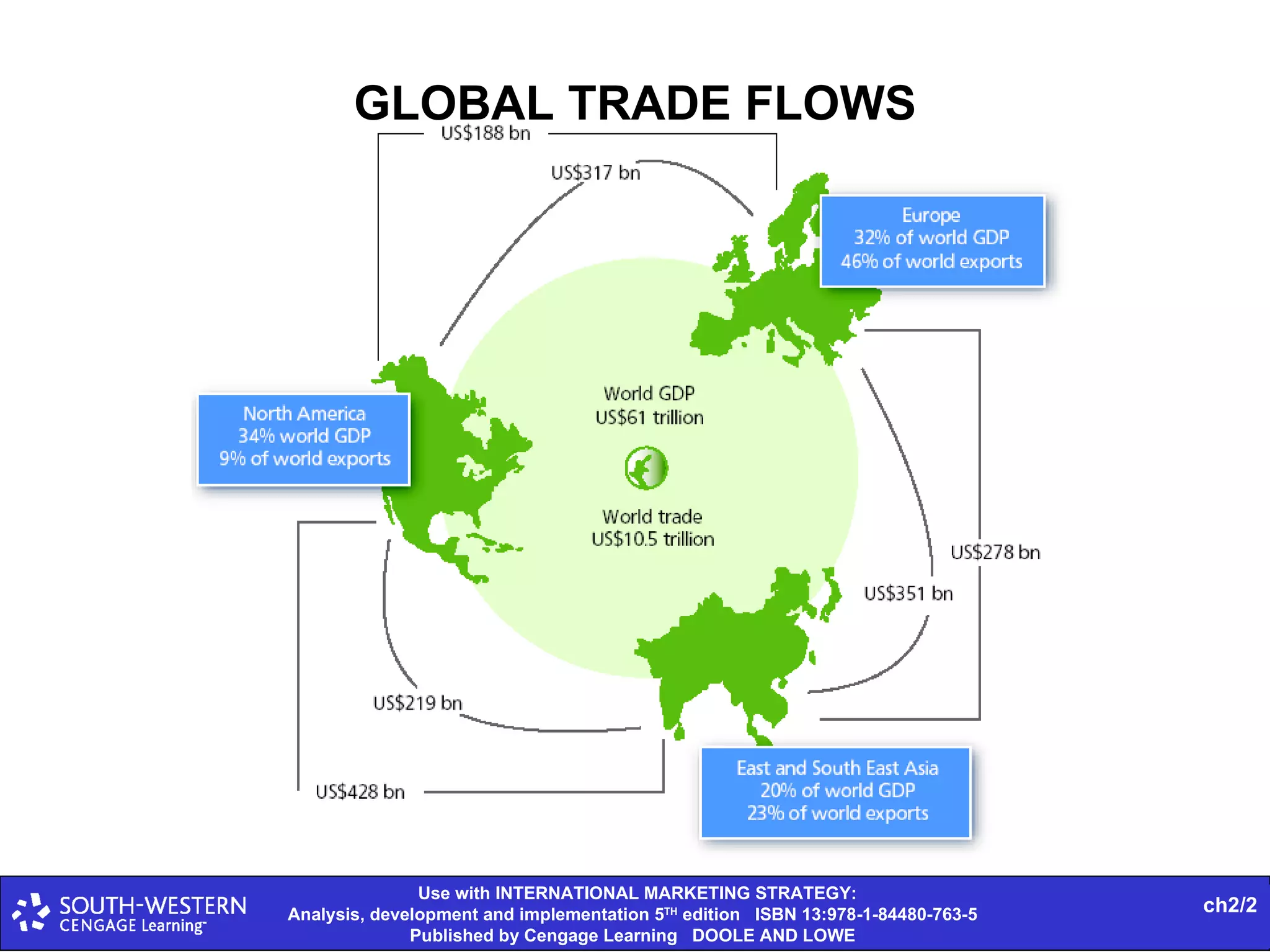
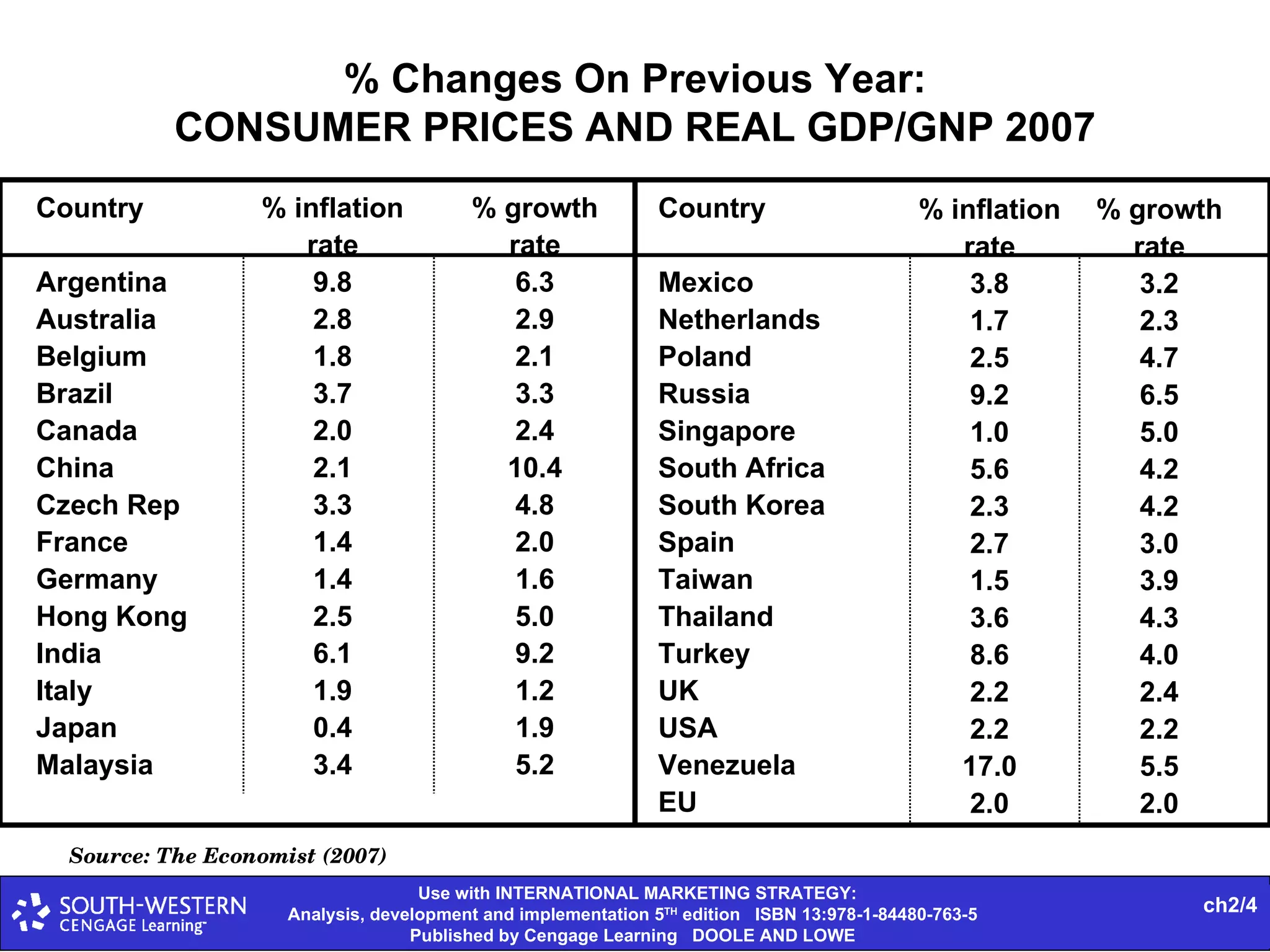
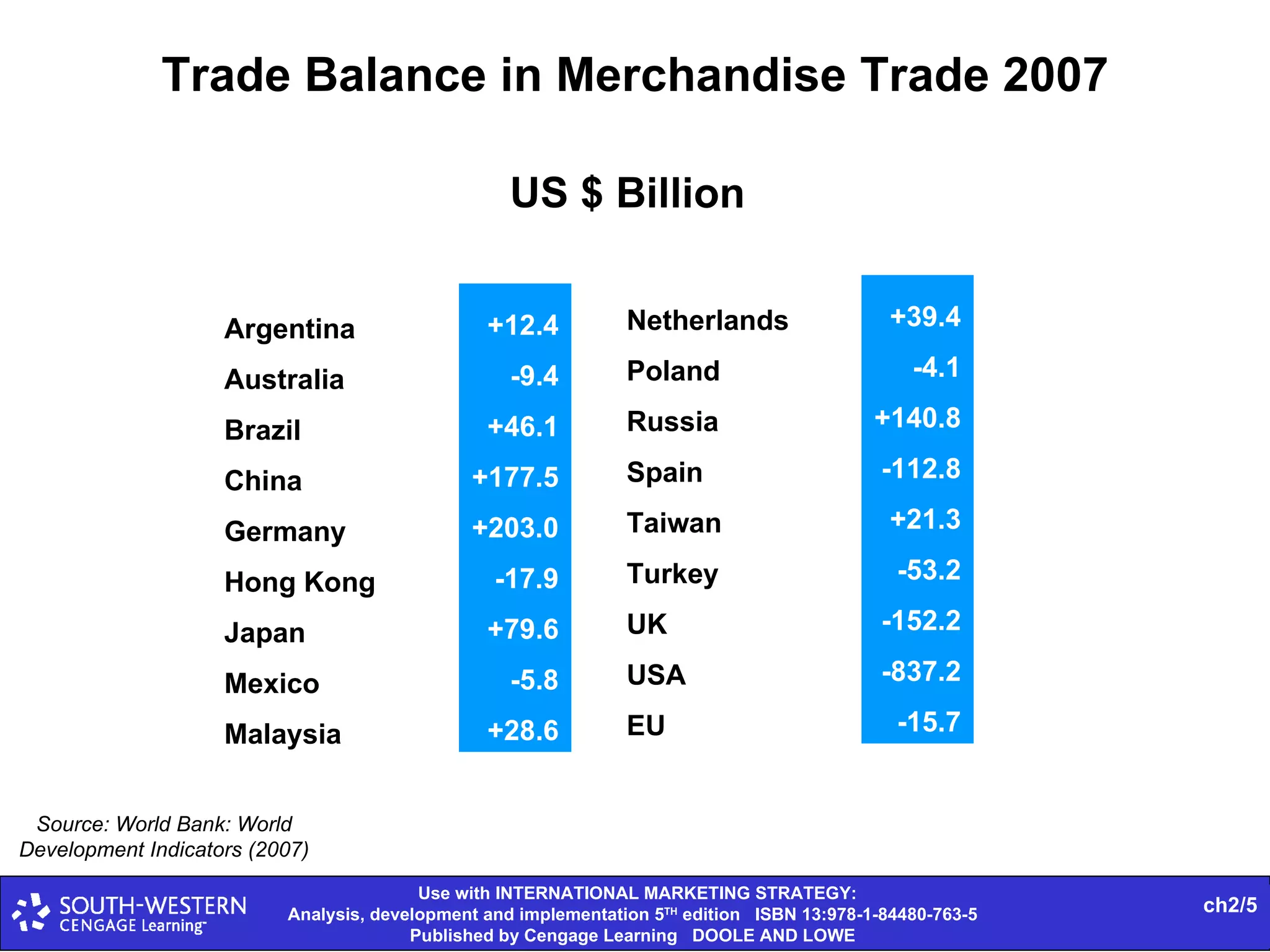
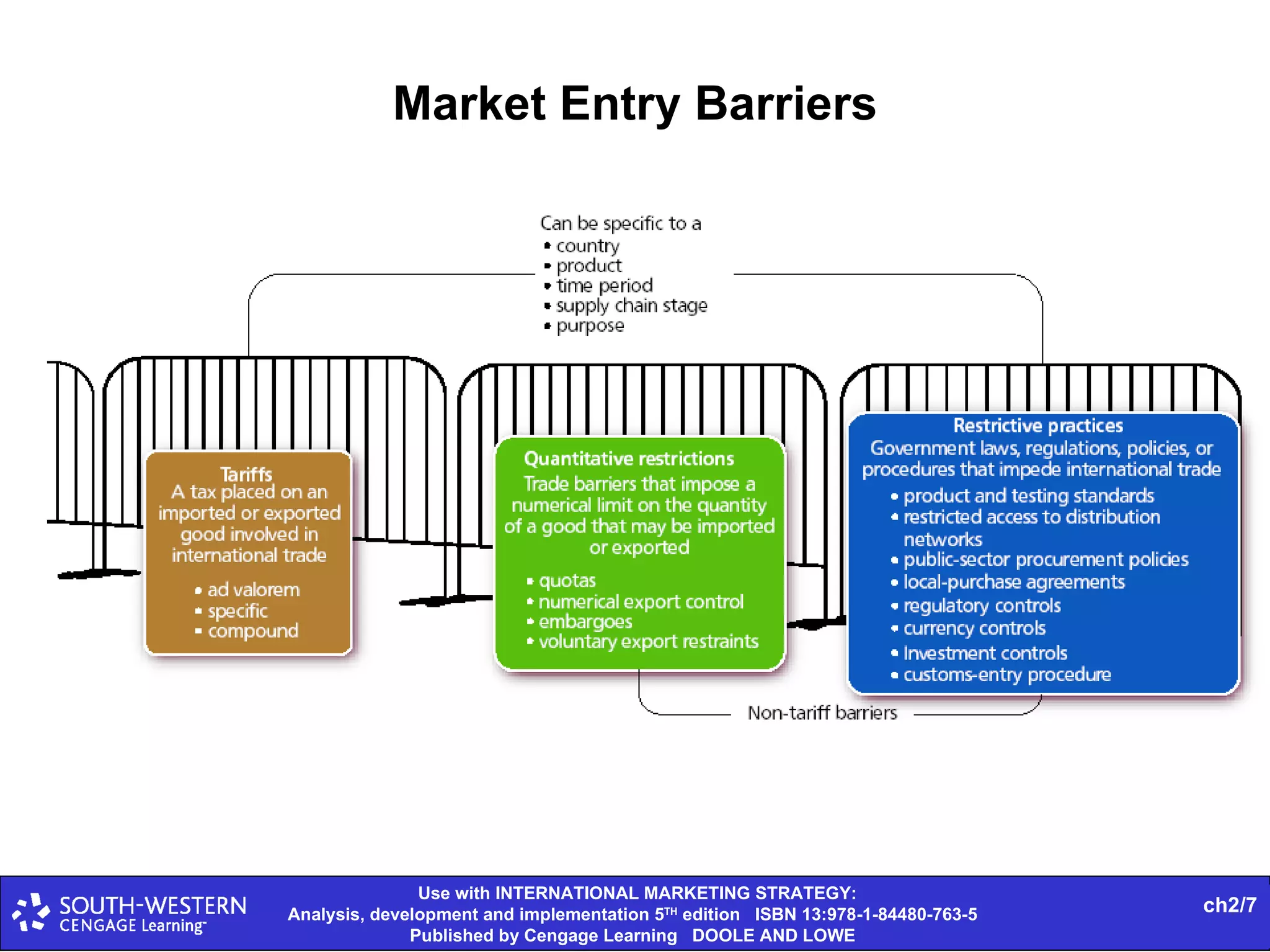
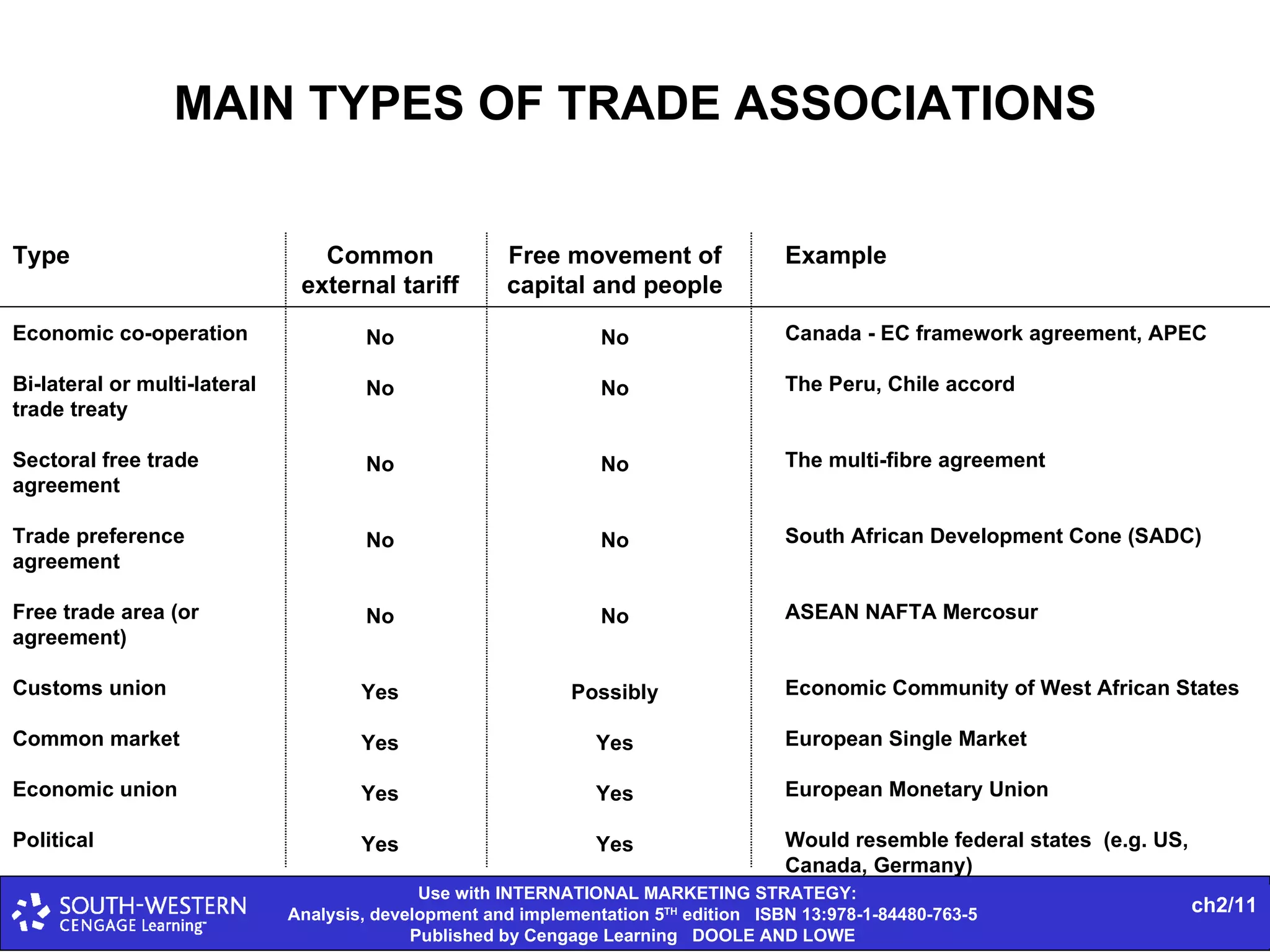
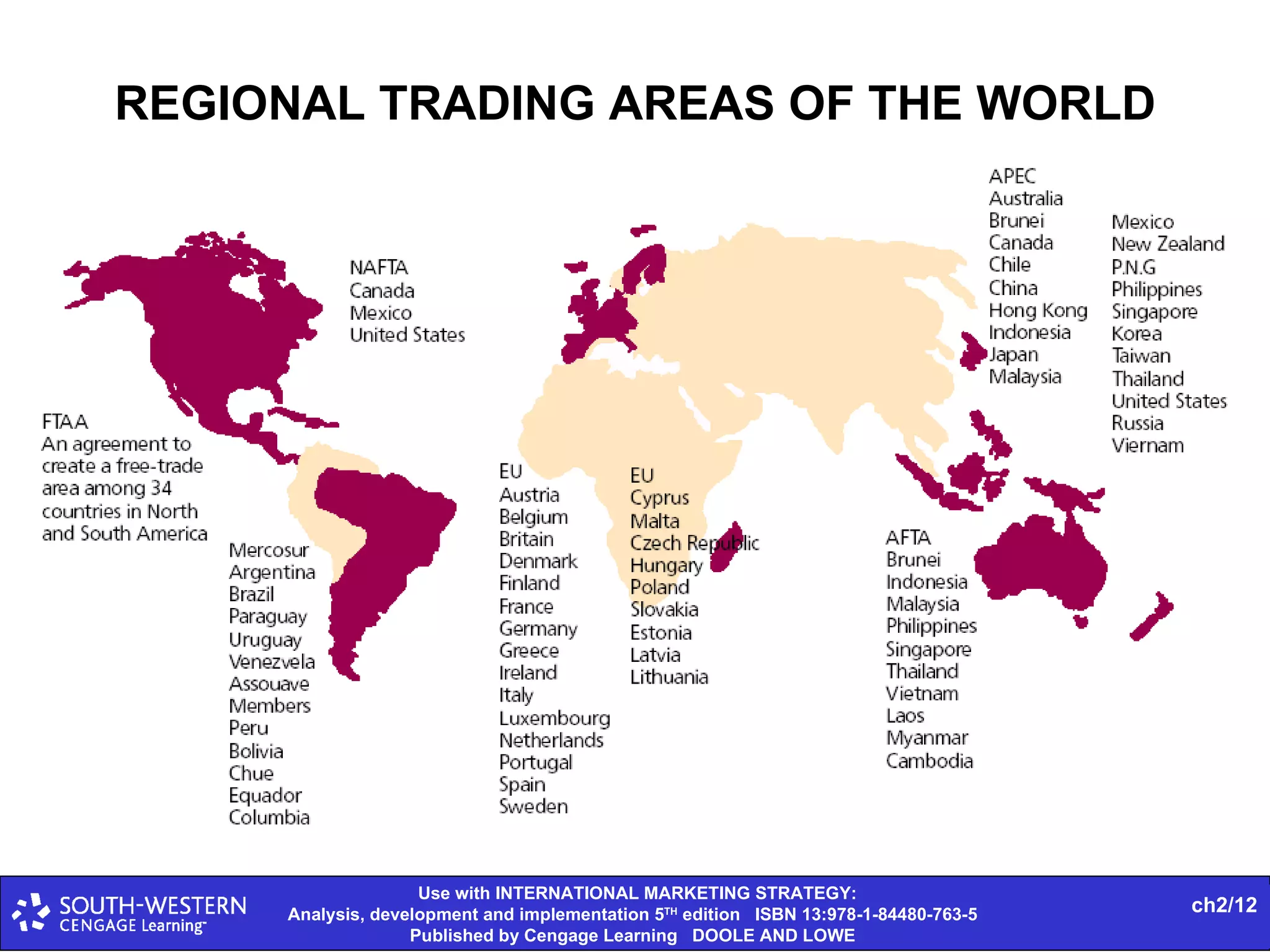
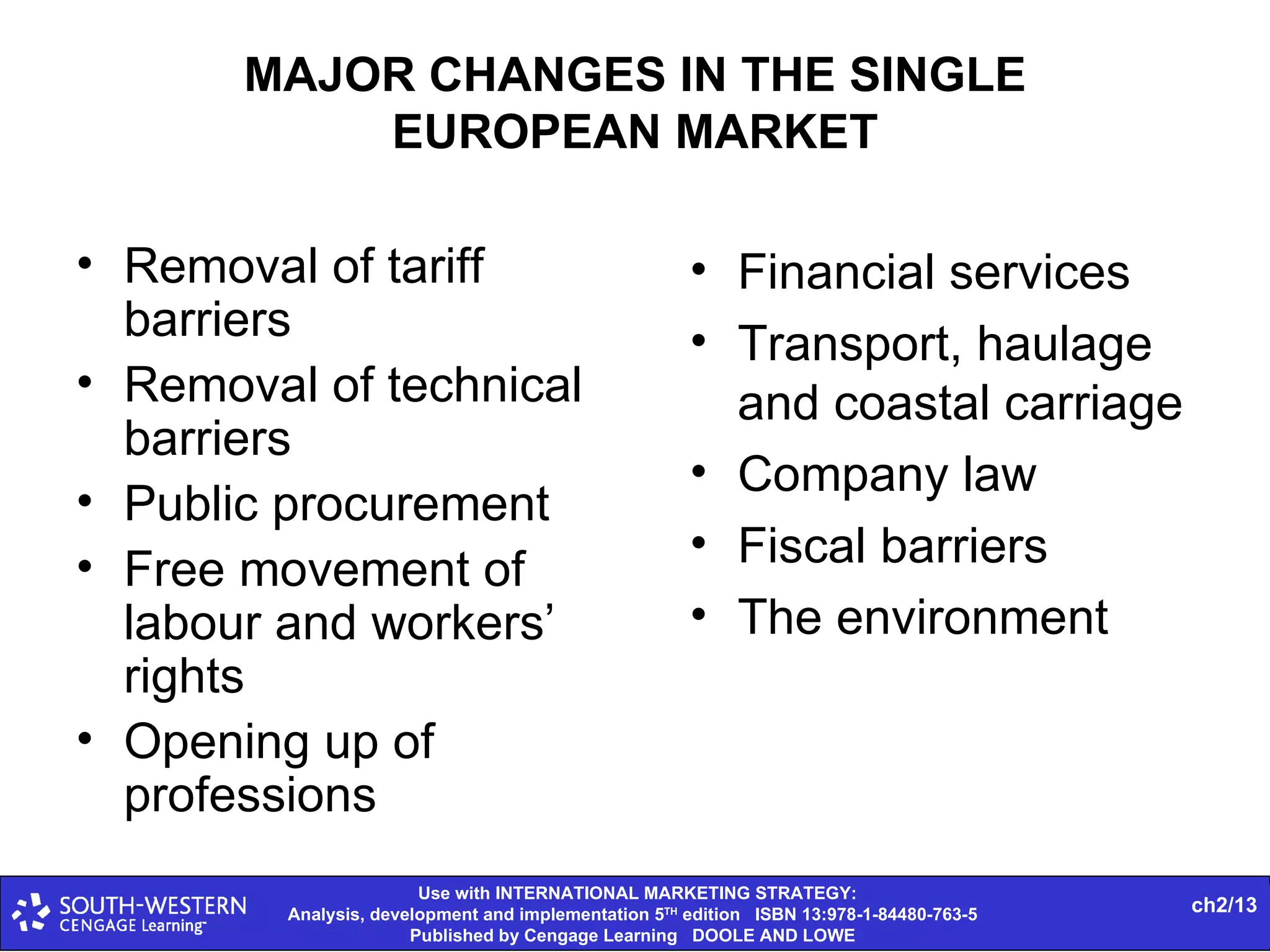
The document provides statistics on global trade flows and the international trading environment. It shows that in 2007, the top exporting countries by percentage of world exports were Germany at 9.3%, the United States at 8.7%, and China at 7.3%. It also includes data on consumer price inflation and GDP growth rates in 2007 for various countries. Additionally, it discusses concepts like comparative advantage, market entry barriers, and major world trading institutions and regions.