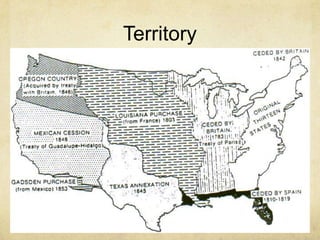
The document discusses the key features and theories of the origins of states and governments. It outlines four essential features of a state: population, territory, sovereignty, and government. It then describes four theories of how governments originated: evolutionary theory, which argues states evolved from families; force theory, which claims governments emerged through conquest; divine right theory, which holds rulers were chosen by gods; and social contract theory, which says people formed governments to protect their rights from the state of nature. The document suggests social contract theory, advocated by thinkers like Hobbes and Locke, most influenced concepts like the U.S. declaration of independence.