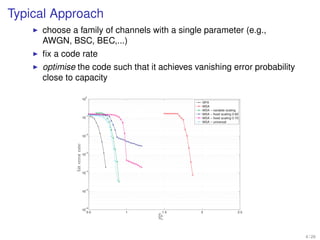
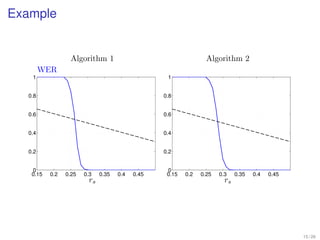
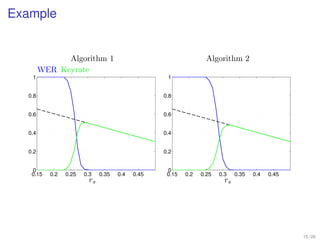
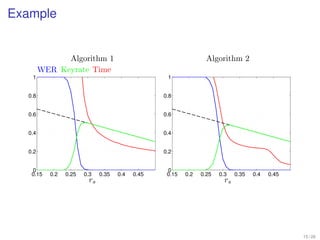
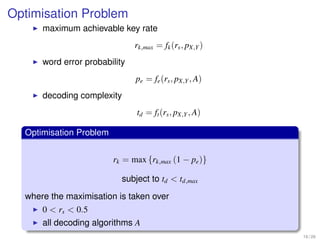
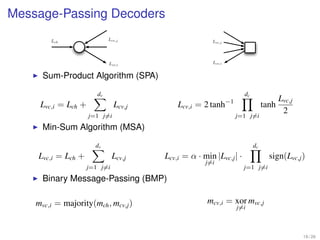
1. Shannon's channel coding theorem states that for any channel with a capacity C and transmission rate Rc < C, it is possible to encode messages into codewords such that the probability of error can be made arbitrarily small as the code length increases.
2. Channel coding involves encoding a message into a codeword for transmission over a noisy channel in order to allow reliable communication up to the channel's capacity.
3. The theorem establishes that for any rate lower than the channel capacity, there exists an encoding and decoding scheme that can achieve arbitrarily reliable communication by making the codewords long enough.


![Shannon: Commiunication in the Presence of Noise
Channel Coding1949 the channel capacity may be defined as
ony, this operation consists of merely changing sound
pressure into a proportional electrical current. In teleg-
,= T-oo
C9g2 M
T
T--a T
A precise meaning will be given later to
of reliable resolution of the M signals.
II. THE SAMPLING THEOR
Let us suppose that the channel has
width W in cps starting at zero frequen
are allowed to use this channel for a c
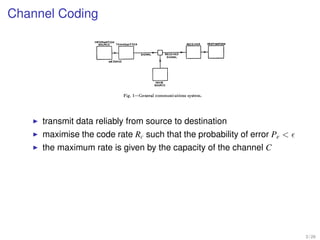
Fig. 1-General communications system. time T. Without any further restrict
mean that we can use as signal functio
of time whose spectra lie entirely with
raphy, we have an encoding operation which produces a and whose time functions lie within th
transmit data reliably from source to
sequence of dots, dashes, and spaces destination though it is not possible to fulfill both
corresponding to
the letters of the message. To take a more complex tions exactly, it is possible to keep the
maximise the example, speech functionsmultiplex sampled, compressed, outside theW, and PeT.< the time fun
different
in the R of
c must be
PCM telephony the the of
code rate case such that the probability banderror to have we describe interval Can
quantized and encoded, and finally interleaved properly way the functions which satisfy these
the maximum to constructgiven by the capacity of the answer is the following:
rate is the signal. channel C
3. The channel. This is merely the medium used to THEOREM 1: If a function f(t) contai
transmit the signal from the transmitting to the receiv- higher than W cps, it is completely dete
ing point. It may be a pair of wires, a coaxial cable, a its ordinates at a series of points space
Channel Coding Theorem [Shannon 1948]
band of radio frequencies, etc. During transmission, or apart.
at the receiving terminal, the signal may be perturbed This is a fact which is common knowl
For any > 0 and by c <orC, for largeand distortion may be dif- munication a code of justificat
Rnoise distortion. Noise enough N, there exists art. The intuitive
ferentiated on the basis that distortion is a fixed opera- contains no frequencies higher than
length N and rate Rc and a decoding algorithm, such that thesubstantially new value in
tion applied to the signal, while noise involves statistical change to a maximal
probability of blockand unpredictable perturbations. Distortion can, in one-half cycle of the highest frequency,
error is less than .
principle, be corrected by applying the inverse opera- mathematical proof showing that this
tion, while a perturbation due to noise cannot always be proximately, but exactly, true can be
removed, since the signal does not always undergo the Let F(w) be the spectrum of f(t). Then
same change during transmission.
4. The receiver. This operates on the received signal 1 a00 3 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/channelcodingforquantumkeydistribution-121214215459-phpapp01/85/Channel-coding-for-quantum-key-distribution-4-320.jpg)