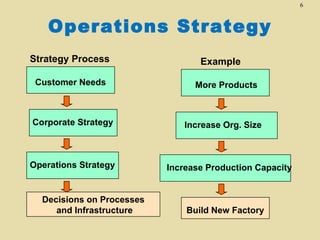
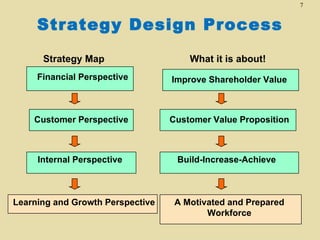
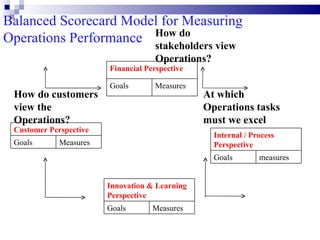
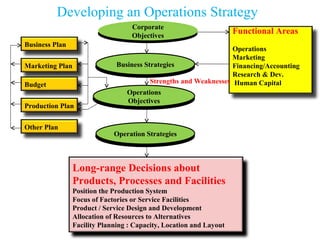
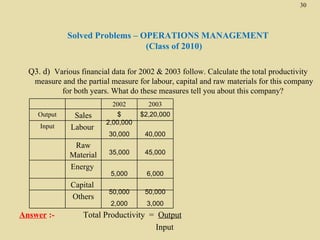
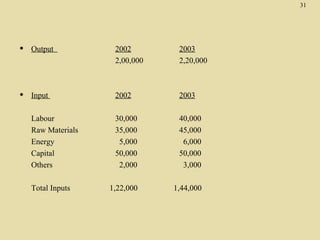
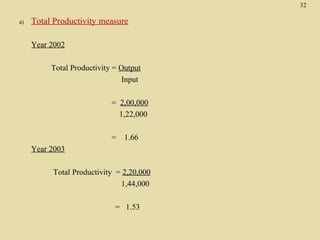
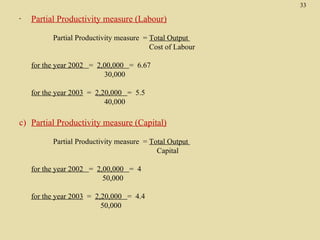
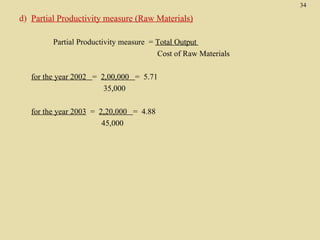
The total productivity and partial productivity measures for labour, capital and raw materials have decreased from 2002 to 2003. This indicates that the company's overall efficiency and utilization of resources have reduced over the years. The company needs to focus on improving its operations to enhance productivity.