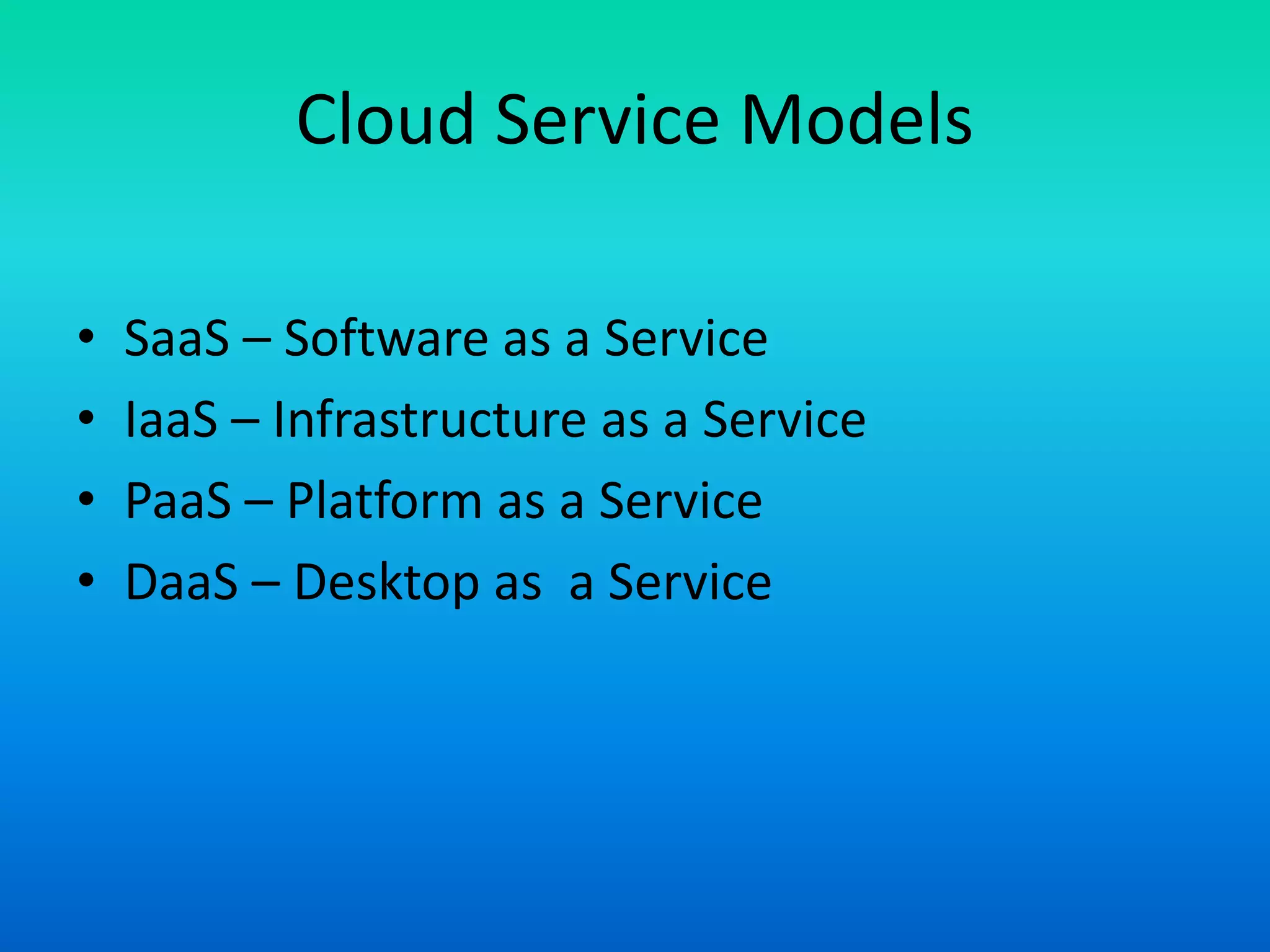
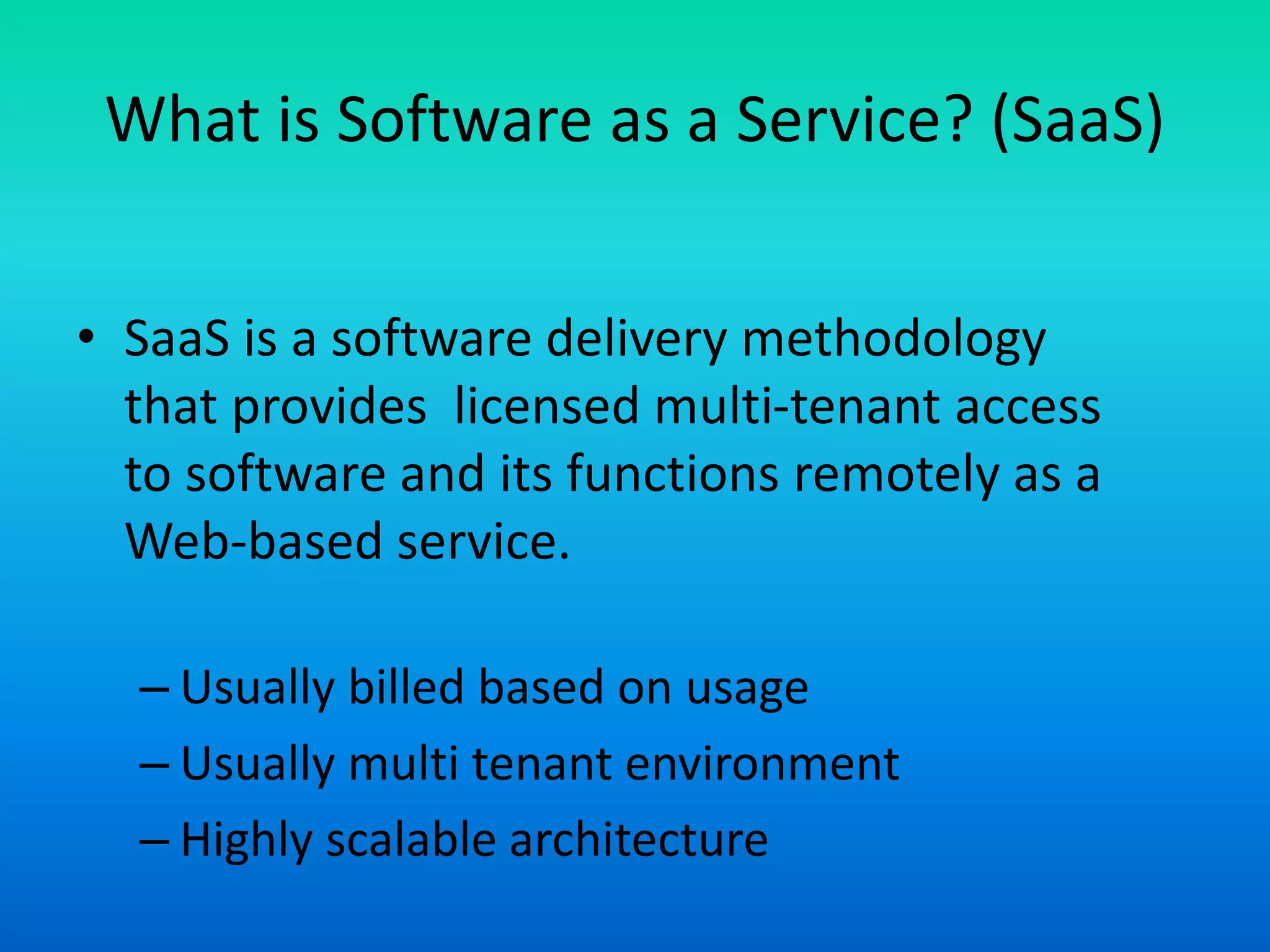
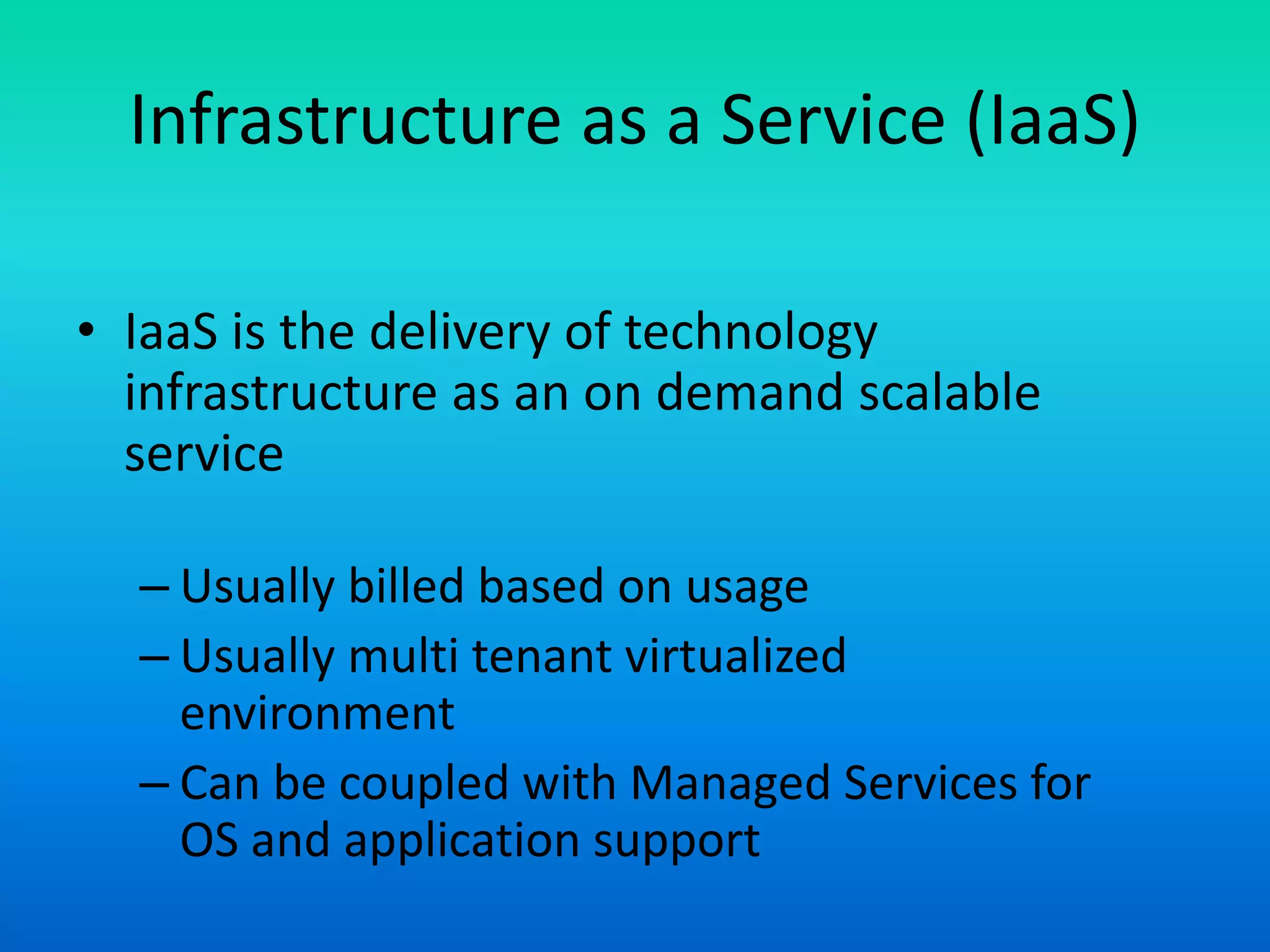
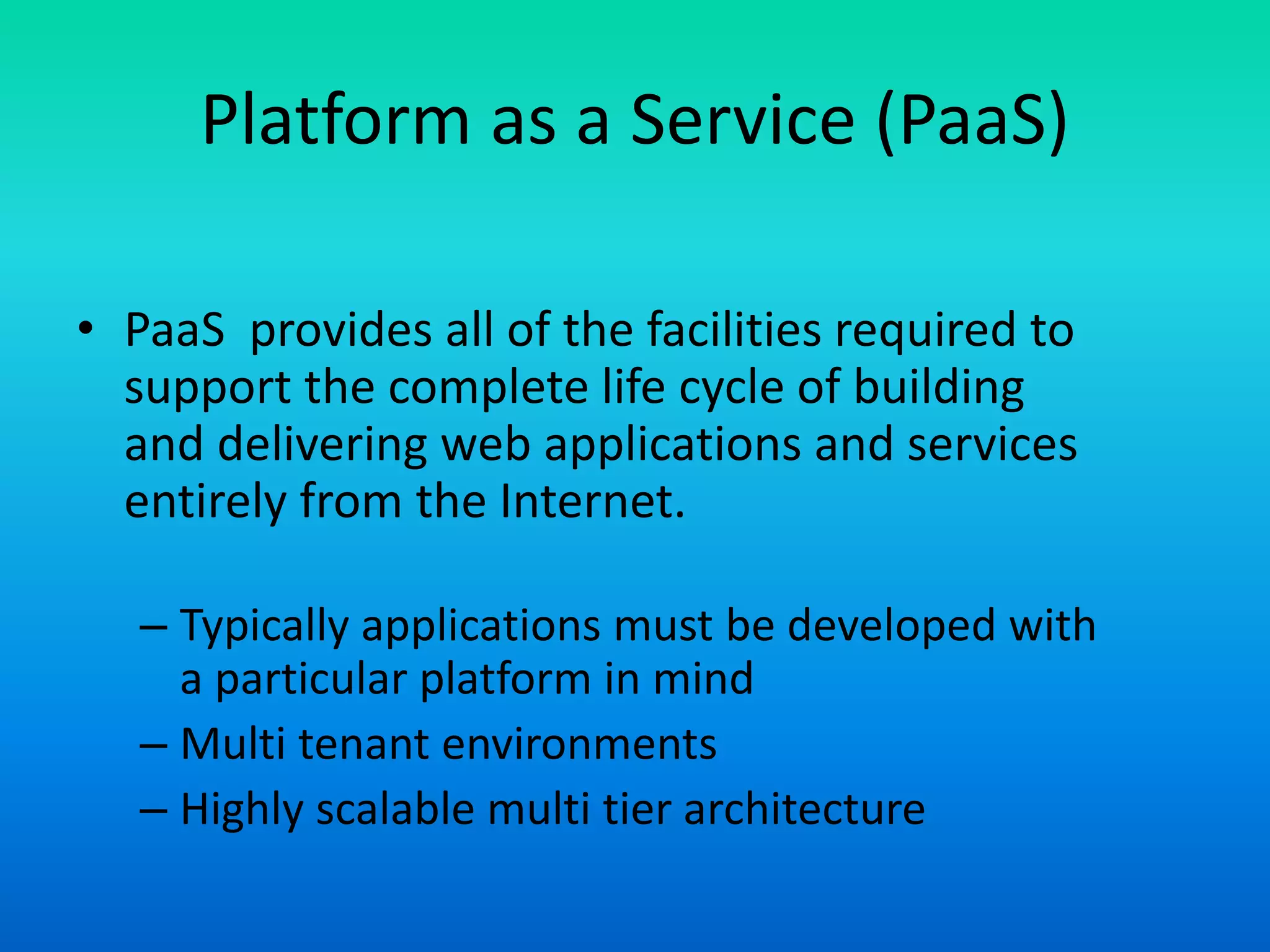
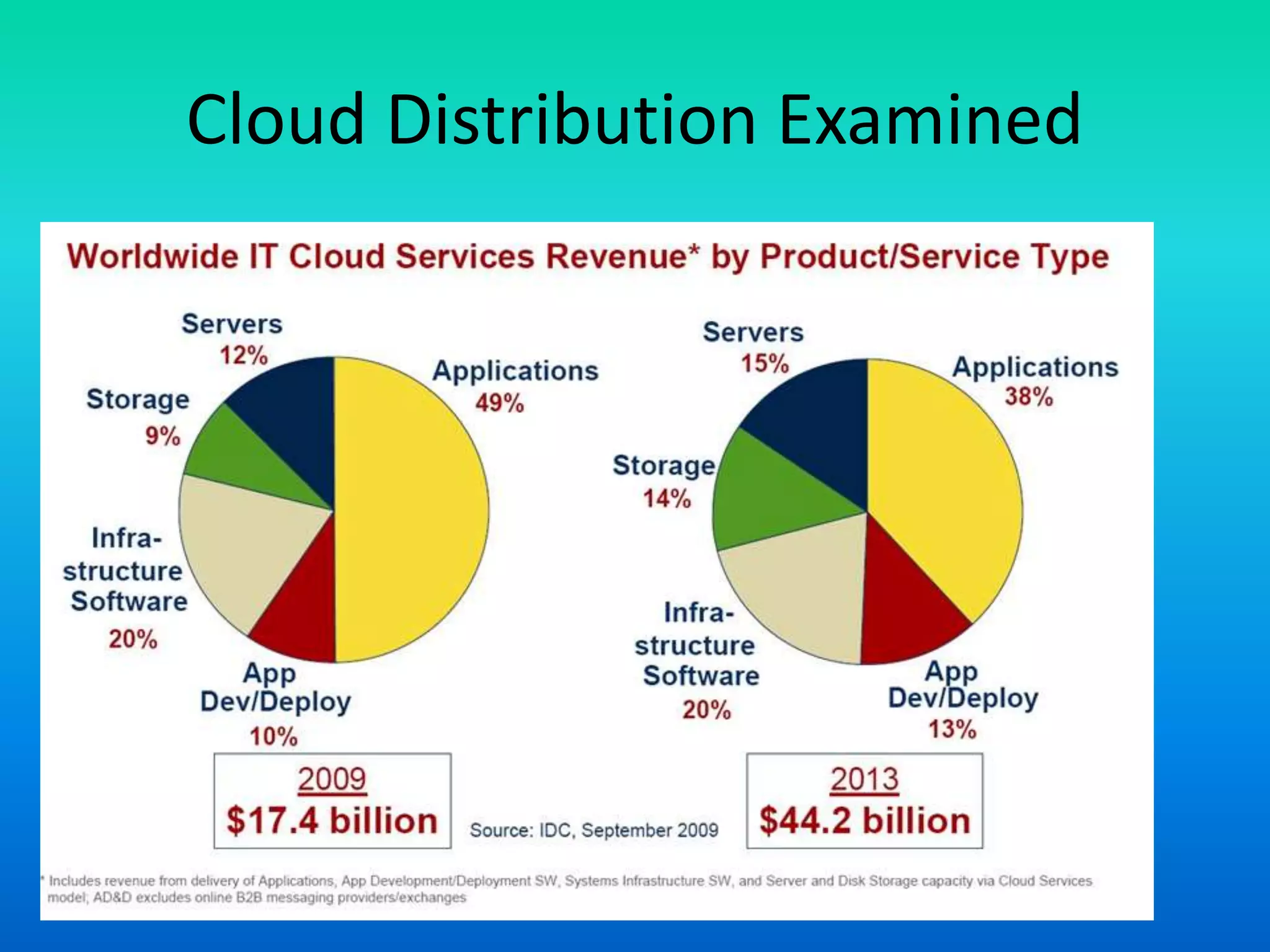
The document outlines various cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS), explaining their distinct characteristics and billing practices. It details deployment models like public, private, hybrid, and community clouds while highlighting growth predictions for public cloud computing. Key factors driving cloud adoption include advancements in hardware virtualization, the ubiquity of the internet, and changing economic considerations regarding IT services.