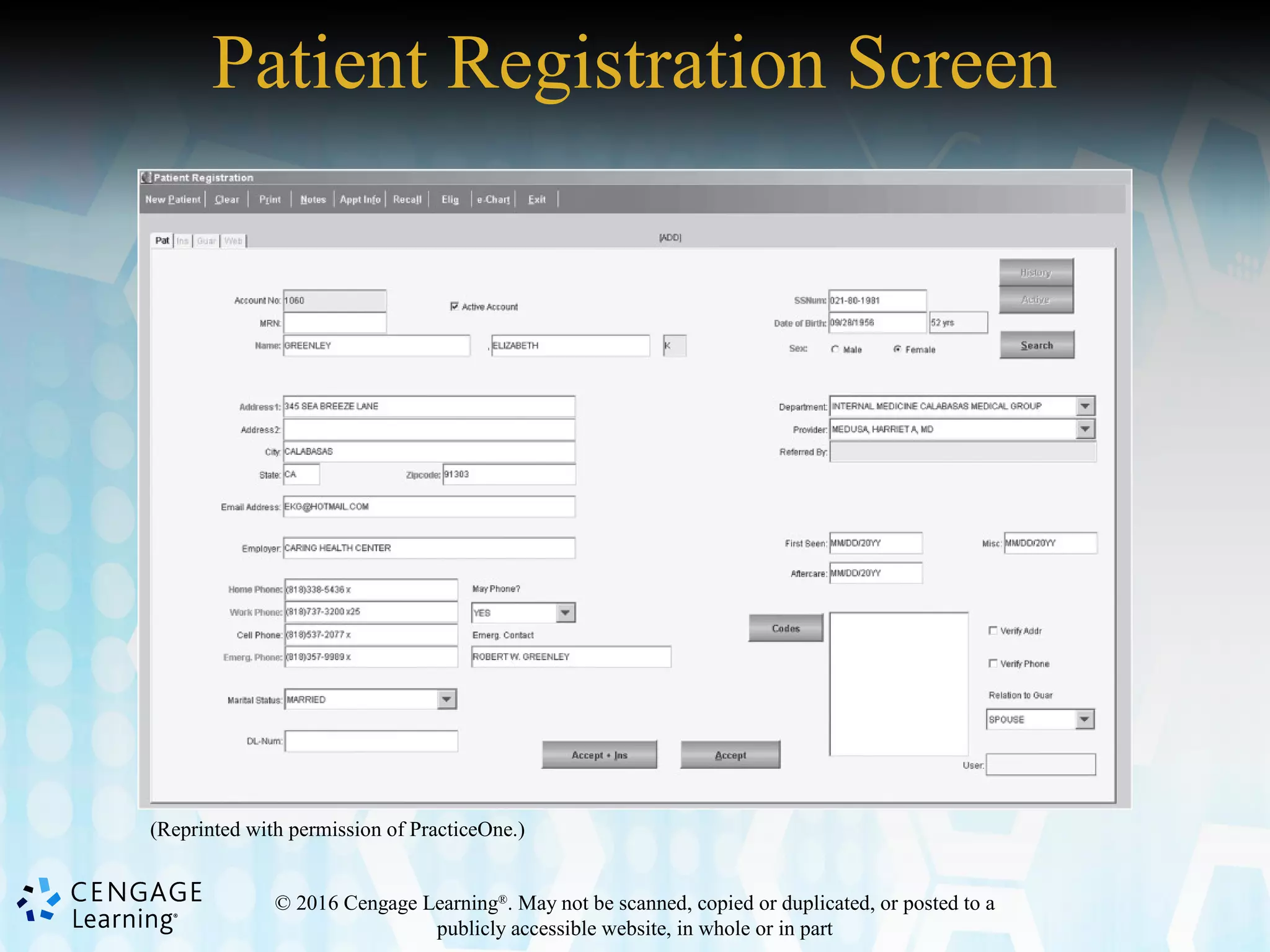
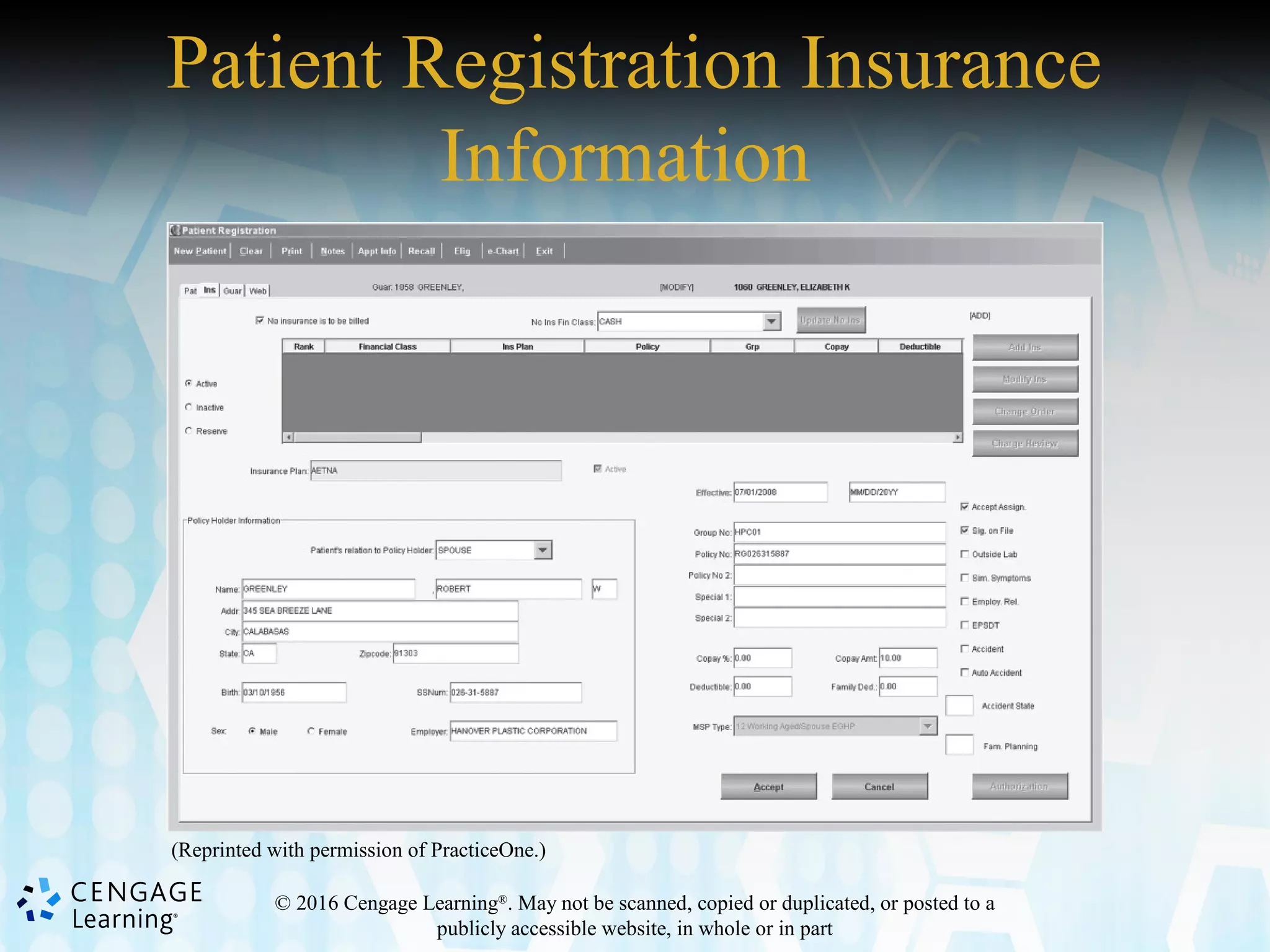
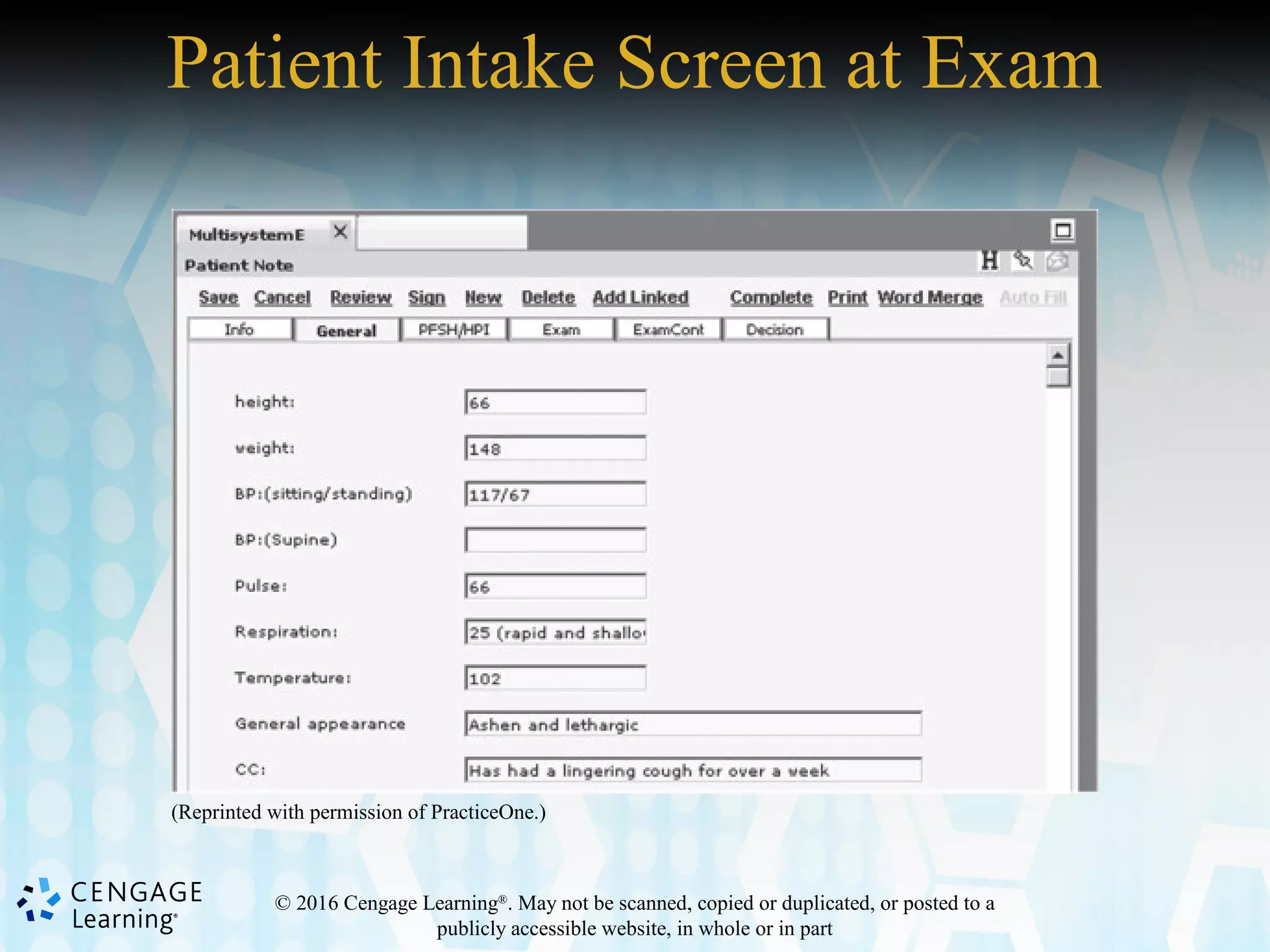
This document discusses the evolution and components of electronic health records (EHRs). It provides an overview of computer hardware and software as they relate to EHRs. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of both manual and automated health records. It also discusses stakeholders in health information exchange, components of EHRs, and challenges in transitioning from manual to electronic records systems.