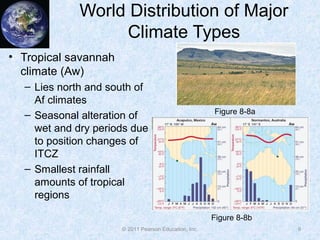
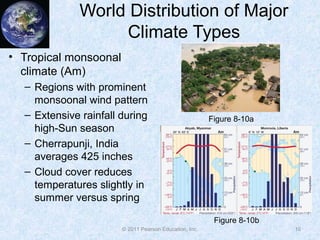
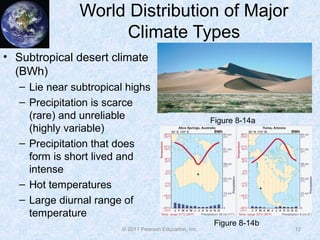
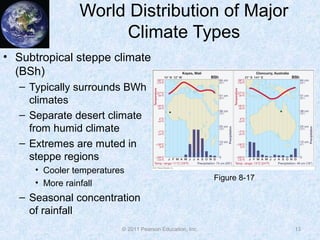
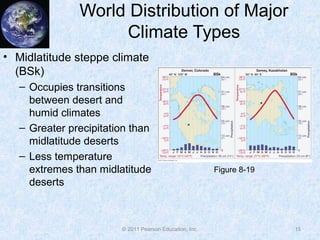
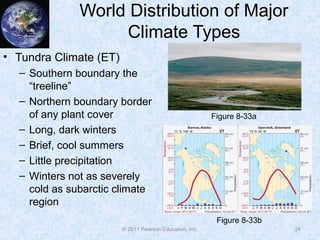
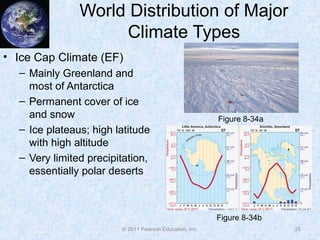
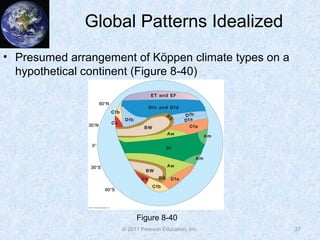
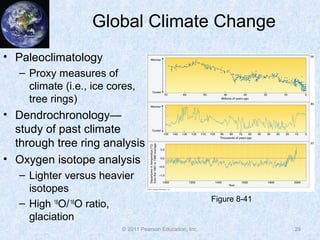
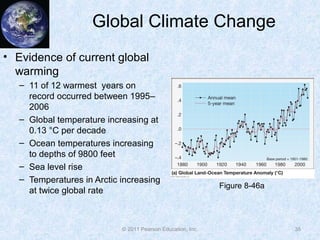
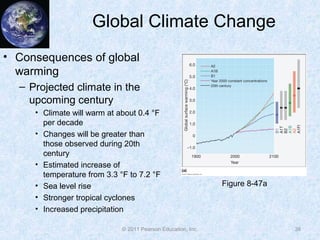
The document discusses climate classification and climate change. It describes the six primary climate groups classified by the Köppen system based on temperature and precipitation. These include tropical humid climates, dry climates, mild midlatitude climates, severe midlatitude climates, polar climates, and highland climates. Paleoclimatology methods are used to study past climate changes. Factors influencing long-term climate change include greenhouse gases, solar output, and ocean currents. Evidence suggests the Earth is currently undergoing global warming due to increased carbon dioxide from human activities.