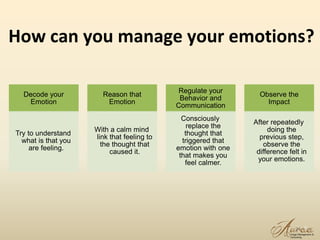
The document outlines strategies for effective change management in organizations, emphasizing the importance of transparency, employee engagement, and clear communication. It details various types of organizational changes and common challenges faced during these processes, while also offering practical approaches to manage change. The text includes theories on change management, such as Kotter's eight stages and the McKinsey 7-S model, along with the significance of emotional maturity for managers in navigating change.