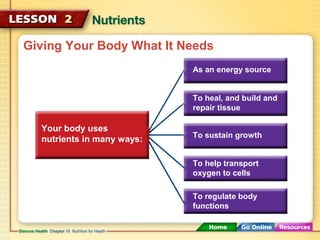
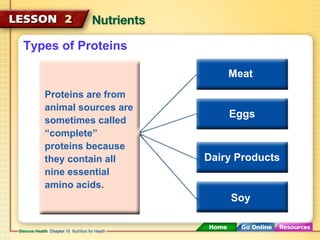
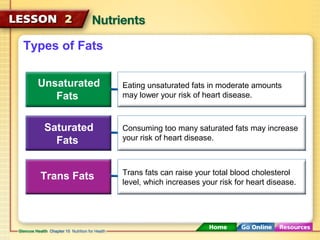
This document discusses the six major types of nutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. It explains the roles and health impacts of each nutrient type. Carbohydrates, proteins and fats provide energy and help build tissues, while vitamins and minerals regulate body processes without providing energy. Each nutrient is essential and performs unique functions in maintaining health. Getting a balance of nutrients during teenage years improves long-term health by supporting growth and reducing risks such as osteoporosis.